
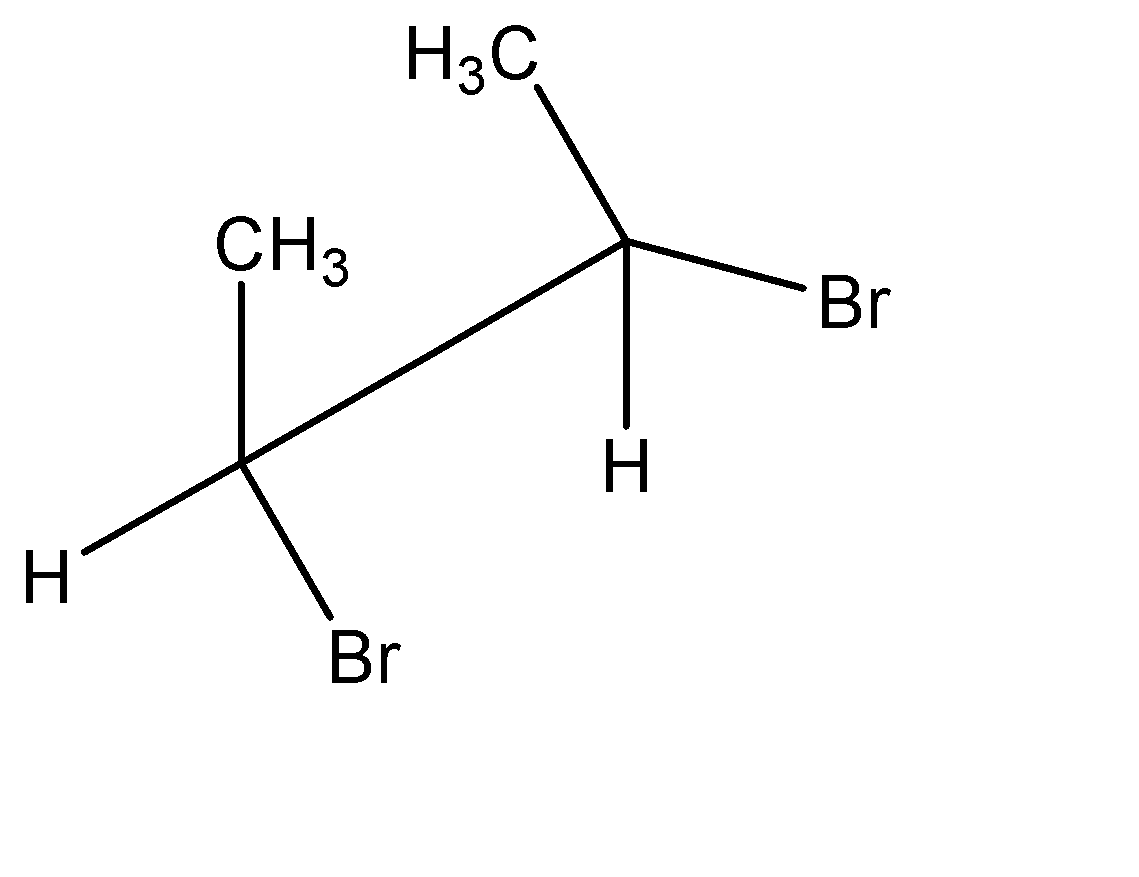
Point out the incorrect sawhorse drawing(s) for the following compound.
