
How many primary amines are possible with the molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{4}}{{\text{H}}_{11}}\text{N}$?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: Primary amines are ${{1}^{\text{o}}}$ amines. Amines have the substituent $-\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$ group. Primary amines $\left( \text{R}-\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{2}} \right)$ basically arise when one of hydrogen from ammonia molecule is replaced by alkyl group or phenyl group. The aliphatic primary amine includes methyl amine and aromatic primary amine includes aniline. The structures of primary amines are like,
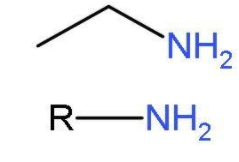
Structures of primary amines will be drawn by making isomers of by this molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{4}}{{\text{H}}_{11}}\text{N}$.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us draw the primary amines with the molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{4}}{{\text{H}}_{11}}\text{N}$, using the chain isomerism.
- Chain isomerism occurs when compounds with the same molecular formula have different arrangements in which the parent carbon chain is reduced by adding branches to the main chain.
- The alkane chain of the molecule ${{\text{C}}_{4}}{{\text{H}}_{11}}\text{N}$ is butane as it has four carbon atoms.
- The simplest primary amine will be butan-1-amine or butylamine. In this primary amine, the amino group is present at the first carbon atom of the butane chain. The molecular formula of butylamine will be $\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$. The structure of butylamine is
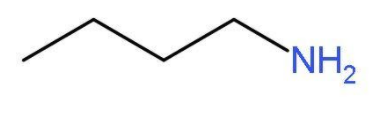
- The other primary amine which can be formed by shifting the position of the amine group will be butan-2-amine. In this primary amine, the amino group is present at the second carbon atom of the butane chain. The molecular formula of butan-2-amine will be $\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{CHN}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}$. The structure of butan-2-amine is
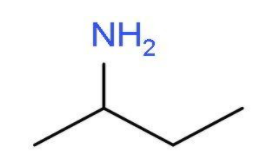
- The other primary amine which can be formed by chain isomerism will be 2-methylpropan-1-amine. In this primary amine, the amino group is present at the first carbon atom of the propane chain and one carbon atom is used as methyl group at second position. The molecular formula of 2-methylpropan-1-amine will be ${{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{NC}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{CH}{{\left( \text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}$. The structure of 2-methylpropan-1-amine is
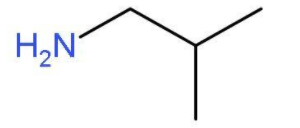
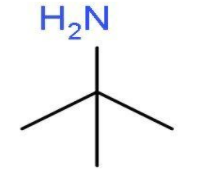
- The other primary amine which can be formed will be 2-methylpropan-2-amine. . In this primary amine, the amino group is present at the second carbon atom of the propane chain and one carbon atom is used as methyl group at second position. The molecular formula of 2-methylpropan-2-amine will be ${{\left( \text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}\text{C}-\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$. The structure of 2-methylpropan-2-amine is
4 primary amines are possible with the molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{4}}{{\text{H}}_{11}}\text{N}$, which is option ‘c’.
Note: ${{1}^{\text{o}}}$ amines have no relation with the type of carbon it is attached. It means that ${{1}^{\text{o}}}$ amine can be attached to primary carbon, secondary carbon and tertiary carbon atoms. ${{1}^{\text{o}}}$ amines does not mean it will be attached to ${{1}^{\text{o}}}$ carbon only. Please do not relate the degree of amines like this. It is the wrong definition and hence, you will get the wrong answer.

Structures of primary amines will be drawn by making isomers of by this molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{4}}{{\text{H}}_{11}}\text{N}$.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us draw the primary amines with the molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{4}}{{\text{H}}_{11}}\text{N}$, using the chain isomerism.
- Chain isomerism occurs when compounds with the same molecular formula have different arrangements in which the parent carbon chain is reduced by adding branches to the main chain.
- The alkane chain of the molecule ${{\text{C}}_{4}}{{\text{H}}_{11}}\text{N}$ is butane as it has four carbon atoms.
- The simplest primary amine will be butan-1-amine or butylamine. In this primary amine, the amino group is present at the first carbon atom of the butane chain. The molecular formula of butylamine will be $\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$. The structure of butylamine is

- The other primary amine which can be formed by shifting the position of the amine group will be butan-2-amine. In this primary amine, the amino group is present at the second carbon atom of the butane chain. The molecular formula of butan-2-amine will be $\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{CHN}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}$. The structure of butan-2-amine is

- The other primary amine which can be formed by chain isomerism will be 2-methylpropan-1-amine. In this primary amine, the amino group is present at the first carbon atom of the propane chain and one carbon atom is used as methyl group at second position. The molecular formula of 2-methylpropan-1-amine will be ${{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{NC}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{CH}{{\left( \text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}$. The structure of 2-methylpropan-1-amine is

- The other primary amine which can be formed will be 2-methylpropan-2-amine. . In this primary amine, the amino group is present at the second carbon atom of the propane chain and one carbon atom is used as methyl group at second position. The molecular formula of 2-methylpropan-2-amine will be ${{\left( \text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}\text{C}-\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$. The structure of 2-methylpropan-2-amine is

4 primary amines are possible with the molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{4}}{{\text{H}}_{11}}\text{N}$, which is option ‘c’.
Note: ${{1}^{\text{o}}}$ amines have no relation with the type of carbon it is attached. It means that ${{1}^{\text{o}}}$ amine can be attached to primary carbon, secondary carbon and tertiary carbon atoms. ${{1}^{\text{o}}}$ amines does not mean it will be attached to ${{1}^{\text{o}}}$ carbon only. Please do not relate the degree of amines like this. It is the wrong definition and hence, you will get the wrong answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




