
Prepare dipeptide from glycine and alanine.
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Peptides are small or short-chain with anywhere between two to fifty amino acids. These small chains are held together by peptide bonds, hence the name. Amino acids can be understood as an organic compound that consists of an amino group, a carboxylic group \[\left( { - COOH} \right)\], and an alkyl or aryl group, also known as sidechains. Hence, amino acids contain primarily nitrogen carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
Before we move forward with the solution to the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
Amino acids are usually classified based on the characteristic properties of the side chains that are attached to them. If the side chain is a polar compound in nature, then that side chain makes the corresponding amino acid hydrophilic. On the other hand, if the side chain is a non – polar compound, then the side makes the corresponding amino acid hydrophobic. The side chains also cause the amino acids to be either weak acidic compounds or weak basic compounds.
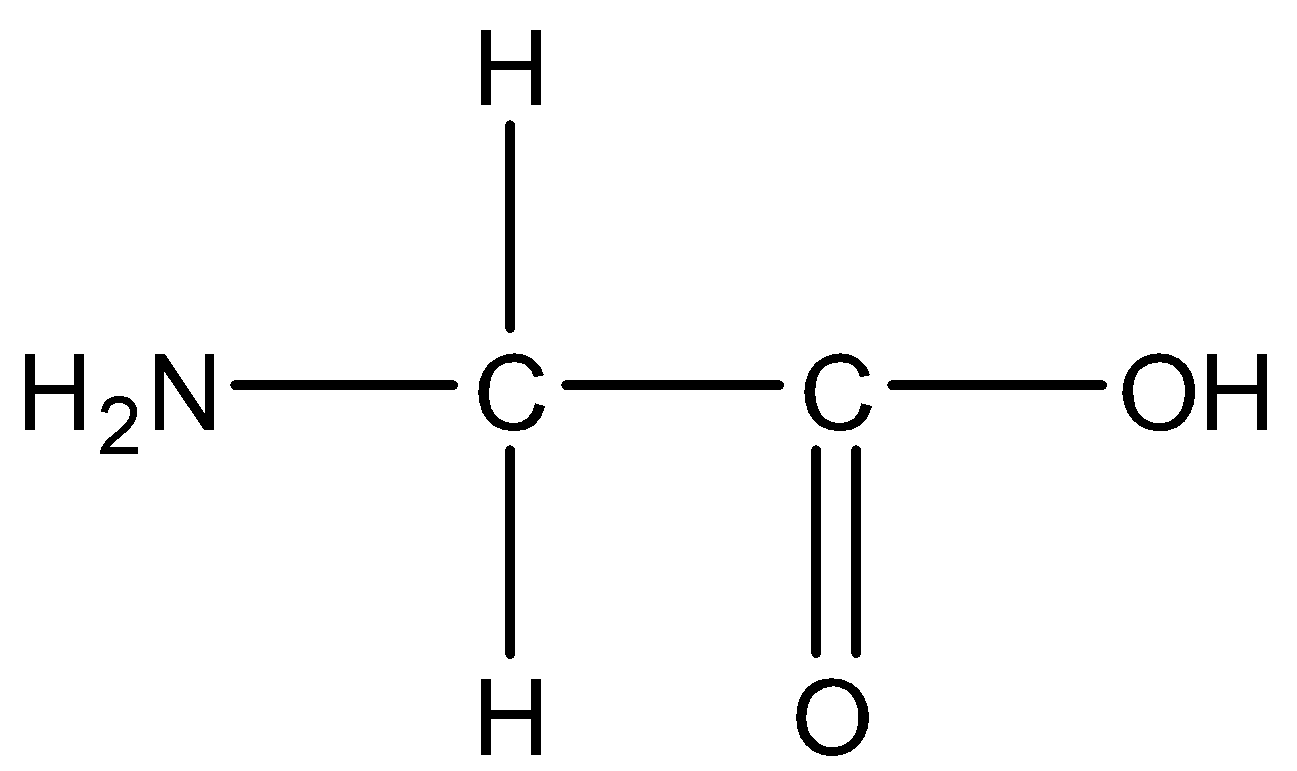
The structure of glycine is,
1.Glycine:
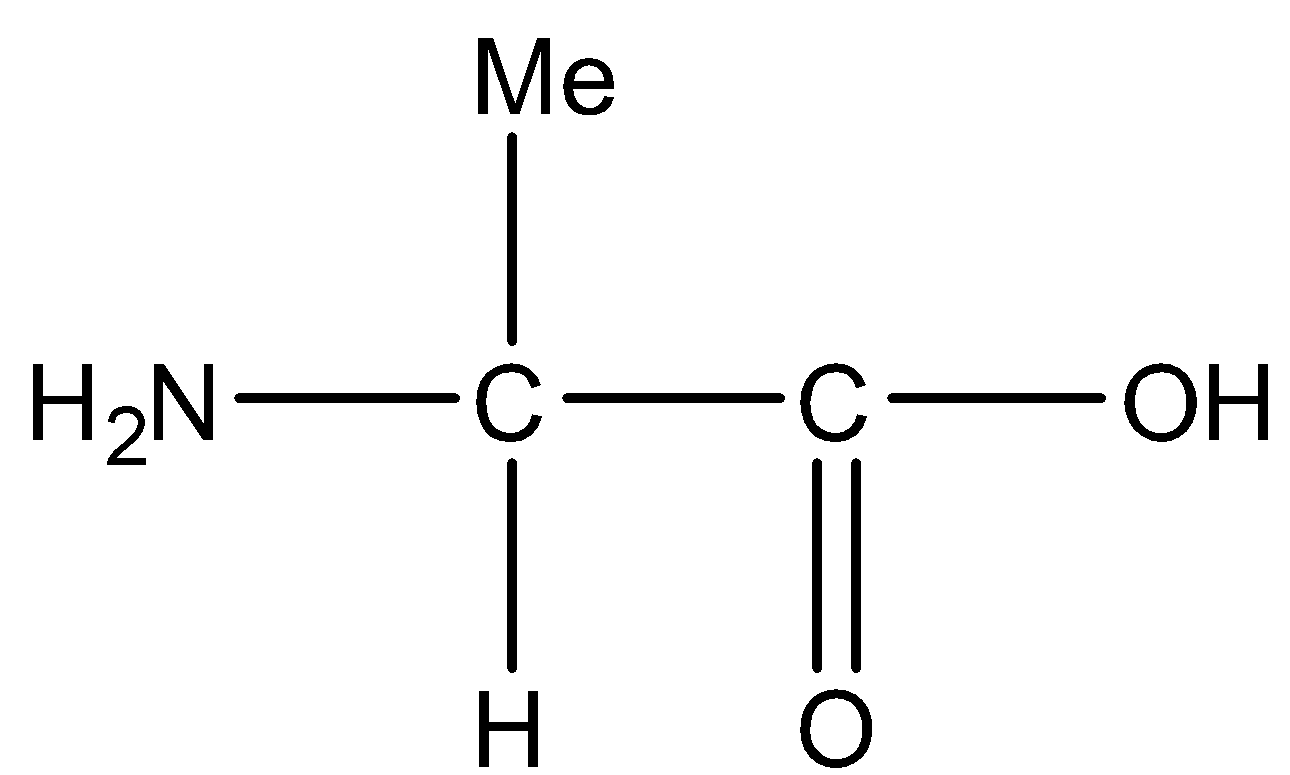
2.Alanine
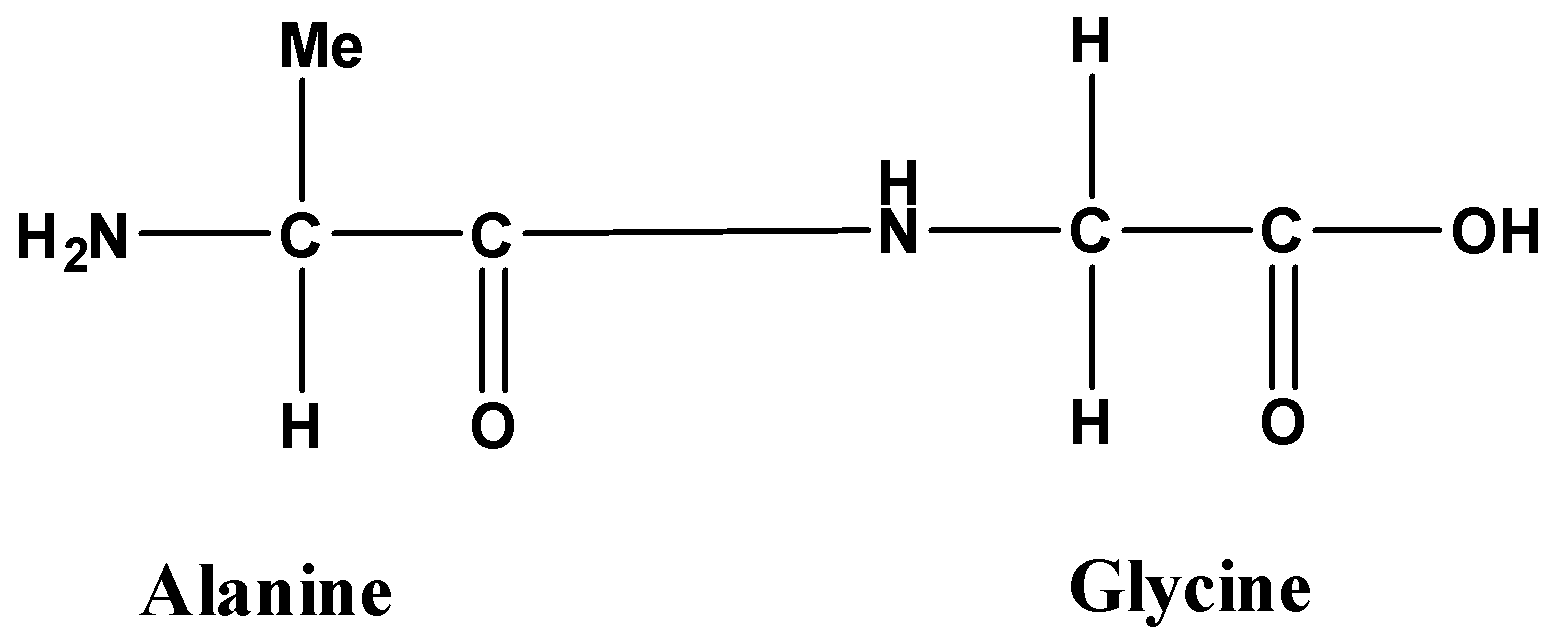
Now, dipeptide means two amino acids combine a follow,
Additional information:
