
Prove that the equal chords of two congruent circles subtend equal angles at their respective centres.
Answer
523.2k+ views
Hint: Use the fact that the radii of two congruent circles are equal and hence prove that OA = O’A’ and OB = O’B’. Use the fact that since the chords are equal AB = A’B’ and hence prove that the triangle ABC and A’B’C’ are congruent and hence prove that $\angle AOC=\angle A'O'C'$. Hence prove that the equal chords of congruent circles subtend equal angles at the centres of their corresponding circles.
Complete step by step answer:
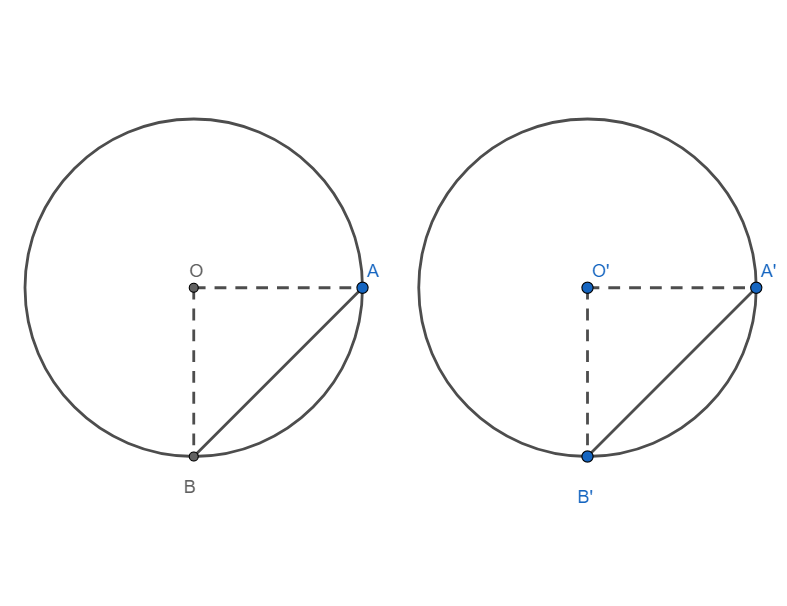
Given: Two circles with centre O and O’ have equal radii. AB is the chord of the circle with centre O and A’B’ is a chord of the circle with centre O’.
To prove $\angle AOB=\angle A'O'B'$
Proof:
Since the circle have equal radii, we have
OA = O’A’ and OB = O’B’
Now, in triangle AOB and A’O’B’, we have
AO = A’O’ (proved above)
OB = O’B’ (Proved above)
AB = A’B’ (Given).
Hence by S.S.S congruence criterion, we have
$\Delta AOB\cong \Delta A'O'B'$
Hence, we have
$\angle AOB=\angle A'O'B'$ (Corresponding parts of congruent triangles)
Hence, equal chords of two congruent circles subtend equal angles at their respective centres.
Hence, proved.
Note: Alternative Solution: Using Sine rule.
We know that if R is the radius of circumcentre of a triangle ABC, then $\dfrac{a}{\sin A}=\dfrac{b}{\sin B}=\dfrac{c}{\sin C}=2R$
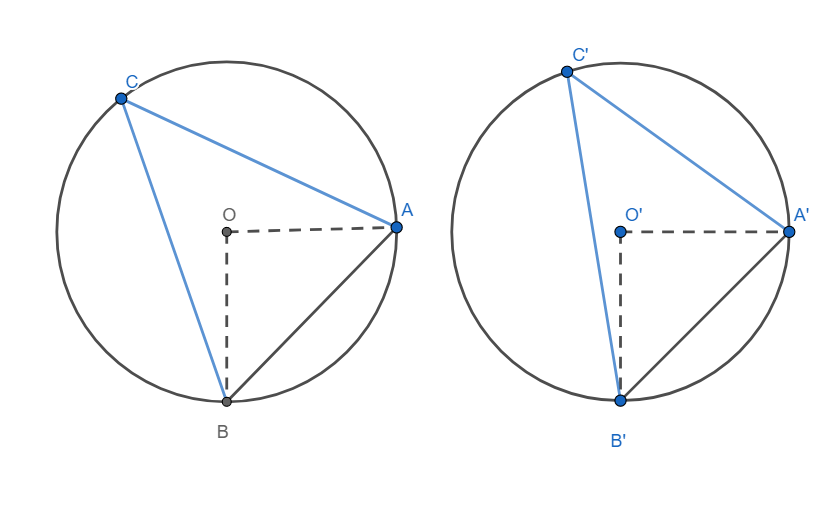
Consider two points C and C’ on the alternate segments as shown in the diagram above.
By sine rule, we have
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AB}{\sin C}=2R \\
& \Rightarrow AB=2R\sin C \\
\end{align}$
Similarly, we have
$A'B'=2R\sin C'$
Since AB = A’B’, we have
$\begin{align}
& 2R\sin C=2R\sin C' \\
& \Rightarrow \sin C=\sin C' \\
& \Rightarrow C=C' \\
\end{align}$
We know that the angle subtended in the alternate segment is half the angle subtended at the centre.
Hence, we have
$\angle AOB=2\angle C$ and $\angle A'O'B'=2\angle C'$
Since $\angle C=\angle C'$, we have
$\angle AOB=\angle A'O'B'$
Q.E.D
Complete step by step answer:

Given: Two circles with centre O and O’ have equal radii. AB is the chord of the circle with centre O and A’B’ is a chord of the circle with centre O’.
To prove $\angle AOB=\angle A'O'B'$
Proof:
Since the circle have equal radii, we have
OA = O’A’ and OB = O’B’
Now, in triangle AOB and A’O’B’, we have
AO = A’O’ (proved above)
OB = O’B’ (Proved above)
AB = A’B’ (Given).
Hence by S.S.S congruence criterion, we have
$\Delta AOB\cong \Delta A'O'B'$
Hence, we have
$\angle AOB=\angle A'O'B'$ (Corresponding parts of congruent triangles)
Hence, equal chords of two congruent circles subtend equal angles at their respective centres.
Hence, proved.
Note: Alternative Solution: Using Sine rule.
We know that if R is the radius of circumcentre of a triangle ABC, then $\dfrac{a}{\sin A}=\dfrac{b}{\sin B}=\dfrac{c}{\sin C}=2R$

Consider two points C and C’ on the alternate segments as shown in the diagram above.
By sine rule, we have
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AB}{\sin C}=2R \\
& \Rightarrow AB=2R\sin C \\
\end{align}$
Similarly, we have
$A'B'=2R\sin C'$
Since AB = A’B’, we have
$\begin{align}
& 2R\sin C=2R\sin C' \\
& \Rightarrow \sin C=\sin C' \\
& \Rightarrow C=C' \\
\end{align}$
We know that the angle subtended in the alternate segment is half the angle subtended at the centre.
Hence, we have
$\angle AOB=2\angle C$ and $\angle A'O'B'=2\angle C'$
Since $\angle C=\angle C'$, we have
$\angle AOB=\angle A'O'B'$
Q.E.D
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




