
Product formed in the reaction is:


Answer
560.4k+ views
Hint: The given compound is a primary alcohol, it is reacting with $\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$. Phosphorus trichloride ($\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$) is a colourless liquid. In this reaction the $\text{(-OH)}$ group of alcohol is replaced by the $\text{(-Cl)}$ group of phosphorus trichloride.
- On reacting with the chlorine derivative of alcohol gives substitution reaction with the sodium methoxide.
- Lesser the steric hindrance faster will be the rate of bimolecular substitution reaction $\text{(}{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2)}$. $\text{(}{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2)}$ Prefers the less hindered side to attack. So ease of $\text{(}{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2)}$ reaction is $\text{(}{{\text{1}}^{\circ }}\text{}\,{{\text{2}}^{\circ }}\text{}\,{{\text{3}}^{\circ }}\text{)}$.
$\text{(}{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2)}$ Reactions involve inversion of configuration of compound stereochemically. So ${{1}^{\circ }}$ alkyl halide is preferred to $\text{(}{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2)}$ reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
This reaction is completed in two steps-
$\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ (Phosphorus trichloride) is good chlorinating agent; it reacts quickly with alcohols and performs substitution reaction.
- In the first step chlorination of substrate takes place in which hydroxyl group of substrate compound is replaced by chlorine atom. This reaction is represented through following chemical reaction-
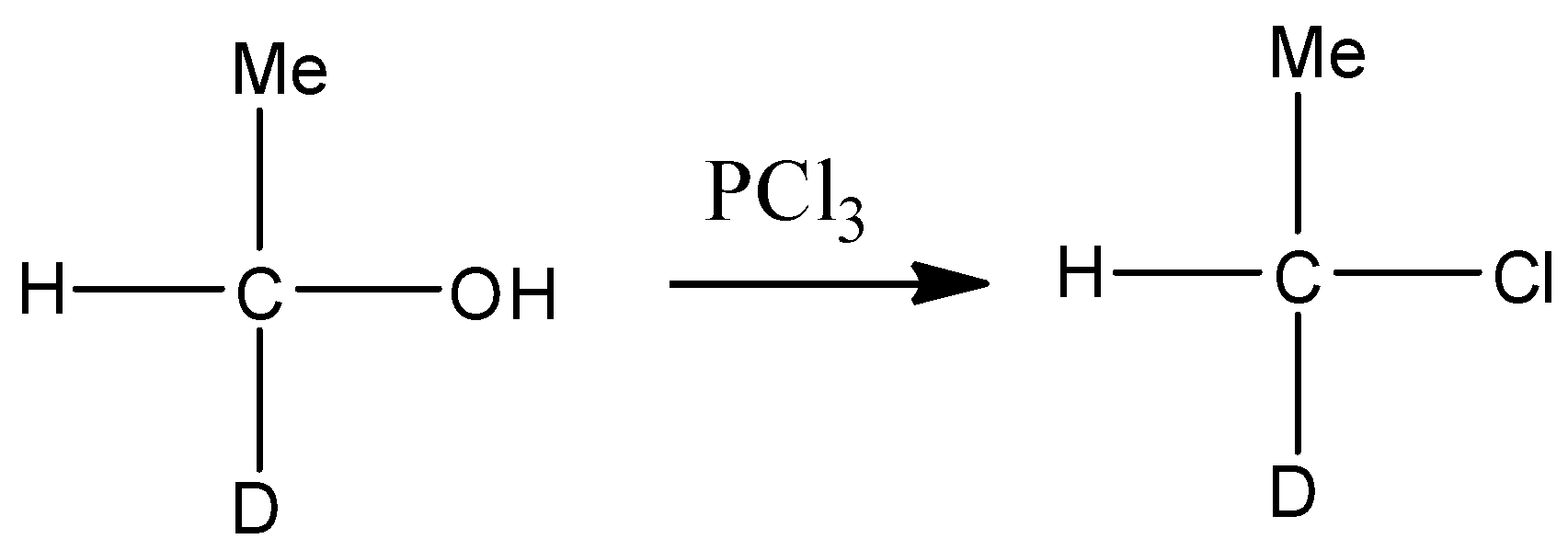
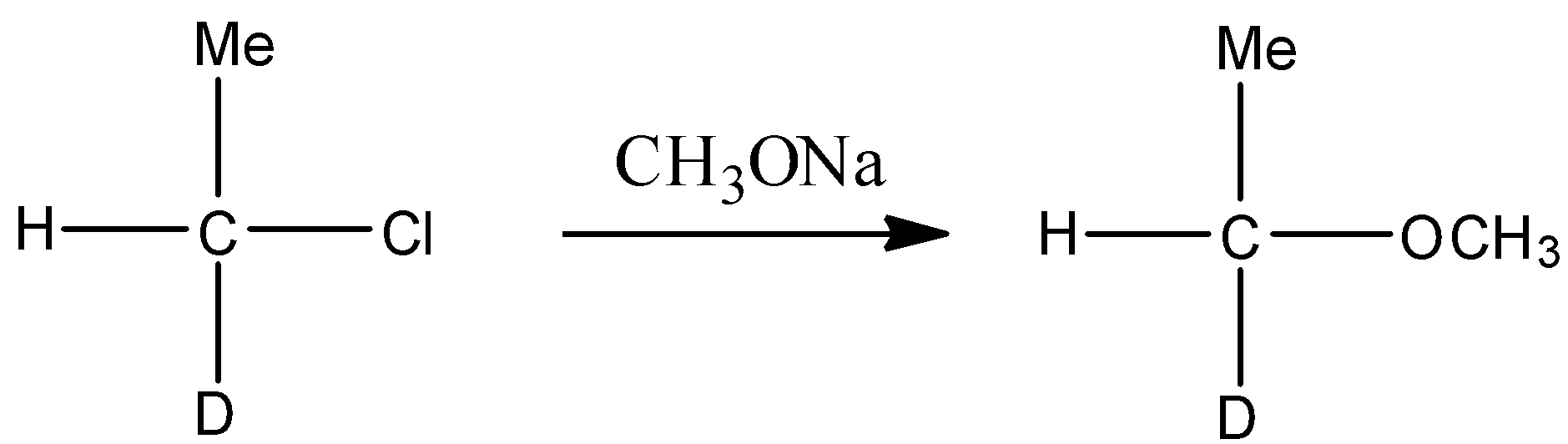
In the second step the chlorinated product of alcohol treated with sodium methoxide in the strong basic medium $\text{(NaOH)}$ . Since chlorine is a poor leaving group, in the presence of polar solvent it gives bimolecular substitution reaction and forms ether. This reaction is represented through the following chemical equation.
Note: - Sterically unhindered primary alkyl haloalkane mainly gives nucleophilic substitution reaction, while sterically hindered (branched primary, secondary and tertiary haloalkane mainly gives elimination reaction.
