
Position of tetrahedral voids in close packed structure are:
A. Edge-center of unit cell
B. Two tetrahedral voids on each body diagonal
C. $\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 a}}{4}$ from corner
D. Face-center of unit cell.
Answer
546.6k+ views
Hint: A solid crystal is arranged in a three-dimensional order where each atom which is considered as a sphere is packed voids are formed. Two types of voids are formed, tetrahedral and octahedral. The tetrahedral voids are formed when four atoms are arranged in tetrahedral like shape, the void or we can say the space between them is tetrahedral void while when atoms are arranged in octahedral order they form an octahedral void.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A unit cell is a small portion of crystal lattice, like as we have in a rhombic cube. In a rhombic cube one small colored portion can be considered as a unit cell. So there are some particular modes in which atoms are arranged in a unit cell, SCC BCC and FCC. In a simple cubic cell eight atoms are present at the corners while in the other two there are some extra atoms. In BCC eight atoms are at the corner and one atom is present at the center. In FCC there are eight atoms at the corners and one at each face.
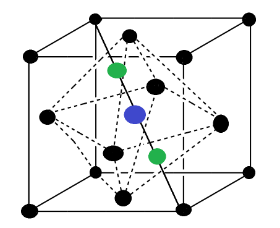
In the above figure the blue color voids are octahedral voids while the green color are tetrahedral voids. Sometimes FCC is also called a closed packed structure. There are two types of voids present at two different positions. It was seen that in one unit cell of FCC type, one octahedral void is present at the body-center while two tetrahedral are present at the body diagonal. So we can say that two tetrahedral voids are present on each body diagonal of FCC at a distance of $\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 a}}{4}$ , thus
Therefore, the correct option is (C).
Note: The type of arrangement will decide the number of voids in a unit cell. As we have FCC face centered unit cells. In this unit cell we have overall four atoms, it means there will be four octahedral voids while the tetrahedral voids are doubled in number. In case of BCC there is only one void which is cubical void.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A unit cell is a small portion of crystal lattice, like as we have in a rhombic cube. In a rhombic cube one small colored portion can be considered as a unit cell. So there are some particular modes in which atoms are arranged in a unit cell, SCC BCC and FCC. In a simple cubic cell eight atoms are present at the corners while in the other two there are some extra atoms. In BCC eight atoms are at the corner and one atom is present at the center. In FCC there are eight atoms at the corners and one at each face.

In the above figure the blue color voids are octahedral voids while the green color are tetrahedral voids. Sometimes FCC is also called a closed packed structure. There are two types of voids present at two different positions. It was seen that in one unit cell of FCC type, one octahedral void is present at the body-center while two tetrahedral are present at the body diagonal. So we can say that two tetrahedral voids are present on each body diagonal of FCC at a distance of $\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 a}}{4}$ , thus
Therefore, the correct option is (C).
Note: The type of arrangement will decide the number of voids in a unit cell. As we have FCC face centered unit cells. In this unit cell we have overall four atoms, it means there will be four octahedral voids while the tetrahedral voids are doubled in number. In case of BCC there is only one void which is cubical void.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




