
Rapid interconversion of $\alpha $-D-glucose and $\beta $-D-glucose in solution is known as:
A. Racemisation
B. Asymmetric induction
C. Fluxional isomerisation
D. Mutarotation
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: Recollect the Haworth structures of glucose. Draw all the Haworth structures of glucose as named in the question. Try to find what each term in the given option means and then think what changes take place when one anomer is converted to another anomer and the name of that process.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all, we should draw the structure of both the structures of glucose. Then only we can find the correct option.
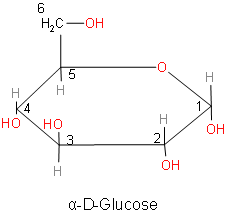
Above is the structure of $\alpha $-D-glucose.
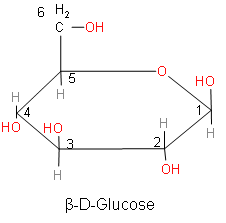
Above is the structure of $\beta $-D-glucose.
When comparing the above structures, we came to know that both the structures of glucose are anomers. Anomers are cyclic monosaccharides or glycosides that are epimers of each other. Epimer is a one pair of diastereoisomer. Two epimers have opposite configurations at only one stereogenic center (stereocenter) out of at least two. The stereocenter is that point on the chain on which interchanging any two substituents leads to a stereoisomer.
So, anomers are defined as cyclic monosaccharides or glycosides that are epimers and they are differing from each other in the configuration of C-1 if they are aldoses and we should also know that the anomers differ at the configuration at C-2 if they are ketoses. The epimeric carbon in anomers is known as anomeric carbon or anomeric center.
So, from the above discussion we now know about anomers. Now, we will answer our question. The process for rapid interconversion of $\alpha $-D-glucose and $\beta $-D-glucose in solution is called Anomerization or mutarotation.
The correct answer of the process for rapid interconversion of $\alpha $-D-glucose and $\beta $ -D-glucose in solution is option D. Mutarotation occurs when the anomeric position (C1) changes its configuration between $\alpha $ and $\beta $ form in the solution. Mutarotation is a deviation from the specific rotation, due to the change in the equilibrium between $\alpha $ anomeric and $\beta $ anomeric form, in the aqueous solution. As observed in the $\alpha $-D- glucose and $\beta $-D- glucose, the carbon centre or anomeric carbon or C-1 carbon changes.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Remember that racemization is a conversion of an optically active compound into an optically inactive form in the presence of heat, in which half of the optically active substance becomes its mirror image (enantiomer) referred to as racemic mixtures (that is, it contains equal amount of (+) and (−) forms).
Complete step by step answer:
First of all, we should draw the structure of both the structures of glucose. Then only we can find the correct option.

Above is the structure of $\alpha $-D-glucose.

Above is the structure of $\beta $-D-glucose.
When comparing the above structures, we came to know that both the structures of glucose are anomers. Anomers are cyclic monosaccharides or glycosides that are epimers of each other. Epimer is a one pair of diastereoisomer. Two epimers have opposite configurations at only one stereogenic center (stereocenter) out of at least two. The stereocenter is that point on the chain on which interchanging any two substituents leads to a stereoisomer.
So, anomers are defined as cyclic monosaccharides or glycosides that are epimers and they are differing from each other in the configuration of C-1 if they are aldoses and we should also know that the anomers differ at the configuration at C-2 if they are ketoses. The epimeric carbon in anomers is known as anomeric carbon or anomeric center.
So, from the above discussion we now know about anomers. Now, we will answer our question. The process for rapid interconversion of $\alpha $-D-glucose and $\beta $-D-glucose in solution is called Anomerization or mutarotation.
The correct answer of the process for rapid interconversion of $\alpha $-D-glucose and $\beta $ -D-glucose in solution is option D. Mutarotation occurs when the anomeric position (C1) changes its configuration between $\alpha $ and $\beta $ form in the solution. Mutarotation is a deviation from the specific rotation, due to the change in the equilibrium between $\alpha $ anomeric and $\beta $ anomeric form, in the aqueous solution. As observed in the $\alpha $-D- glucose and $\beta $-D- glucose, the carbon centre or anomeric carbon or C-1 carbon changes.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Remember that racemization is a conversion of an optically active compound into an optically inactive form in the presence of heat, in which half of the optically active substance becomes its mirror image (enantiomer) referred to as racemic mixtures (that is, it contains equal amount of (+) and (−) forms).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