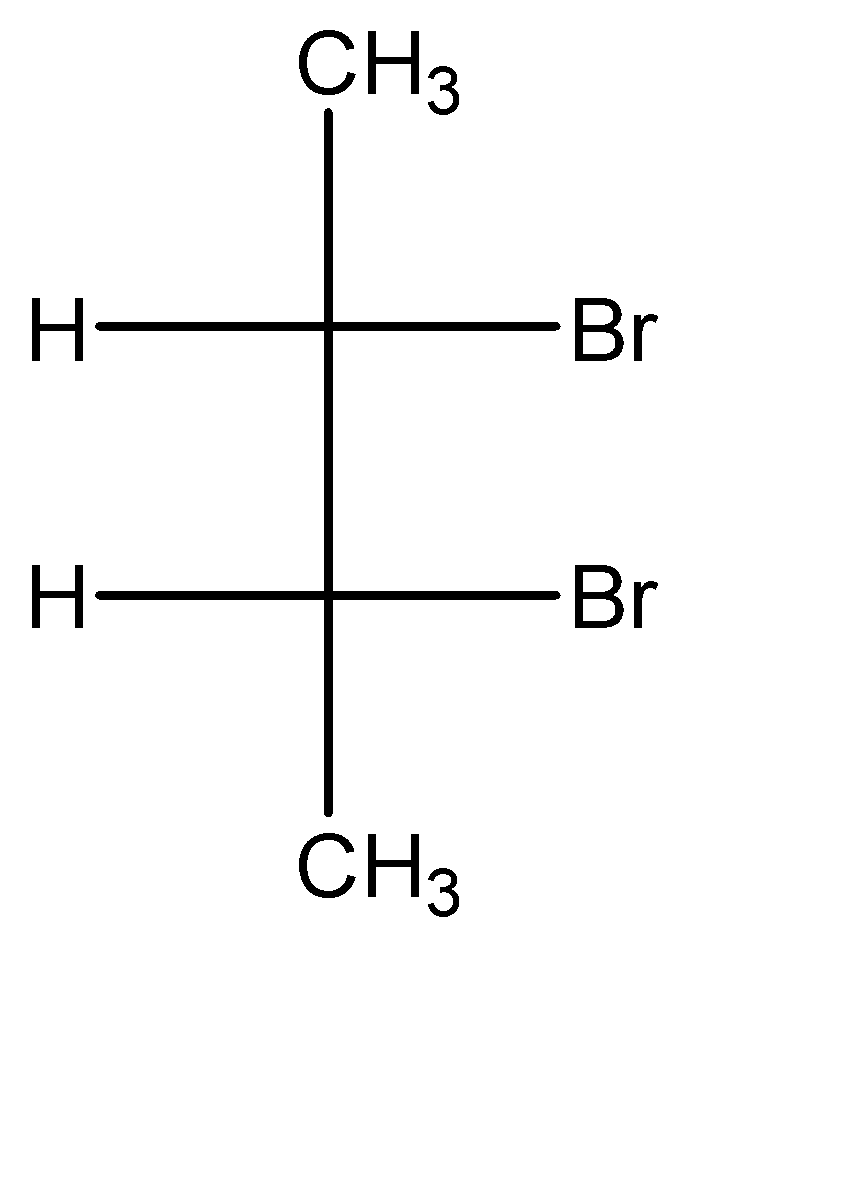
A.
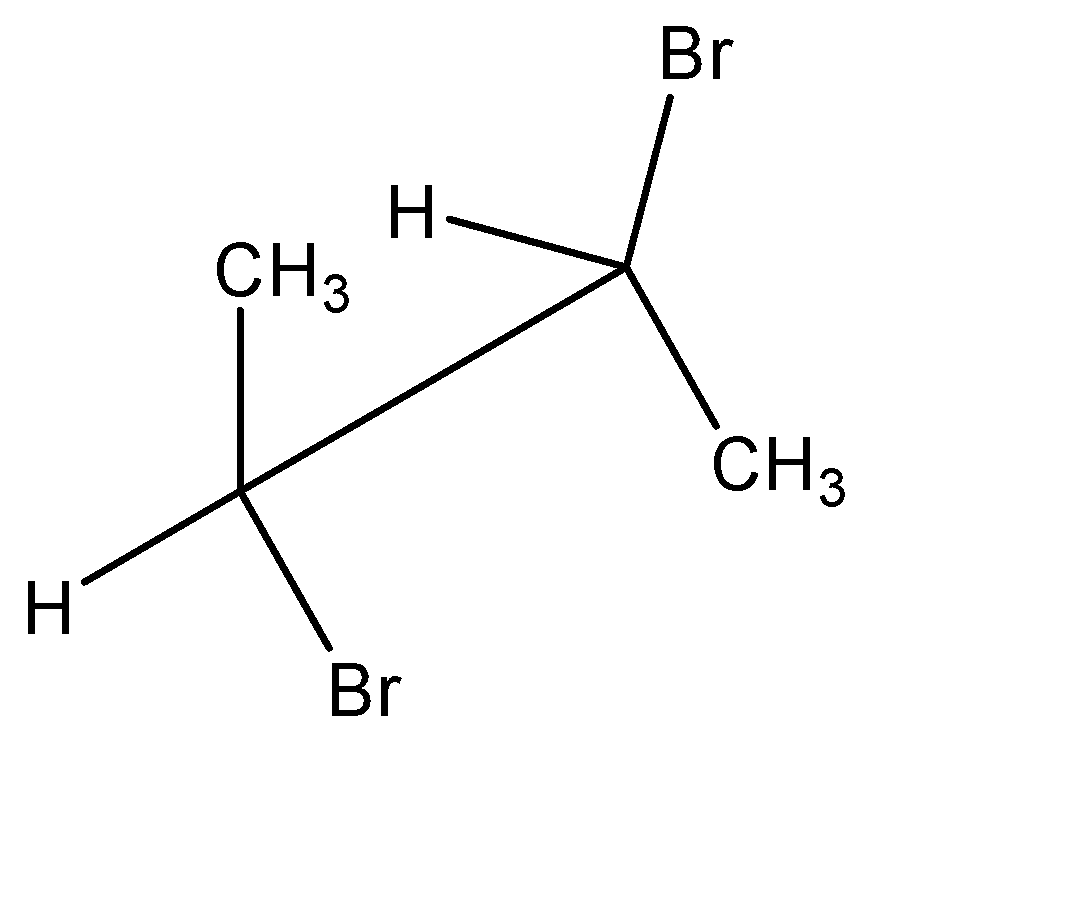
