
Product (A) and (C) for the given reaction:
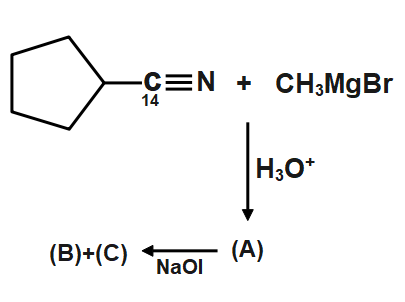
A.
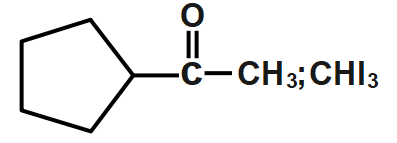
B.
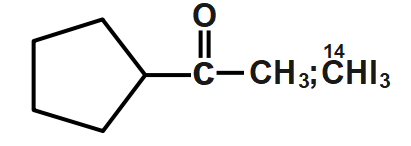
C.




Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint: In this reaction, a Grignard reagent will attack on the cyanide which has a positive metal center and a negative carbon center. Write the mechanism with the happening of iodoform reaction at the end. After an iodoform reaction a yellow color iodoform is formed and this reaction is used to detect the $-CO-C{{H}_{3}}$ group.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s start with the cyanide. We all know that in cyanide carbon is joined with the nitrogen atom with a triple bond. When addition takes place the methyl group from methyl magnesium bromide attacks on the electrophilic carbon of cyanide, like shown in figure. Then after the formation of hydrolysis takes place which cleaves the double bond between carbon and nitrogen. The bond cleaves in such a way that carbon gets the oxygen of water and nitrogen gets the two hydrogen atoms. Therefore, a cleavage happens very easily. We got the acetone which is having a $carbon-14$ nuclei, which is radioactive in nature thus its detection is important.
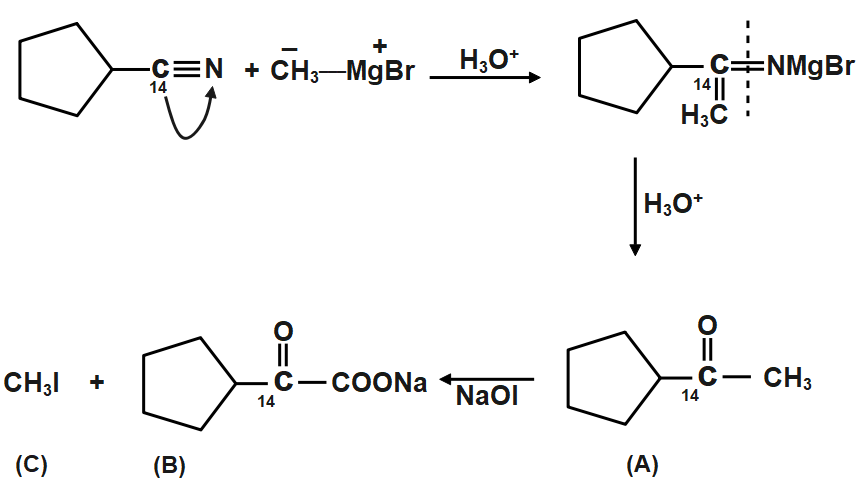
Now the next step is the iodoform reaction whose reagent is formed when sodium hydroxide $NaOH$ will react with iodine ${{I}_{2}}$. The iodoform reaction can be predicted when we see $NaOI$ sometimes in a reaction. During the iodoform reaction, the $-CO-C{{H}_{3}}$ group gets converted to sodium salt of carboxylic acid and we get iodoform. So in the above reaction we get a carbonyl compound in which the carbonyl group is of $carbon-14$ and the methyl group which will form iodoform is normally formed as $carbon-12$ .
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: The question is checking your mechanism solving part of reactions where Grignard reagent attack and also the iodoform reaction. Here, as carbon is given as normal and also as isotope, thus while forming the acetone you should keep in mind that $carbon-14$ nuclei is present in the acetone molecule as carbonyl and also with the iodoform reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s start with the cyanide. We all know that in cyanide carbon is joined with the nitrogen atom with a triple bond. When addition takes place the methyl group from methyl magnesium bromide attacks on the electrophilic carbon of cyanide, like shown in figure. Then after the formation of hydrolysis takes place which cleaves the double bond between carbon and nitrogen. The bond cleaves in such a way that carbon gets the oxygen of water and nitrogen gets the two hydrogen atoms. Therefore, a cleavage happens very easily. We got the acetone which is having a $carbon-14$ nuclei, which is radioactive in nature thus its detection is important.

Now the next step is the iodoform reaction whose reagent is formed when sodium hydroxide $NaOH$ will react with iodine ${{I}_{2}}$. The iodoform reaction can be predicted when we see $NaOI$ sometimes in a reaction. During the iodoform reaction, the $-CO-C{{H}_{3}}$ group gets converted to sodium salt of carboxylic acid and we get iodoform. So in the above reaction we get a carbonyl compound in which the carbonyl group is of $carbon-14$ and the methyl group which will form iodoform is normally formed as $carbon-12$ .
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: The question is checking your mechanism solving part of reactions where Grignard reagent attack and also the iodoform reaction. Here, as carbon is given as normal and also as isotope, thus while forming the acetone you should keep in mind that $carbon-14$ nuclei is present in the acetone molecule as carbonyl and also with the iodoform reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




