
Polarization power of a cation increases when
A.Charge on the cation increases
B.Size of the cation increases
C.Charge on the cation decreases
D.Both charge and size of cation increase
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: The equation used to find charge density is ${\text{Charge density = }}\dfrac{{{\text{charge}}}}{{{\text{surface area}}}}$ , we can understand that charge is inversely proportional to the surface area or size. Ionic bond also called electrovalent bond is formed by the electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions. This type of bond is formed when the outermost electron of one atom is transferred to another.
Complete step by step answer:
Now we know what an ionic bond is. It has a cation and anion in which the opposite charges are attracted to each other
So let us look at how an ionic bond is formed. Let us take an example of NaCl. It is formed by an ionic bond. Na has 1 electron in its valence shell whereas Cl needs one more electron in its valence shell to have an octet.
Thus, NaCl loses one electron and Cl gains an electron. Therefore charge on Na will be positive whereas it is negative on Cl.
Polarization happens only in ionic bonding.
Since the ions are oppositely charged, they are attracted. The positive ion (cation) attracts the electrons in the negative ion.
Thus, we can see that there is a disturbance in the electron density around the anion towards the positive charge. We already saw that cation attracts electrons from the anion towards itself.
So, the anion is said to be polarized.
Polarizing power is the ability of the cation to attract electrons from the anion towards itself.
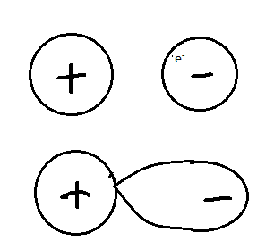
Now let us understand what the factors that affect polarization are.
A cation highly charged will have a greater polarizing ability.
Let us compare ${\text{M}}{{\text{g}}^{2 + }}$ and ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^{\text{ + }}}$ ions. ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^{\text{ + }}}$ has 1 positive charge and ${\text{M}}{{\text{g}}^{2 + }}$ has 2 positive charges. Therefore, ${\text{M}}{{\text{g}}^{2 + }}$ has more charge density and it can attract electrons better than ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^{\text{ + }}}$. Therefore, we can conclude that as the charge density around a cation increases, its ability to polarize also increases.
As we said above, Charge density is larger in ${\text{M}}{{\text{g}}^{2 + }}$.
${\text{Charge density = }}\dfrac{{{\text{charge}}}}{{{\text{surface area}}}}$
So, As the charge density increases, the surface area decreases which means that size decreases.
${\text{M}}{{\text{g}}^{2 + }}$ is smaller in size than ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^{\text{ + }}}$. Thus ${\text{M}}{{\text{g}}^{2 + }}$ has more covalent character.
Thus, we can conclude that the polarizing ability of a cation increases with an increase in charge and a decrease in the size of the cation.
The correct option is (A).
Note:Polarization implies that the bonds are not purely ionic. As the charge density increases, size decreases. This is a property shown by ionic compounds. A large anion with a high charge is polarized better by the cation. The amount of covalent character on these bonds depends on the polarizing power of cation and polarizability of the anion. An anion with larger size and the high charge will have the greatest polarizability.
Complete step by step answer:
Now we know what an ionic bond is. It has a cation and anion in which the opposite charges are attracted to each other
So let us look at how an ionic bond is formed. Let us take an example of NaCl. It is formed by an ionic bond. Na has 1 electron in its valence shell whereas Cl needs one more electron in its valence shell to have an octet.
Thus, NaCl loses one electron and Cl gains an electron. Therefore charge on Na will be positive whereas it is negative on Cl.
Polarization happens only in ionic bonding.
Since the ions are oppositely charged, they are attracted. The positive ion (cation) attracts the electrons in the negative ion.
Thus, we can see that there is a disturbance in the electron density around the anion towards the positive charge. We already saw that cation attracts electrons from the anion towards itself.
So, the anion is said to be polarized.
Polarizing power is the ability of the cation to attract electrons from the anion towards itself.
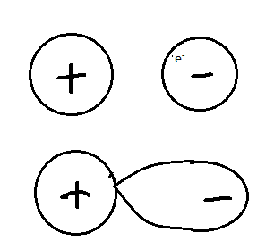
Now let us understand what the factors that affect polarization are.
A cation highly charged will have a greater polarizing ability.
Let us compare ${\text{M}}{{\text{g}}^{2 + }}$ and ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^{\text{ + }}}$ ions. ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^{\text{ + }}}$ has 1 positive charge and ${\text{M}}{{\text{g}}^{2 + }}$ has 2 positive charges. Therefore, ${\text{M}}{{\text{g}}^{2 + }}$ has more charge density and it can attract electrons better than ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^{\text{ + }}}$. Therefore, we can conclude that as the charge density around a cation increases, its ability to polarize also increases.
As we said above, Charge density is larger in ${\text{M}}{{\text{g}}^{2 + }}$.
${\text{Charge density = }}\dfrac{{{\text{charge}}}}{{{\text{surface area}}}}$
So, As the charge density increases, the surface area decreases which means that size decreases.
${\text{M}}{{\text{g}}^{2 + }}$ is smaller in size than ${\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^{\text{ + }}}$. Thus ${\text{M}}{{\text{g}}^{2 + }}$ has more covalent character.
Thus, we can conclude that the polarizing ability of a cation increases with an increase in charge and a decrease in the size of the cation.
The correct option is (A).
Note:Polarization implies that the bonds are not purely ionic. As the charge density increases, size decreases. This is a property shown by ionic compounds. A large anion with a high charge is polarized better by the cation. The amount of covalent character on these bonds depends on the polarizing power of cation and polarizability of the anion. An anion with larger size and the high charge will have the greatest polarizability.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




