
Polymerisation of DNA nucleotides during the synthesis of lagging strand occurs in:
A. 3’-> 5’ direction
B. 5’-> 3’ direction
C. Any direction
D. Promoter to terminator direction
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: DNA replication is a process in which DNA strands get replicated into four DNA strands. This process is different in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Different proteins and enzymes are required for the completion of the process.
Complete answer:
Let’s discuss DNA replication in prokaryotes. To initiate unwinding of the double helix of DNA, some proteins bind to the origin of replication and start the process. After this an RNA primer comes and joins the origin of replication and DNA polymerase starts the process of replication.
Both strands of DNA act as template strands for the formation of replicated DNA strands. A replication site is called a replication fork. Which moves ahead as replication proceeds. Here is a diagram of DNA replication in E. coli.
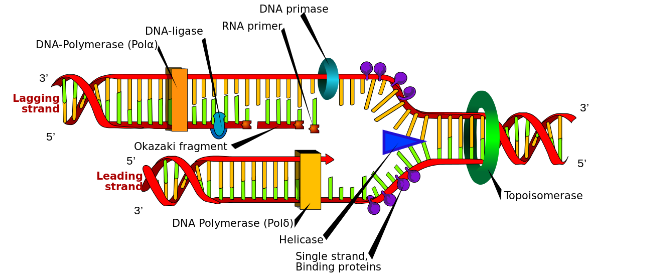
Single strand binding proteins, topoisomerase and helicase enzymes help in keeping replication forks open. DNA polymerase can synthesize only in one direction, that is, 5’-> 3’ direction. Thus, one strand is synthesised continuously, called as leading strand and another strand is synthesised in fragments called as Okazaki fragments, and this strand is known as lagging strand.
Thus, we can conclude that Polymerisation of DNA nucleotides during the synthesis of lagging strand occurs in 5’-> 3’ direction. And option ‘B’ is the correct answer.
Note: DNA replication occurs to double the genetic material whenever required for cell division. It is a process in which firstly, double stranded DNA opens up from the origin of replication (ori). Origin of replication in prokaryotes is only one and in eukaryotes multiple origins of replications are present.
Complete answer:
Let’s discuss DNA replication in prokaryotes. To initiate unwinding of the double helix of DNA, some proteins bind to the origin of replication and start the process. After this an RNA primer comes and joins the origin of replication and DNA polymerase starts the process of replication.
Both strands of DNA act as template strands for the formation of replicated DNA strands. A replication site is called a replication fork. Which moves ahead as replication proceeds. Here is a diagram of DNA replication in E. coli.

Single strand binding proteins, topoisomerase and helicase enzymes help in keeping replication forks open. DNA polymerase can synthesize only in one direction, that is, 5’-> 3’ direction. Thus, one strand is synthesised continuously, called as leading strand and another strand is synthesised in fragments called as Okazaki fragments, and this strand is known as lagging strand.
Thus, we can conclude that Polymerisation of DNA nucleotides during the synthesis of lagging strand occurs in 5’-> 3’ direction. And option ‘B’ is the correct answer.
Note: DNA replication occurs to double the genetic material whenever required for cell division. It is a process in which firstly, double stranded DNA opens up from the origin of replication (ori). Origin of replication in prokaryotes is only one and in eukaryotes multiple origins of replications are present.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




