
How many products are formed in the given reaction?
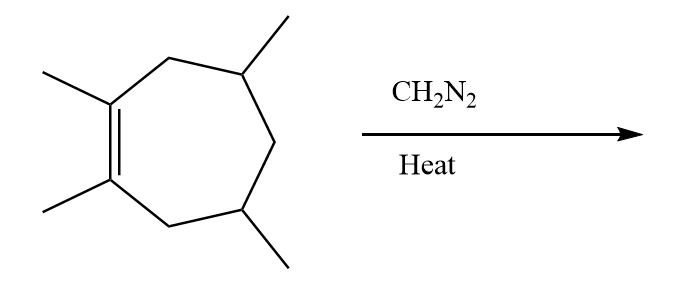

Answer
509.1k+ views
Hint: A carbene is an intermediate containing a neutral carbon atom with two unshared valence electrons. It is generally represented as $R' - (:C) - R$. If the two alkyl groups are replaced by hydrogen atoms, then the carbene is specifically known as methylene. Due to instability, the carbenes are very short lived and hence are very reactive in nature.
Complete answer:
For the given conditions, reaction mechanism is as follows:
Step-1: Formation of carbene (methylene) from diazomethane:
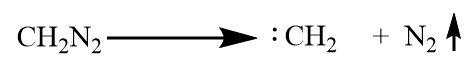
Step-2: Reaction of carbene with the given compound.
Methylene reacts with the given compound and breaks the double bond of the ring and forms a three membered ring-like structure on the ring. Generally, in this reaction the stereochemistry of the double bond remains unchanged. The reaction proceeds as follows:
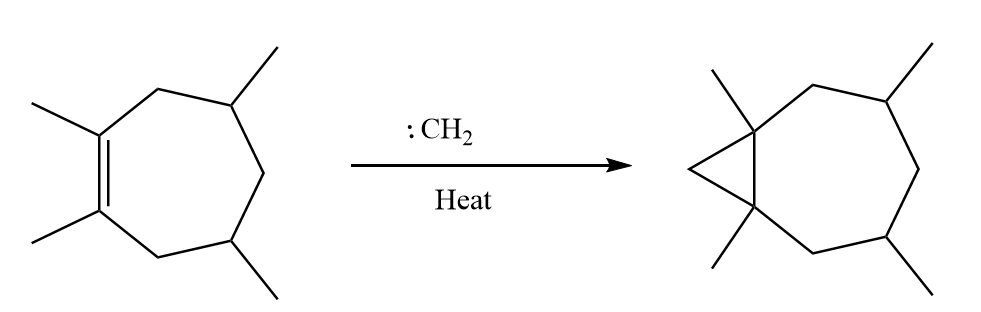
Now, the two possibilities with which the carbene can attack the double bond are as follows:
Possibility-1: Attack of methylene from above the plane of the double bond. The product formed in this case will be as follows:
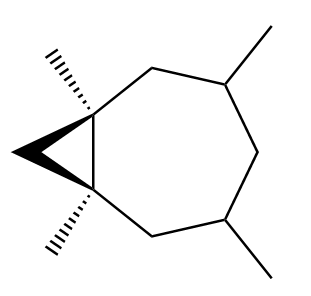
Possibility-2: Attack of methylene from below the plane of the double bond. The product formed in this case will be as follows:
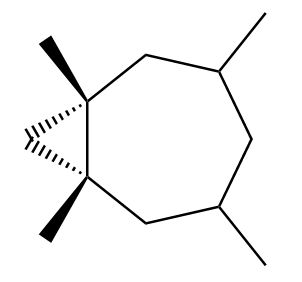
Although these compounds seem to be enantiomers, but if we rotate the product considered in possibility 1 to an angle of ${180^o}$, we observe that the new product formed will be the same as the product considered in possibility 2. So, we can conclude that both the products are identical to each other.
Hence, there is formation of only one product for the given reaction conditions.
Note:
It is important to note that the major difference between identical compounds and enantiomers is that in identical compounds, all the stereo centres have the same absolute configuration whereas in enantiomers, at least one chiral carbon will have a relatively opposite configuration.
Complete answer:
For the given conditions, reaction mechanism is as follows:
Step-1: Formation of carbene (methylene) from diazomethane:

Step-2: Reaction of carbene with the given compound.
Methylene reacts with the given compound and breaks the double bond of the ring and forms a three membered ring-like structure on the ring. Generally, in this reaction the stereochemistry of the double bond remains unchanged. The reaction proceeds as follows:

Now, the two possibilities with which the carbene can attack the double bond are as follows:
Possibility-1: Attack of methylene from above the plane of the double bond. The product formed in this case will be as follows:

Possibility-2: Attack of methylene from below the plane of the double bond. The product formed in this case will be as follows:

Although these compounds seem to be enantiomers, but if we rotate the product considered in possibility 1 to an angle of ${180^o}$, we observe that the new product formed will be the same as the product considered in possibility 2. So, we can conclude that both the products are identical to each other.
Hence, there is formation of only one product for the given reaction conditions.
Note:
It is important to note that the major difference between identical compounds and enantiomers is that in identical compounds, all the stereo centres have the same absolute configuration whereas in enantiomers, at least one chiral carbon will have a relatively opposite configuration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




