
Prove that angle in a semi circle is a right angle by vector method.
Answer
531.6k+ views
Hint: Now to solve prove the result we will first draw the required figure. Now we will form two triangles by the diameter and join the center of the circle to point on circumference. Now in both triangles we will use triangle law of addition of vectors and take dot product of the two vectors which subtend the required angle. Now we will simplify the equation. Now we know that if the dot product of two vectors is zero then the vectors are at right angles. Hence the required result is proved.
Complete step by step answer:
Now first consider the given figure
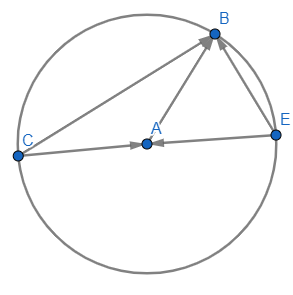
Now here we know that $\overrightarrow{EA}=-\vec{r}$ and $\overrightarrow{CA}=\vec{r}$
Now let $\overrightarrow{AB}=\vec{a}$
Now we know that the radius of the circle is equal.
Hence we get $\left| {\vec{a}} \right|=\left| {\vec{r}} \right|$
Now by the vector addition law we have $\overrightarrow{CA}+\overrightarrow{AB}=\overrightarrow{CB}$
Hence we get, $\overrightarrow{CB}=\vec{a}+\vec{r}........\left( 1 \right)$
Now similarly $\overrightarrow{EB}=\overrightarrow{EA}+\overrightarrow{AB}$
Hence we get $\overrightarrow{EB}=-\vec{r}+\vec{a}.......\left( 2 \right)$
Now from equation (1) and equation (2) we get, $\overrightarrow{CB}.\overrightarrow{EB}=\left( \vec{a}+\vec{r} \right).\left( \vec{a}-\vec{r} \right)$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{CB}.\overrightarrow{EB}=\left( \vec{a}+\vec{r} \right).\left( \vec{a}-\vec{r} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{CB}.\overrightarrow{EB}=\vec{a}.\vec{a}+\vec{a}\vec{r}-\vec{a}\vec{r}-\vec{r}.\vec{r} \\
\end{align}$
Now we know that \[\vec{x}.\vec{x}=\left| x \right|\]
Hence we get,
$\Rightarrow \overrightarrow{CB}.\overrightarrow{EB}=\left| {\vec{a}} \right|-\left| {\vec{r}} \right|$
Now we know that $\left| {\vec{a}} \right|=\left| {\vec{r}} \right|$ as they are the radius of the circle.
Hence we get,
$\overrightarrow{CB}.\overrightarrow{EB}=0$
Now we know that the dot product of two quantities is only if they are perpendicular. Hence we get the two vectors $\overrightarrow{CB}$ and $\overrightarrow{EB}$ are perpendicular.
Hence the required result is proved.
Note: Now note that vector has magnitude as well as direction. Hence though vector AC and vector AB are radii their subtraction will not be zero. Also note that since A, C and E lie on the same line which is diameter we can take the vectors CA and CE as $\vec{r}$ and $-\vec{r}$.
Complete step by step answer:
Now first consider the given figure

Now here we know that $\overrightarrow{EA}=-\vec{r}$ and $\overrightarrow{CA}=\vec{r}$
Now let $\overrightarrow{AB}=\vec{a}$
Now we know that the radius of the circle is equal.
Hence we get $\left| {\vec{a}} \right|=\left| {\vec{r}} \right|$
Now by the vector addition law we have $\overrightarrow{CA}+\overrightarrow{AB}=\overrightarrow{CB}$
Hence we get, $\overrightarrow{CB}=\vec{a}+\vec{r}........\left( 1 \right)$
Now similarly $\overrightarrow{EB}=\overrightarrow{EA}+\overrightarrow{AB}$
Hence we get $\overrightarrow{EB}=-\vec{r}+\vec{a}.......\left( 2 \right)$
Now from equation (1) and equation (2) we get, $\overrightarrow{CB}.\overrightarrow{EB}=\left( \vec{a}+\vec{r} \right).\left( \vec{a}-\vec{r} \right)$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{CB}.\overrightarrow{EB}=\left( \vec{a}+\vec{r} \right).\left( \vec{a}-\vec{r} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{CB}.\overrightarrow{EB}=\vec{a}.\vec{a}+\vec{a}\vec{r}-\vec{a}\vec{r}-\vec{r}.\vec{r} \\
\end{align}$
Now we know that \[\vec{x}.\vec{x}=\left| x \right|\]
Hence we get,
$\Rightarrow \overrightarrow{CB}.\overrightarrow{EB}=\left| {\vec{a}} \right|-\left| {\vec{r}} \right|$
Now we know that $\left| {\vec{a}} \right|=\left| {\vec{r}} \right|$ as they are the radius of the circle.
Hence we get,
$\overrightarrow{CB}.\overrightarrow{EB}=0$
Now we know that the dot product of two quantities is only if they are perpendicular. Hence we get the two vectors $\overrightarrow{CB}$ and $\overrightarrow{EB}$ are perpendicular.
Hence the required result is proved.
Note: Now note that vector has magnitude as well as direction. Hence though vector AC and vector AB are radii their subtraction will not be zero. Also note that since A, C and E lie on the same line which is diameter we can take the vectors CA and CE as $\vec{r}$ and $-\vec{r}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




