
Prove that:
$\cos \theta + \sin \left( {{{270}^ \circ } + \theta } \right) - \sin \left( {{{270}^ \circ } - \theta } \right) + \cos \left( {{{180}^ \circ } + \theta } \right) = 0$.
Answer
562.8k+ views
Hint: In the given equation right hand side (RHS) is zero and we have to prove that the given equation is correct. So, we need to show the LHS of the equation that is $\cos \theta + \sin \left( {{{270}^ \circ } + \theta } \right) - \sin \left( {{{270}^ \circ } - \theta } \right) + \cos \left( {{{180}^ \circ } + \theta } \right)$is equal to zero. Here, we need to use some trigonometric formula to show that its value is zero that is,
(1) $\sin \left( {A + B} \right) = \sin A\cos B + \cos A\sin B$.
(2) $\sin \left( {A - B} \right) = \sin A\cos B - \cos A\sin B$.
(3) $\cos \left( {A + B} \right) = \cos A\cos B - \sin A\sin B$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given: LHS of the equation is
$\Rightarrow$ $\cos \theta + \sin \left( {{{270}^ \circ } + \theta } \right) - \sin \left( {{{270}^ \circ } - \theta } \right) + \cos \left( {{{180}^ \circ } + \theta } \right)$.
RHS of the equation is zero.
Now, we have to calculate the value of expression on the LHS of the equation.
$\Rightarrow$ $ \cos \theta + \sin \left( {{{270}^ \circ } + \theta } \right) - \sin \left( {{{270}^ \circ } - \theta } \right) + \cos \left( {{{180}^ \circ } + \theta } \right)$
By using the formula,
$\Rightarrow$ $\sin \left( {A + B} \right) = \sin A\cos B + \cos A\sin B$ we can expand,
$\Rightarrow$$\sin \left( {{{270}^ \circ } + \theta } \right)$ where,
$\Rightarrow$$A = 27{0^ \circ }$ and $B = \theta $.
And similarly, we can expand,
$\Rightarrow$$\sin \left( {27{0^ \circ } - \theta } \right)$ by using the formula,
$\Rightarrow$$\sin \left( {A - B} \right) = \sin A\cos B - \cos A\sin B$, And $\cos \left( {{{180}^ \circ } + \theta } \right)$ by using the formula,
$\cos \left( {A + B} \right) = \cos A\cos B - \sin A\sin B$.
Then we get,
$\Rightarrow$$ \cos \theta + \sin {270^ \circ }\cos \theta + \cos {270^ \circ }\sin \theta - \sin {270^ \circ }\cos \theta + \cos {270^ \circ }\sin \theta + \cos {180^ \circ }\cos \theta - \sin {180^ \circ }\sin \theta .$
Now, putting the value of
$\sin {270^ \circ } = - 1$ ,
$\cos {270^ \circ } = 0$ ,
$\cos {180^ \circ } = - 1$ and
$\sin {180^ \circ } = 0$ in the above equation. We get,
$\Rightarrow$$ \cos \theta + \left( { - 1} \right)\cos \theta + \left( 0 \right)\sin \theta - \left( { - 1} \right)\cos \theta + \left( 0 \right)\sin \theta + \left( { - 1} \right)\cos \theta - \left( 0 \right)\sin \theta$
$\Rightarrow \cos \theta - \cos \theta + \cos \theta - \cos \theta$
$\Rightarrow 0 $
Thus, we get the left hind side of the equation is zero.
Since LHS is equal to RHS. So, the given equation is proved.
Note:
Alternative method:
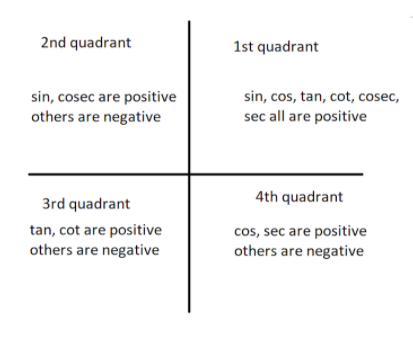
If we add or subtract any angle $\theta $ to/from ${180^ \circ }$ and ${360^ \circ }$(angles on $X$- axis) then the trigonometric function like $\sin $,$\cos $, $\tan $ etc. remain same only there is change in sign according to quadrant. That is if adding $\theta $ angles goes in the third quadrant then only $\tan \theta $ and $\cot \theta $ are positive and others are negative. If we add or subtract any angle $\theta $ from ${90^ \circ }$(angles on the $Y$- axis) then the trigonometric function $\sin $ convert to $\cos $, $\tan $ convert to $\cot $ and $\sec $ convert to $\cos ec$ and vice-versa. Some examples are
$
\sin \left( {{{270}^ \circ } + \theta } \right) = - \cos \theta \\
\sin \left( {{{270}^ \circ } - \theta } \right) = - \cos \theta \\
\cos \left( {{{180}^ \circ } + \theta } \right) = - \cos \theta \\
$
Then, putting this value we get the value of expression on the left side of the equation.
(1) $\sin \left( {A + B} \right) = \sin A\cos B + \cos A\sin B$.
(2) $\sin \left( {A - B} \right) = \sin A\cos B - \cos A\sin B$.
(3) $\cos \left( {A + B} \right) = \cos A\cos B - \sin A\sin B$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given: LHS of the equation is
$\Rightarrow$ $\cos \theta + \sin \left( {{{270}^ \circ } + \theta } \right) - \sin \left( {{{270}^ \circ } - \theta } \right) + \cos \left( {{{180}^ \circ } + \theta } \right)$.
RHS of the equation is zero.
Now, we have to calculate the value of expression on the LHS of the equation.
$\Rightarrow$ $ \cos \theta + \sin \left( {{{270}^ \circ } + \theta } \right) - \sin \left( {{{270}^ \circ } - \theta } \right) + \cos \left( {{{180}^ \circ } + \theta } \right)$
By using the formula,
$\Rightarrow$ $\sin \left( {A + B} \right) = \sin A\cos B + \cos A\sin B$ we can expand,
$\Rightarrow$$\sin \left( {{{270}^ \circ } + \theta } \right)$ where,
$\Rightarrow$$A = 27{0^ \circ }$ and $B = \theta $.
And similarly, we can expand,
$\Rightarrow$$\sin \left( {27{0^ \circ } - \theta } \right)$ by using the formula,
$\Rightarrow$$\sin \left( {A - B} \right) = \sin A\cos B - \cos A\sin B$, And $\cos \left( {{{180}^ \circ } + \theta } \right)$ by using the formula,
$\cos \left( {A + B} \right) = \cos A\cos B - \sin A\sin B$.
Then we get,
$\Rightarrow$$ \cos \theta + \sin {270^ \circ }\cos \theta + \cos {270^ \circ }\sin \theta - \sin {270^ \circ }\cos \theta + \cos {270^ \circ }\sin \theta + \cos {180^ \circ }\cos \theta - \sin {180^ \circ }\sin \theta .$
Now, putting the value of
$\sin {270^ \circ } = - 1$ ,
$\cos {270^ \circ } = 0$ ,
$\cos {180^ \circ } = - 1$ and
$\sin {180^ \circ } = 0$ in the above equation. We get,
$\Rightarrow$$ \cos \theta + \left( { - 1} \right)\cos \theta + \left( 0 \right)\sin \theta - \left( { - 1} \right)\cos \theta + \left( 0 \right)\sin \theta + \left( { - 1} \right)\cos \theta - \left( 0 \right)\sin \theta$
$\Rightarrow \cos \theta - \cos \theta + \cos \theta - \cos \theta$
$\Rightarrow 0 $
Thus, we get the left hind side of the equation is zero.
Since LHS is equal to RHS. So, the given equation is proved.
Note:

Alternative method:
If we add or subtract any angle $\theta $ to/from ${180^ \circ }$ and ${360^ \circ }$(angles on $X$- axis) then the trigonometric function like $\sin $,$\cos $, $\tan $ etc. remain same only there is change in sign according to quadrant. That is if adding $\theta $ angles goes in the third quadrant then only $\tan \theta $ and $\cot \theta $ are positive and others are negative. If we add or subtract any angle $\theta $ from ${90^ \circ }$(angles on the $Y$- axis) then the trigonometric function $\sin $ convert to $\cos $, $\tan $ convert to $\cot $ and $\sec $ convert to $\cos ec$ and vice-versa. Some examples are
$
\sin \left( {{{270}^ \circ } + \theta } \right) = - \cos \theta \\
\sin \left( {{{270}^ \circ } - \theta } \right) = - \cos \theta \\
\cos \left( {{{180}^ \circ } + \theta } \right) = - \cos \theta \\
$
Then, putting this value we get the value of expression on the left side of the equation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




