
What is the radius of Sodium atom if it crystallizes in BCC unit cell edge length of $ 400pm $?
Answer
478.8k+ views
Hint: The unit cell is the smallest repeating unit of a crystal lattice. There are different types of crystal lattices, out of which one is body-centered cubic BCC which can be seen in the below image:
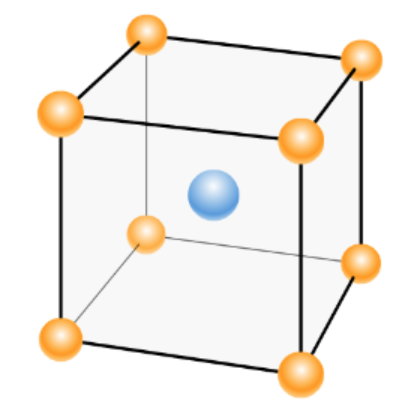
When any atoms are arranged in a body-centered cubic cell, the radius will be determined by substituting the edge length in the below formula.
$ r = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4} \times a $
$ r $ is radius of a body centered cubic unit cell
$ a $ is edge length.
Complete answer:
Given that the sodium atom is crystallized in a body-centered cubic cell, with the edge length of $ 400pm $.
We know the radius formula in BCC as
$ r = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4} \times a $
Substituting this edge length in the above formula,
$ r = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4} \times 400 $
On simplification, we get the radius as
$ r = 173.2pm $
Thus, the radius of the sodium atom if it crystallizes in BCC unit cell edge length of $ 400pm $ is $ 173.2pm $ .
Additional information:
• Crystallography is a branch that deals mainly with crystal structures. According to this concept, the crystal structure is an order of the arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules.
• The crystal lattice is also known as crystal structure which is nothing but the arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in the form of a space lattice.
• They are different types of crystal structures like body-centered cubic (BCC), face-centered cubic (FCC), and hexagonal cubic packing (HCP).
Note:
• While calculating the radius of a crystal lattice, the edge length is usually taken in the units of picometers as these measurements are very minute.
• 1 picometer is equal to $10^{-12}$ meters. Picometers can be simply represented as $ pm $.
• If the edge length is given in meters or angstroms, conversion should be made. Where one angstrom is equal to $ 100 $ picometers.

When any atoms are arranged in a body-centered cubic cell, the radius will be determined by substituting the edge length in the below formula.
$ r = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4} \times a $
$ r $ is radius of a body centered cubic unit cell
$ a $ is edge length.
Complete answer:
Given that the sodium atom is crystallized in a body-centered cubic cell, with the edge length of $ 400pm $.
We know the radius formula in BCC as
$ r = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4} \times a $
Substituting this edge length in the above formula,
$ r = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4} \times 400 $
On simplification, we get the radius as
$ r = 173.2pm $
Thus, the radius of the sodium atom if it crystallizes in BCC unit cell edge length of $ 400pm $ is $ 173.2pm $ .
Additional information:
• Crystallography is a branch that deals mainly with crystal structures. According to this concept, the crystal structure is an order of the arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules.
• The crystal lattice is also known as crystal structure which is nothing but the arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in the form of a space lattice.
• They are different types of crystal structures like body-centered cubic (BCC), face-centered cubic (FCC), and hexagonal cubic packing (HCP).
Note:
• While calculating the radius of a crystal lattice, the edge length is usually taken in the units of picometers as these measurements are very minute.
• 1 picometer is equal to $10^{-12}$ meters. Picometers can be simply represented as $ pm $.
• If the edge length is given in meters or angstroms, conversion should be made. Where one angstrom is equal to $ 100 $ picometers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




