
What is the product obtained in this reaction?
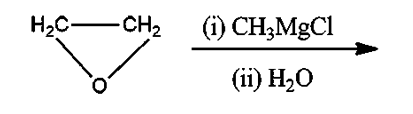
A. $C{H_3}C{H_2}OH$
B. ${(C{H_3})_2}CHOH$
C.\[C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}OH\]
D. $HO - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - OH$
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: Ethylene oxide on reaction with grignard’s reaction will first form an additive product and then it will undergo hydrolysis to produce primary alcohol with release of Mg(OH)X. The reaction follows the ${S_N}2$ mechanism.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, either present is Ethylene Oxide, $C{H_3}MgCl$ is known as Methylmagnesium Chloride which is Grignard’s Reagent and ${H_2}O$ is water.
Grignard Reagent- A Grignard reagent is a chemical compound with the generic formula R−Mg−X, where X is a halogen and R is an organic group.
Grignard reacts with ethylene oxide to produce a primary alcohol containing two more carbon atoms than the original Grignard reagent. This reaction follows the same ${S_N}2$ mechanism as the opening of epoxide rings under basic conditions since Grignard reagents are both strong nucleophiles and strong bases.
Ethylene oxide when reacts with Grignard reagent forms an additive product which undergoes hydrolysis to give primary alcohol as the final product.
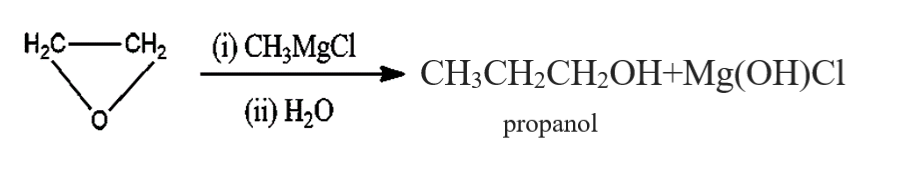
In the options given above, primary, secondary, tertiary and cyclopropyl alcohol is present. As mentioned above, when an ether reacts with the grignard's reagent under presence of water, primary alcohol is formed. So, $C{H_3}C{H_2}OH$ which is a primary alcohol is formed.
Hence option A is correct.
Note:
Reaction of Ester with Grignard’s Reagent-
An ester reacts first with Grignard’s reagent to form a ketone, which reacts with water further to give alcohol.
Reaction of Alcohol with Grignard’s Reagent-
An alcohol reacts with Grignard’s Reagent to form an alkane.
Reaction of Aldehyde/Ketone with Grignard Reagent-
Aldehyde/Ketone reacts with Grignard’s reagent to alcohol.
${S_N}2$ reaction mechanism -The ${S_N}2$ reaction mechanism involves the nucleophilic substitution reaction of the leaving group with a nucleophile in a given organic compound.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, either present is Ethylene Oxide, $C{H_3}MgCl$ is known as Methylmagnesium Chloride which is Grignard’s Reagent and ${H_2}O$ is water.
Grignard Reagent- A Grignard reagent is a chemical compound with the generic formula R−Mg−X, where X is a halogen and R is an organic group.
Grignard reacts with ethylene oxide to produce a primary alcohol containing two more carbon atoms than the original Grignard reagent. This reaction follows the same ${S_N}2$ mechanism as the opening of epoxide rings under basic conditions since Grignard reagents are both strong nucleophiles and strong bases.
Ethylene oxide when reacts with Grignard reagent forms an additive product which undergoes hydrolysis to give primary alcohol as the final product.

In the options given above, primary, secondary, tertiary and cyclopropyl alcohol is present. As mentioned above, when an ether reacts with the grignard's reagent under presence of water, primary alcohol is formed. So, $C{H_3}C{H_2}OH$ which is a primary alcohol is formed.
Hence option A is correct.
Note:
Reaction of Ester with Grignard’s Reagent-
An ester reacts first with Grignard’s reagent to form a ketone, which reacts with water further to give alcohol.
Reaction of Alcohol with Grignard’s Reagent-
An alcohol reacts with Grignard’s Reagent to form an alkane.
Reaction of Aldehyde/Ketone with Grignard Reagent-
Aldehyde/Ketone reacts with Grignard’s reagent to alcohol.
${S_N}2$ reaction mechanism -The ${S_N}2$ reaction mechanism involves the nucleophilic substitution reaction of the leaving group with a nucleophile in a given organic compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




