
How is propyne prepared from an:
(i) alkylene dihalide
(ii) alkylidene dihalide
(iii) tetra haloalkane
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: Propyne is an alkyne who can be prepared from the alkane derivatives by substitution reaction. We need to have general information and understanding about the reactions that would take place to prepare propyne.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us firstly understand about the reagents given for the preparation of propyne;
1. Alkylene dihalide- It is a di-halogen derivative of an alkane in which the two halogens are attached to the adjacent carbon atoms of the chain. Since, the position of halogens are on adjacent carbon atoms; alkylene dihalides are also known as vicinal dihalides.
2. Alkylidene dihalide-It is a di-halogen derivative of an alkane in which the two halogens are attached to the same carbon atom of the chain. Since, the position of halogens are on the same carbon atom; alkylidene dihalides are also known as geminal dihalides.
3. Tetra haloalkane-The general formula of tetra haloalkane is ${{C}_{n}}{{H}_{2n-2}}{{X}_{4}}$ where, n = 1, 2, 3, 4…
The position of the halogen atom is indicated by the ‘n’ on the carbon chain.
Now, let us move towards the reaction giving propyne as the product from;
(i) Alkylene dihalide -Dehydrohalogenation of vicinal dihalides takes place to give alkyne as a product.
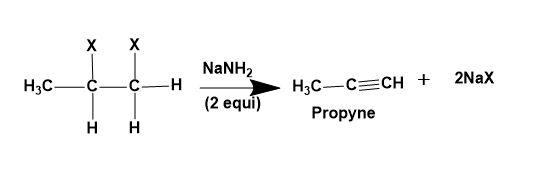
(ii) Alkylidene dihalide-Dehydrohalogenation of geminal dihalides takes place to give alkyne as a product.
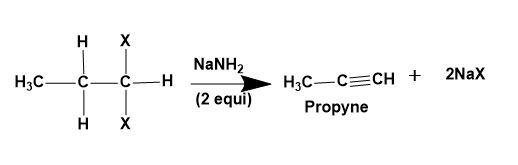
(iii) Tetra-haloalkane-Dehalogenation of vicinal tetra-haloalkane takes place to give alkyne as a product.
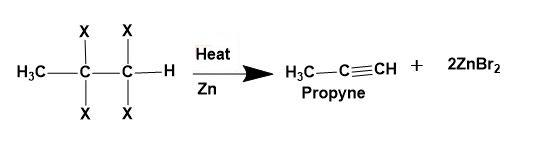
Note: These are the laboratory methods for the preparation of alkynes. Also, they have their own drawbacks too; as the halogen compounds are themselves prepared by halogen addition to alkynes.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us firstly understand about the reagents given for the preparation of propyne;
1. Alkylene dihalide- It is a di-halogen derivative of an alkane in which the two halogens are attached to the adjacent carbon atoms of the chain. Since, the position of halogens are on adjacent carbon atoms; alkylene dihalides are also known as vicinal dihalides.
2. Alkylidene dihalide-It is a di-halogen derivative of an alkane in which the two halogens are attached to the same carbon atom of the chain. Since, the position of halogens are on the same carbon atom; alkylidene dihalides are also known as geminal dihalides.
3. Tetra haloalkane-The general formula of tetra haloalkane is ${{C}_{n}}{{H}_{2n-2}}{{X}_{4}}$ where, n = 1, 2, 3, 4…
The position of the halogen atom is indicated by the ‘n’ on the carbon chain.
Now, let us move towards the reaction giving propyne as the product from;
(i) Alkylene dihalide -Dehydrohalogenation of vicinal dihalides takes place to give alkyne as a product.

(ii) Alkylidene dihalide-Dehydrohalogenation of geminal dihalides takes place to give alkyne as a product.

(iii) Tetra-haloalkane-Dehalogenation of vicinal tetra-haloalkane takes place to give alkyne as a product.

Note: These are the laboratory methods for the preparation of alkynes. Also, they have their own drawbacks too; as the halogen compounds are themselves prepared by halogen addition to alkynes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




