
Product obtained in following reactions $(1),(2)\And (3)$ is:
(a) $A=B,C$ is different
(b) $A=C,B$ is different
(c) $B=C,A$ is different
(d) $A=B=C$ is same



Answer
538.2k+ views
Hint: Alcoholic potassium hydroxide $ KOH$ acts as a strong base; it is used in the elimination reactions where unsaturated products are obtained from saturated compounds.
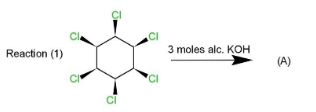
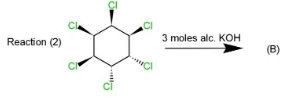
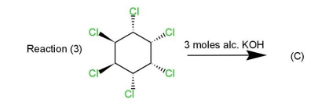
Complete step by step solution: Three reactions $(1),(2)\And (3)$ are given that involves $1,2,3,4,5,6-$ chloro cyclohexane, which is treated with three moles of alcoholic potassium hydroxide. The reaction is a type of $\beta -$ elimination reaction that results in double bonds in the product.
The first reaction is accompanied by the removal of hydrogen from$\beta -$ position which is at the anti position, so this will be the type of ${{E}_{2}}$ anti-elimination reaction. This reaction is carried in the way that alternate double bond formation takes place when $\beta -$ hydrogens from $1,3,5$ positions get removed along with chlorine from $2,4,6$ positions as $3$ moles of $KOH$ are used. Hence the product formed will be $1,3,5$ trichlorobenzene.

This product will be obtained in the first case. While in the second and third case, the product obtained will be the same as in reaction $(2)$ four $Cl$ atoms are on the same side while two are on opposite sides which will retain the symmetry and $1,3,5$ trichlorobenzene. Same will happen in reaction $(3)$ as four $Cl$ atoms are on the same side and two on the opposite. The geometry in all the three reactions will be such that the elimination will occur of $Cl$ and hydrogen to retain $Cl$ at $1,3,5$ positions along with double bonds.
Therefore, option (d) is correct as products $A=B=C$ are the same.
Note: Anti-elimination takes place when the $\beta -$ hydrogen is removed from the opposite side to that of the leaving group (here chlorine). Syn elimination takes place when $\beta -$ hydrogen is removed from the same side to that of the leaving group.
Complete step by step solution: Three reactions $(1),(2)\And (3)$ are given that involves $1,2,3,4,5,6-$ chloro cyclohexane, which is treated with three moles of alcoholic potassium hydroxide. The reaction is a type of $\beta -$ elimination reaction that results in double bonds in the product.
The first reaction is accompanied by the removal of hydrogen from$\beta -$ position which is at the anti position, so this will be the type of ${{E}_{2}}$ anti-elimination reaction. This reaction is carried in the way that alternate double bond formation takes place when $\beta -$ hydrogens from $1,3,5$ positions get removed along with chlorine from $2,4,6$ positions as $3$ moles of $KOH$ are used. Hence the product formed will be $1,3,5$ trichlorobenzene.

This product will be obtained in the first case. While in the second and third case, the product obtained will be the same as in reaction $(2)$ four $Cl$ atoms are on the same side while two are on opposite sides which will retain the symmetry and $1,3,5$ trichlorobenzene. Same will happen in reaction $(3)$ as four $Cl$ atoms are on the same side and two on the opposite. The geometry in all the three reactions will be such that the elimination will occur of $Cl$ and hydrogen to retain $Cl$ at $1,3,5$ positions along with double bonds.
Therefore, option (d) is correct as products $A=B=C$ are the same.
Note: Anti-elimination takes place when the $\beta -$ hydrogen is removed from the opposite side to that of the leaving group (here chlorine). Syn elimination takes place when $\beta -$ hydrogen is removed from the same side to that of the leaving group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




