
What is the position of an object relative to the objective of a compound microscope? Where is its image formed?
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint:
A compound microscope is made of two lenses, one lens is called an objective lens and another lens is called eyepiece. The lens which is near to the object is called objective lens and the lens near to the eye is called eyepiece.
Depending on the position of the object from the microscope the position of the final image gets changed. The image formation follows the lens formula.
Step-by-step solution:
The purpose of a microscope is to magnify small objects, and both lenses contribute to the final magnification.
The final enlarged image is produced far enough from the observer’s eye to be viewed with a relaxed eye. As we know that there is a limit of closeness of an object from the eye to see it clearly. An eye can’t see the object very clearly if the object is kept very close to the eye.
The focal length of the objective lens is greater than the focal length of the eyepiece. When an object is placed in front of the objective lens then image is formed behind the lens on the other side of the lens. The image formed by the objective lens acts as the object for the eyepiece. Then the final image is formed by the eyepiece at a far away distance from the eye.
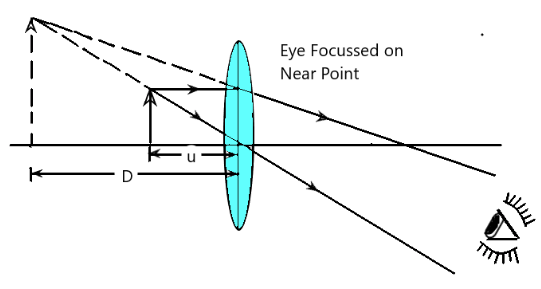
The object is placed in front of the objective lens just beyond the focal distance. The object distance from the objective lens is greater than the focal length of the objective lens.
Using lens formula,
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
The image is formed at a distance much larger than its focal length behind the lens and in front of the eyepiece.
Note:
We should be careful about the condition of the eye to decide the location of the final image formed by the compound microscope. When the eye is relaxed then the final image is formed at infinity.
The image formed by the objective lens must be formed between the objective lens and the eyepiece.
A compound microscope is made of two lenses, one lens is called an objective lens and another lens is called eyepiece. The lens which is near to the object is called objective lens and the lens near to the eye is called eyepiece.
Depending on the position of the object from the microscope the position of the final image gets changed. The image formation follows the lens formula.
Step-by-step solution:
The purpose of a microscope is to magnify small objects, and both lenses contribute to the final magnification.
The final enlarged image is produced far enough from the observer’s eye to be viewed with a relaxed eye. As we know that there is a limit of closeness of an object from the eye to see it clearly. An eye can’t see the object very clearly if the object is kept very close to the eye.
The focal length of the objective lens is greater than the focal length of the eyepiece. When an object is placed in front of the objective lens then image is formed behind the lens on the other side of the lens. The image formed by the objective lens acts as the object for the eyepiece. Then the final image is formed by the eyepiece at a far away distance from the eye.

The object is placed in front of the objective lens just beyond the focal distance. The object distance from the objective lens is greater than the focal length of the objective lens.
Using lens formula,
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
The image is formed at a distance much larger than its focal length behind the lens and in front of the eyepiece.
Note:
We should be careful about the condition of the eye to decide the location of the final image formed by the compound microscope. When the eye is relaxed then the final image is formed at infinity.
The image formed by the objective lens must be formed between the objective lens and the eyepiece.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