- Sterically unhindered nucleophiles mainly give substitution reactions. Branched or bulky substrate mainly gives a unimolecular substitution reaction $\text{(}{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{1)}$.
- On reacting with the chlorine derivative of alcohol gives substitution reaction with the sodium methoxide.
- Lesser the steric hindrance faster will be the rate of bimolecular substitution reaction $\text{(}{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2)}$. $\text{(}{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2)}$ Prefers the less hindered side to attack. So ease of $\text{(}{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2)}$ reaction is $\text{(}{{\text{1}}^{\circ }}\text{}\,{{\text{2}}^{\circ }}\text{}\,{{\text{3}}^{\circ }}\text{)}$.
$\text{(}{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2)}$ Reactions involve inversion of configuration of compound stereochemically. So ${{1}^{\circ }}$ alkyl halide is preferred to $\text{(}{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2)}$ reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
This reaction is completed in two steps-
$\text{PC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ (Phosphorus trichloride) is good chlorinating agent; it reacts quickly with alcohols and performs substitution reaction.
- In the first step chlorination of substrate takes place in which hydroxyl group of substrate compound is replaced by chlorine atom. This reaction is represented through following chemical reaction-

In the second step the chlorinated product of alcohol treated with sodium methoxide in the strong basic medium $\text{(NaOH)}$ . Since chlorine is a poor leaving group, in the presence of polar solvent it gives bimolecular substitution reaction and forms ether. This reaction is represented through the following chemical equation.

Note: - Sterically unhindered primary alkyl haloalkane mainly gives nucleophilic substitution reaction, while sterically hindered (branched primary, secondary and tertiary haloalkane mainly gives elimination reaction.
- Sterically unhindered nucleophiles mainly give substitution reactions. Branched or bulky substrate mainly gives a unimolecular substitution reaction $\text{(}{{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{1)}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