B.
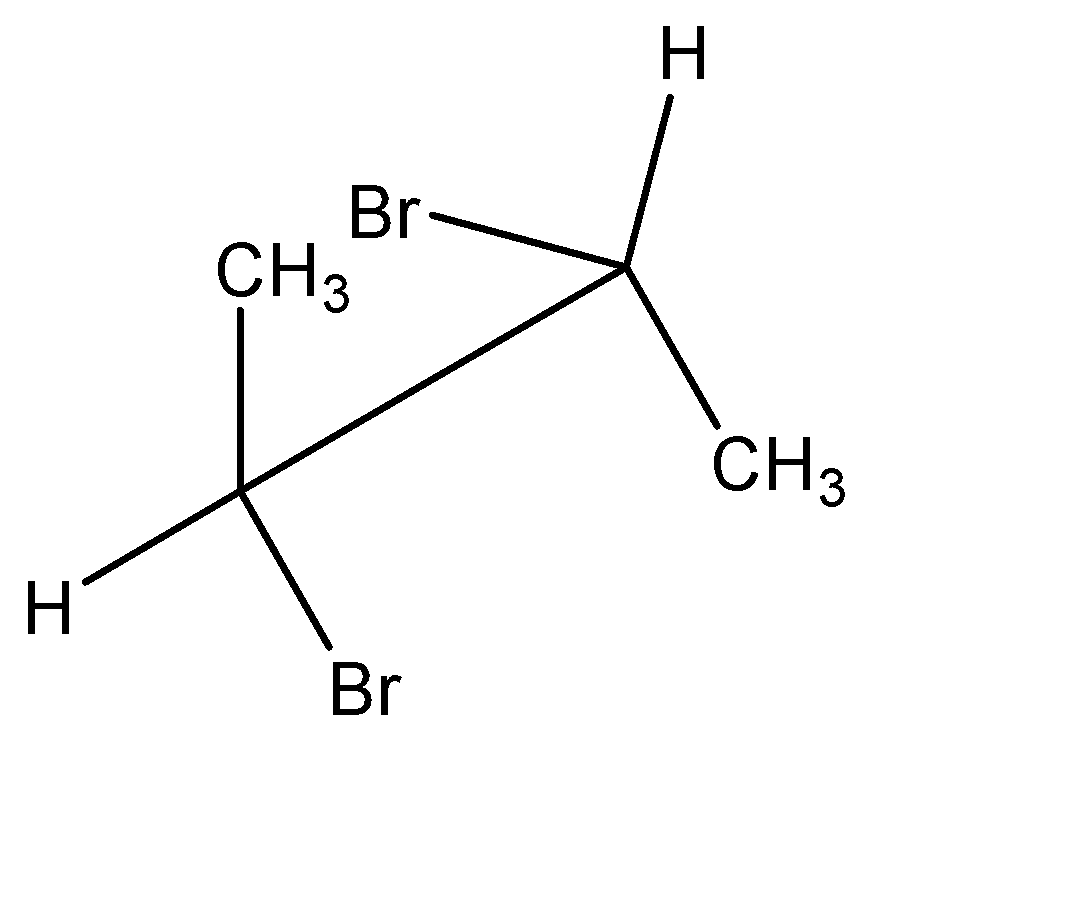
C.