The Carbylamine’s test is a method for detecting or determining primary amines given in the present compounds, by heating the given substance with chloroform in a basic solution. The test shows positive results for the presence of a primary amine, by emitting a characteristic foul smell, which is caused by the release of isocyanide.
Ceric ammonium nitrate test is used for identifying the existence of an alcoholic functional group. In this test, a sample of the given compound is dissolved in an appropriate solvent. If the solution turns red, then the test result is positive.
The given peptides are:
1.Lysine (Lys)-
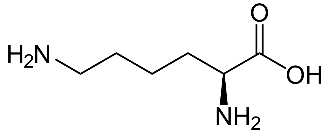
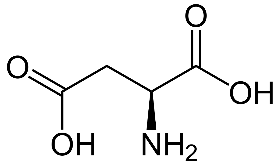
2.Aspartic acid (Asp)-
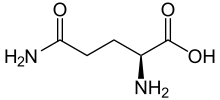
3.Glutamine (Gln) –
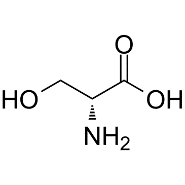
4.Serine (Ser) –
We can see that as a combination, only serine and lysine would be able to give a positive result for both the tests due to the presence of \[ - OH\] and \[ - N{H_2}\] functional groups.
Note: Glycine is a colorless, sweet-tasting crystalline solid. It is the only achiral proteinogenic amino acid. It can fit into hydrophilic or hydrophobic environments, due to its minimal side chain of only one hydrogen atom.
Complete step by step answer:
Before we move forward with the solution to the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
Amino acids are usually classified based on the characteristic properties of the side chains that are attached to them. If the side chain is a polar compound in nature, then that side chain makes the corresponding amino acid hydrophilic. On the other hand, if the side chain is a non – polar compound, then the side makes the corresponding amino acid hydrophobic. The side chains also cause the amino acids to be either weak acidic compounds or weak basic compounds.
The structure of glycine is,
1.Glycine:

2.Alanine

Now, dipeptide means two amino acids combine a follow,

Additional information:
The Carbylamine’s test is a method for detecting or determining primary amines given in the present compounds, by heating the given substance with chloroform in a basic solution. The test shows positive results for the presence of a primary amine, by emitting a characteristic foul smell, which is caused by the release of isocyanide.
Ceric ammonium nitrate test is used for identifying the existence of an alcoholic functional group. In this test, a sample of the given compound is dissolved in an appropriate solvent. If the solution turns red, then the test result is positive.
The given peptides are:
1.Lysine (Lys)-

2.Aspartic acid (Asp)-

3.Glutamine (Gln) –

4.Serine (Ser) –

We can see that as a combination, only serine and lysine would be able to give a positive result for both the tests due to the presence of \[ - OH\] and \[ - N{H_2}\] functional groups.
Note: Glycine is a colorless, sweet-tasting crystalline solid. It is the only achiral proteinogenic amino acid. It can fit into hydrophilic or hydrophobic environments, due to its minimal side chain of only one hydrogen atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




