
Prove theoretically the relation between emf induced in a coil and the rate of change of magnetic flux in electromagnetic induction. A parallel plate air condenser has a capacitor of 20\[\mu F\]. What will the new capacity if:
(a) The distance between the two plates is doubled?
(b) A marble slab of dielectric constant 8 is introduced between the two plates?
Answer
579k+ views
Hint: We can easily prove the relation between the induced emf in a coil and the electromagnetic induction by the Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. Also, we can find the relation between the distance between the plates and the medium between them in a capacitor.
Complete answer:
According to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, the change of magnetic flux with time around a conductor can cause an induced emf in it. i.e., an emf is induced in a conductor which is equal to the rate of change of magnetic flux. This is given by –
\[\varepsilon =-N\dfrac{d{{\phi }_{B}}}{dt}\]
Where, N is the number of turns of the coil used,
\[{{\phi }_{B}}\] is the magnetic flux
\[\varepsilon \]is the induced emf
When a coil is subjected to a change in the magnetic flux with time the coil experiences an induced emf, which it opposes and therefore, the negative symbol.
Now, let us consider a parallel plate capacitor as shown in the figure –
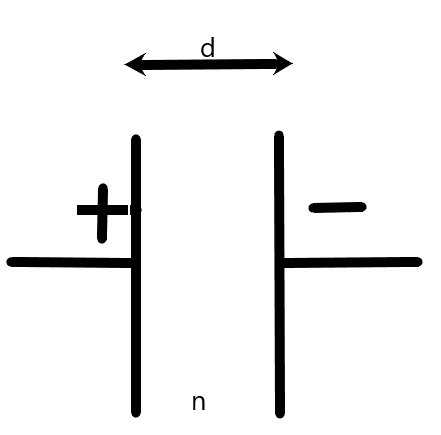
Where, d is the distance between the two plates,
n is the dielectric constant of the medium
We know the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitors is given by –
\[C=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{d}\]
Where A is the area of the plate and
\[{{\varepsilon }_{0}}\] is the dielectric constant of the medium, here air.
(a)The capacitor plates are said to be moved away, or, their distance has been doubled. i.e.,
\[d'=2d\]
So, the capacitance becomes –
\[\begin{align}
& C'=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{d'} \\
& \Rightarrow C'=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{2d}=\dfrac{C}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
The capacitance becomes half of the initial condition.
(b) When a medium of dielectric constant 8 is added to the parallel plate capacitor, the permittivity becomes –
\[\begin{align}
& \varepsilon ={{\varepsilon }_{0}}K \\
& K=8 \\
& \Rightarrow \varepsilon =8{{\varepsilon }_{0}} \\
\end{align}\]
The capacitance of the system becomes –
\[C'=\dfrac{8{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{d}=8C\]
The capacitance becomes eight times the initial condition.
The required solutions are –
(a) The capacitance becomes half, i.e., 10\[\mu F\].
(b) The capacitance becomes eight times, i.e., 80\[\mu F\].
Note:
The above calculations are based on the assumption that the capacitor is not connected to an external power supply. The value of capacitance will be different if there is a voltage that feeds the plates continuously. So we should be careful with such cases.
Complete answer:
According to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, the change of magnetic flux with time around a conductor can cause an induced emf in it. i.e., an emf is induced in a conductor which is equal to the rate of change of magnetic flux. This is given by –
\[\varepsilon =-N\dfrac{d{{\phi }_{B}}}{dt}\]
Where, N is the number of turns of the coil used,
\[{{\phi }_{B}}\] is the magnetic flux
\[\varepsilon \]is the induced emf
When a coil is subjected to a change in the magnetic flux with time the coil experiences an induced emf, which it opposes and therefore, the negative symbol.
Now, let us consider a parallel plate capacitor as shown in the figure –

Where, d is the distance between the two plates,
n is the dielectric constant of the medium
We know the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitors is given by –
\[C=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{d}\]
Where A is the area of the plate and
\[{{\varepsilon }_{0}}\] is the dielectric constant of the medium, here air.
(a)The capacitor plates are said to be moved away, or, their distance has been doubled. i.e.,
\[d'=2d\]
So, the capacitance becomes –
\[\begin{align}
& C'=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{d'} \\
& \Rightarrow C'=\dfrac{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{2d}=\dfrac{C}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
The capacitance becomes half of the initial condition.
(b) When a medium of dielectric constant 8 is added to the parallel plate capacitor, the permittivity becomes –
\[\begin{align}
& \varepsilon ={{\varepsilon }_{0}}K \\
& K=8 \\
& \Rightarrow \varepsilon =8{{\varepsilon }_{0}} \\
\end{align}\]
The capacitance of the system becomes –
\[C'=\dfrac{8{{\varepsilon }_{0}}A}{d}=8C\]
The capacitance becomes eight times the initial condition.
The required solutions are –
(a) The capacitance becomes half, i.e., 10\[\mu F\].
(b) The capacitance becomes eight times, i.e., 80\[\mu F\].
Note:
The above calculations are based on the assumption that the capacitor is not connected to an external power supply. The value of capacitance will be different if there is a voltage that feeds the plates continuously. So we should be careful with such cases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE

Calculate the equivalent resistance between a and b class 12 physics CBSE

How many states of matter are there in total class 12 chemistry CBSE

Which of the following is the best conductor of electricity class 12 physics CBSE




