
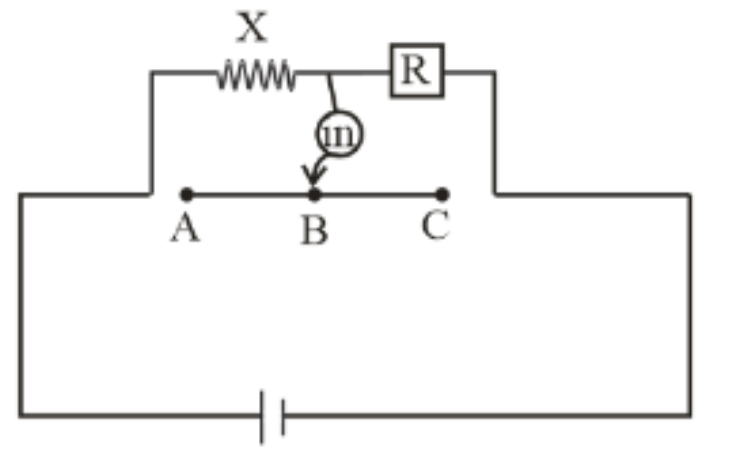
${R_1},{R_2},{R_3}$ are different values of R. A, B, C are the null paints obtained corresponding to ${R_1},{R_2}$ and ${R_3}$ respectively. For which resistor, the value of X will be the most accurate and why ?
(A) ${R_1}$
(B) ${R_2}$
(C) ${R_3}$
(D) All same

Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint:In this problem,we are going to apply the balancing condition of the meter bridge and after calculating the null point for ${R_1},{R_2}$ and ${R_3}$ respectively.
At least, compare the value of X for all 3 resistances, we will get a desired solution.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{X}{\ell } = \dfrac{R}{{100 - \ell }}$ …..(1)
Where
$\ell = $ Reading at meter bridge scale for null point.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the null point of meter bridge is at which the deflection in galvanometer becomes zero, and with the help of this concept we can calculate the unknown resistance X which is given as
\[\dfrac{X}{\ell } = \dfrac{R}{{100 - \ell }}\]
Here the length of the meter bridge is 100 cm.
According to given situation when R is ${R_1}$ then null point is A
So, \[\dfrac{{{X_A}}}{{{\ell _A}}} = \dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{100 - {\ell _A}}}\] …..(1)
When R is ${R_2}$ then null point is B
So, \[\dfrac{{{X_B}}}{{{\ell _B}}} = \dfrac{{{R_2}}}{{100 - {\ell _B}}}\] …..(2)
When R is ${R_3}$ then null point is C
So, \[\dfrac{{{X_C}}}{{{\ell _C}}} = \dfrac{{{R_3}}}{{100 - {\ell _C}}}\] …..(3)
Now, we have to find which value is most accurate. We know that the value for which cross resistance of the meter bridge is comparable will be most accurate.
So, according to the given circuit diagram, point B is situated nearly half of the length of the meter bridge. So, ${X_B}$ is most accurate.
Hence, for the resistor ${R_2}$ the value of X is most accurate.So, option B is the correct answer.
Note: Alternatively, the accuracy is maximum when null point is near the midpoint and point B is nearest to the midpoint. Hence, ${R_2}$ must be chosen to calculate X.
At least, compare the value of X for all 3 resistances, we will get a desired solution.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{X}{\ell } = \dfrac{R}{{100 - \ell }}$ …..(1)
Where
$\ell = $ Reading at meter bridge scale for null point.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the null point of meter bridge is at which the deflection in galvanometer becomes zero, and with the help of this concept we can calculate the unknown resistance X which is given as
\[\dfrac{X}{\ell } = \dfrac{R}{{100 - \ell }}\]
Here the length of the meter bridge is 100 cm.
According to given situation when R is ${R_1}$ then null point is A
So, \[\dfrac{{{X_A}}}{{{\ell _A}}} = \dfrac{{{R_1}}}{{100 - {\ell _A}}}\] …..(1)
When R is ${R_2}$ then null point is B
So, \[\dfrac{{{X_B}}}{{{\ell _B}}} = \dfrac{{{R_2}}}{{100 - {\ell _B}}}\] …..(2)
When R is ${R_3}$ then null point is C
So, \[\dfrac{{{X_C}}}{{{\ell _C}}} = \dfrac{{{R_3}}}{{100 - {\ell _C}}}\] …..(3)
Now, we have to find which value is most accurate. We know that the value for which cross resistance of the meter bridge is comparable will be most accurate.
So, according to the given circuit diagram, point B is situated nearly half of the length of the meter bridge. So, ${X_B}$ is most accurate.
Hence, for the resistor ${R_2}$ the value of X is most accurate.So, option B is the correct answer.
Note: Alternatively, the accuracy is maximum when null point is near the midpoint and point B is nearest to the midpoint. Hence, ${R_2}$ must be chosen to calculate X.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which country did Danny Casey play for class 12 english CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE




