
Prove that $\cos \left( { - x} \right) = \cos x{\text{ }}{\text{.}}$
Answer
493.8k+ views
Hint: In this question, a trigonometric identity has been given and we are asked to prove it. One way is that we can apply the difference formula for cosine function by putting the appropriate values and solving it. The other method is to analyze the behavior of the cosine function by plotting it’s graph and find out whether it is an odd function or even function and then by the definition of even or odd function we can prove the given identity. $\left( 1 \right)$ Even functions: cosine and secant are even functions i.e. $\cos \left( { - x} \right) = \cos x$ and $\sec \left( { - x} \right) = \sec x$ . $\left( 2 \right)$ Odd functions: sine, tangent, cosecant, cotangent all are odd functions i.e. $\sin \left( { - x} \right) = - \sin x,{\text{ }}\tan \left( { - x} \right) = - \tan x,{\text{ }}\cos ec\left( { - x} \right) = - \cos ecx,{\text{ }}\cot \left( { - x} \right) = - \cot x$.
Complete step-by-step solution:
To prove: $\cos \left( { - x} \right) = \cos x$
Method $1{\text{ :}}$
By the difference of angle formula for cosine function, we know that;
$ \Rightarrow \cos \left( {A - B} \right) = \cos A\cos B + \sin A\sin B{\text{ }}......\left( 1 \right)$
Put $A = 0{\text{ , }}B = x$ in the above formula, we get the L.H.S. ;
L.H.S. $ \Rightarrow \cos \left( {0 - x} \right) = \cos {0^0} \times \cos x + \sin {0^0} \times \sin x$
We know that;
$\because \sin {0^0} = 0$ and
$\because \cos {0^0} = 1$
The above equation can be further simplified as;
L.H.S. $ \Rightarrow \cos \left( { - x} \right) = 1 \times \cos x + 0 \times \sin x$
On further simplification;
L.H.S. $ \Rightarrow \cos \left( { - x} \right) = \cos x$
L.H.S. = R.H.S.
Hence proved.
Method $2{\text{ :}}$
By using the property of even and odd function:
$\left( {\text{i}} \right)$ Odd function:
Definition: A function $y = f\left( x \right)$ is called an odd function if $f\left( { - x} \right) = - f\left( x \right)$ for every $x$ in the function’s domain. In simple words we can say that if we replace $x$ with $ - x$ , the value of the function becomes negative.
Example: $\sin \left( { - x} \right) = - \sin x$ ( sine is a odd function )
Important point: The graph of an odd function is symmetrical about the origin ( by ${180^0}$ rotation ) . The graph for sine function is shown below:-
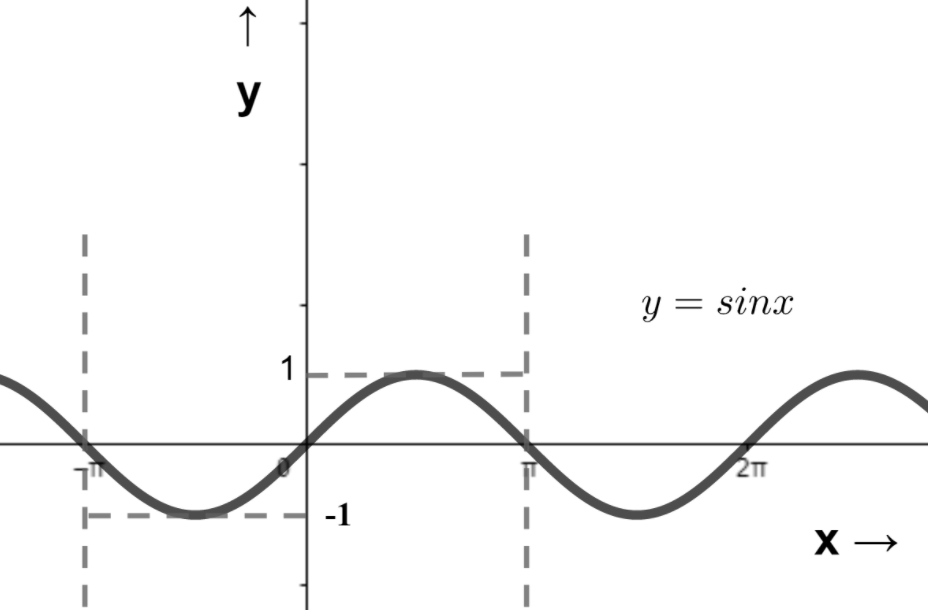
Figure $1$ : Graph of sine function ( time period $ = 2\pi $ )
From the graph we can see that the value of $\sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) = 1$ but the value of $\sin \left( { - \dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) = - 1$ , hence our definition holds true i.e. $f\left( { - x} \right) = - f\left( x \right)$ .
$\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right)$ Even function:
Definition: A function $y = f\left( x \right)$ is called an even function if $f\left( { - x} \right) = f\left( x \right)$ for every $x$ in the function’s domain. In simple words we can say that if we replace $x$ with $ - x$ , the value of the function does not change.
Example: $\cos \left( { - x} \right) = \cos x$ ( cosine is an even function )
Important point: The graph of an even function is symmetrical about the vertical axis or y-axis. The graph for cosine function is shown below:-
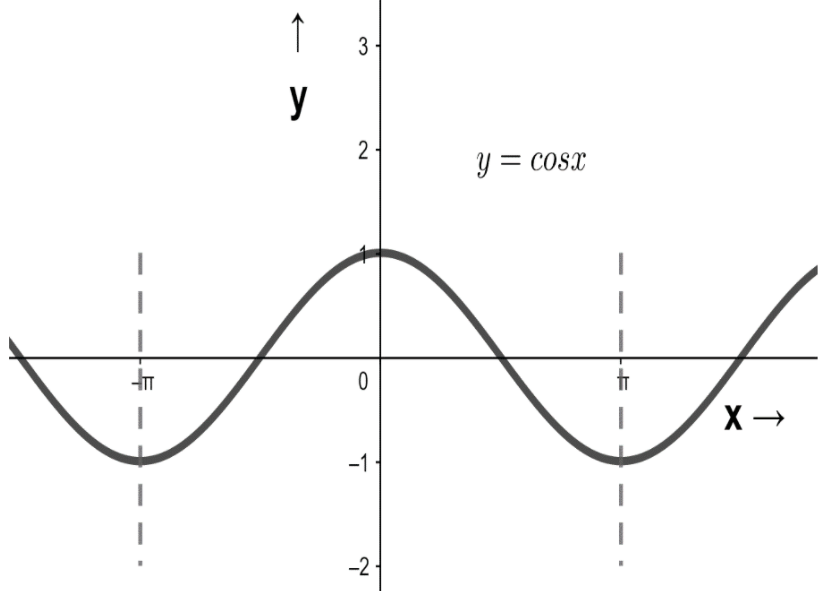
Figure $2$ : Graph of cosine function ( time period $ = 2\pi $ )
From the graph we can see that the value of $\cos \pi = - 1$ and also the value of $\cos \left( { - \pi } \right) = - 1$ , hence our definition holds true i.e. $f\left( { - x} \right) = f\left( x \right)$ .
So, from the above figure we can directly state that;
$ \Rightarrow \cos \left( { - x} \right) = \cos x$
Hence proved.
Note: The even and odd properties of functions can be really useful while solving this type of questions. The functions can be of three types: $\left( {\text{i}} \right)$ Even function: As we have already seen cosine is an even function. $\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right)$ Odd function: We have discussed that the sine function is an odd function. $\left( {{\text{iii}}} \right)$ Neither even nor odd function: It is a possibility that a function is neither even nor odd. For example: Check if the given function is even or odd; $y \Rightarrow f\left( x \right) = \tan x + \sec x$ . Put $x = - x$ , we get $f\left( { - x} \right) = \tan \left( { - x} \right) + \sec \left( { - x} \right)$ . We know that tangent is a odd function i.e. $\tan \left( { - x} \right) = - \tan x$ and secant is an even function i.e. $\sec \left( { - x} \right) = \sec x$ . Therefore, $f\left( { - x} \right) = - \tan x + \sec x$ . So, in this case $f\left( { - x} \right) \ne f\left( x \right)$ or $f\left( { - x} \right) \ne - f\left( x \right)$ ; hence this function is neither even nor odd.
