
Polythene is prepared by :
(A) Isomerization
(B) Polymerisation
(C) Hydrogenation
(D) All of the above
Answer
544.2k+ views
Hint: As the name suggests , polythene is a polymer of ethene monomer and it is prepared by polymerising the ethene at higher temperatures.
Complete step by step solution:
Before deciding by which process polythene is prepared , let us first understand what each of these reactions means.
Isomerization : This refers to the type of process in which a compound is transformed into an isomer with a different chemical structure and same chemical formula .
Polymerisation: It is a chemical reaction in which smaller units called monomers combine to form a large molecule called polymer. The combining units i.e. monomers can be the same or different molecules.
Hydrogenation: It is simply the addition of hydrogen to any compound . The alkynes are converted to alkenes by the process called hydrogenation.
Now , we have known what each of the processes mean .
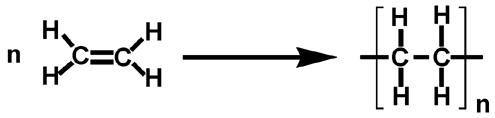
Ethene is taken as a monomeric unit here and a large number of these monomeric units are combined with each other at elevated temperatures. The process is carried out at a temperature range of $ 350^\circ C $ to $ 570^\circ C $ and at very high pressures of about $ 1000 $ to $ 2000 $ atm. Ethene is a stable molecule which in addition to catalysts participate in the polymerisation process.
Polythene as the name suggests is the polymer of ethene . Now , we know that polythene is prepared by the polymerisation of ethene. It is a homo-polymer i.e. it consists of the same type of monomers which is ethene.
Hence, the correct answer is B .
Note:
Poly means “many”, when two or more simpler units combine to form a more complex meaning by some means of chemical and physical process , is called polymerisation. The polymers are of two types i.e addition polymers and condensation polymers.
Complete step by step solution:
Before deciding by which process polythene is prepared , let us first understand what each of these reactions means.
Isomerization : This refers to the type of process in which a compound is transformed into an isomer with a different chemical structure and same chemical formula .
Polymerisation: It is a chemical reaction in which smaller units called monomers combine to form a large molecule called polymer. The combining units i.e. monomers can be the same or different molecules.

Hydrogenation: It is simply the addition of hydrogen to any compound . The alkynes are converted to alkenes by the process called hydrogenation.
Now , we have known what each of the processes mean .
Ethene is taken as a monomeric unit here and a large number of these monomeric units are combined with each other at elevated temperatures. The process is carried out at a temperature range of $ 350^\circ C $ to $ 570^\circ C $ and at very high pressures of about $ 1000 $ to $ 2000 $ atm. Ethene is a stable molecule which in addition to catalysts participate in the polymerisation process.
Polythene as the name suggests is the polymer of ethene . Now , we know that polythene is prepared by the polymerisation of ethene. It is a homo-polymer i.e. it consists of the same type of monomers which is ethene.
Hence, the correct answer is B .
Note:
Poly means “many”, when two or more simpler units combine to form a more complex meaning by some means of chemical and physical process , is called polymerisation. The polymers are of two types i.e addition polymers and condensation polymers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