Complete step-by-step solution:
To prove: $\cos \left( { - x} \right) = \cos x$
Method $1{\text{ :}}$
By the difference of angle formula for cosine function, we know that;
$ \Rightarrow \cos \left( {A - B} \right) = \cos A\cos B + \sin A\sin B{\text{ }}......\left( 1 \right)$
Put $A = 0{\text{ , }}B = x$ in the above formula, we get the L.H.S. ;
L.H.S. $ \Rightarrow \cos \left( {0 - x} \right) = \cos {0^0} \times \cos x + \sin {0^0} \times \sin x$
We know that;
$\because \sin {0^0} = 0$ and
$\because \cos {0^0} = 1$
The above equation can be further simplified as;
L.H.S. $ \Rightarrow \cos \left( { - x} \right) = 1 \times \cos x + 0 \times \sin x$
On further simplification;
L.H.S. $ \Rightarrow \cos \left( { - x} \right) = \cos x$
L.H.S. = R.H.S.
Hence proved.
Method $2{\text{ :}}$
By using the property of even and odd function:
$\left( {\text{i}} \right)$ Odd function:
Definition: A function $y = f\left( x \right)$ is called an odd function if $f\left( { - x} \right) = - f\left( x \right)$ for every $x$ in the function’s domain. In simple words we can say that if we replace $x$ with $ - x$ , the value of the function becomes negative.
Example: $\sin \left( { - x} \right) = - \sin x$ ( sine is a odd function )
Important point: The graph of an odd function is symmetrical about the origin ( by ${180^0}$ rotation ) . The graph for sine function is shown below:-

Figure $1$ : Graph of sine function ( time period $ = 2\pi $ )
From the graph we can see that the value of $\sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) = 1$ but the value of $\sin \left( { - \dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) = - 1$ , hence our definition holds true i.e. $f\left( { - x} \right) = - f\left( x \right)$ .
$\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right)$ Even function:
Definition: A function $y = f\left( x \right)$ is called an even function if $f\left( { - x} \right) = f\left( x \right)$ for every $x$ in the function’s domain. In simple words we can say that if we replace $x$ with $ - x$ , the value of the function does not change.
Example: $\cos \left( { - x} \right) = \cos x$ ( cosine is an even function )
Important point: The graph of an even function is symmetrical about the vertical axis or y-axis. The graph for cosine function is shown below:-

Figure $2$ : Graph of cosine function ( time period $ = 2\pi $ )
From the graph we can see that the value of $\cos \pi = - 1$ and also the value of $\cos \left( { - \pi } \right) = - 1$ , hence our definition holds true i.e. $f\left( { - x} \right) = f\left( x \right)$ .
So, from the above figure we can directly state that;
$ \Rightarrow \cos \left( { - x} \right) = \cos x$
Hence proved.
Note: The even and odd properties of functions can be really useful while solving this type of questions. The functions can be of three types: $\left( {\text{i}} \right)$ Even function: As we have already seen cosine is an even function. $\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right)$ Odd function: We have discussed that the sine function is an odd function. $\left( {{\text{iii}}} \right)$ Neither even nor odd function: It is a possibility that a function is neither even nor odd. For example: Check if the given function is even or odd; $y \Rightarrow f\left( x \right) = \tan x + \sec x$ . Put $x = - x$ , we get $f\left( { - x} \right) = \tan \left( { - x} \right) + \sec \left( { - x} \right)$ . We know that tangent is a odd function i.e. $\tan \left( { - x} \right) = - \tan x$ and secant is an even function i.e. $\sec \left( { - x} \right) = \sec x$ . Therefore, $f\left( { - x} \right) = - \tan x + \sec x$ . So, in this case $f\left( { - x} \right) \ne f\left( x \right)$ or $f\left( { - x} \right) \ne - f\left( x \right)$ ; hence this function is neither even nor odd.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