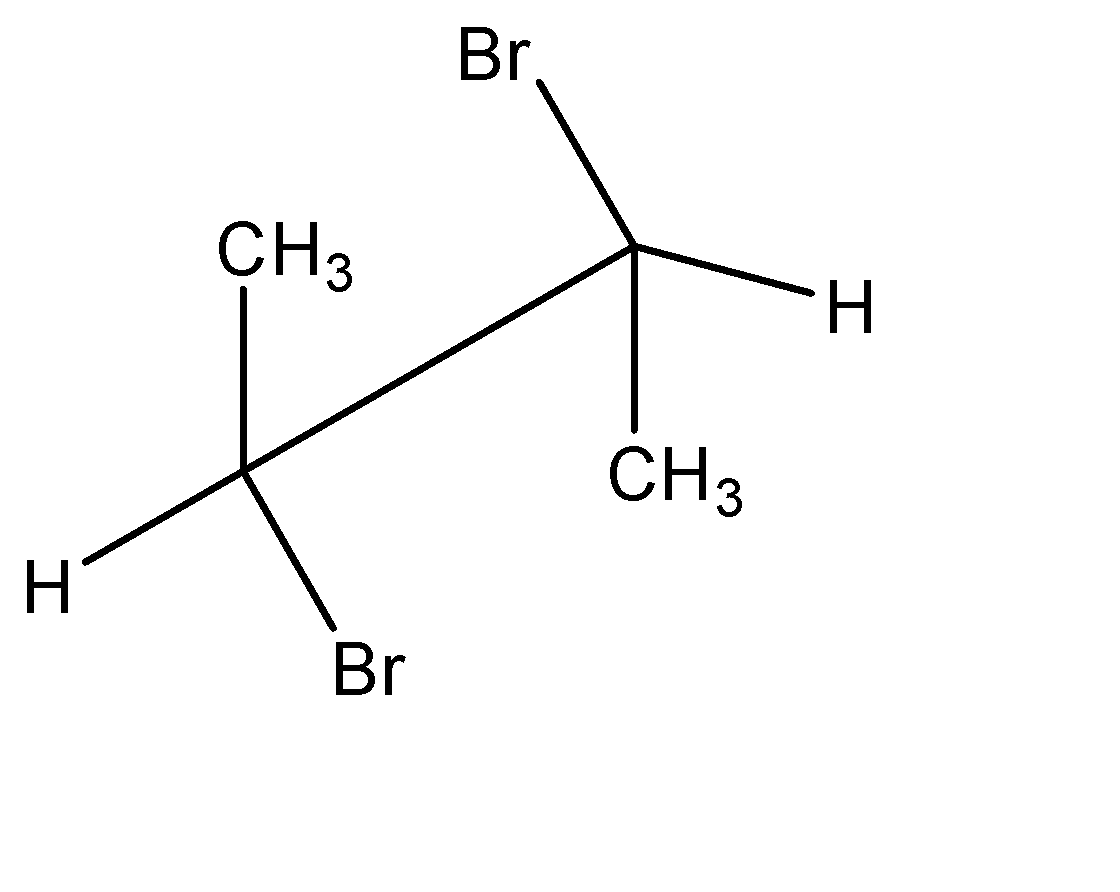
D.





Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we need to first understand in detail about sawhorse projection. On the basis of that discussion, we can identify the possible projection structures that can be formed by this projection method. And then, we can eliminate the option that does not conform to the rules.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
Sawhorse projection can be explained as a form of molecular projection, that helps us in visualizing the positions of the substituent molecules placed along a carbon – carbon bond. To make the sawhorse projection structures of a molecule, we need to first decide the carbon – carbon bond that we are going to use for projection. Then we need to assess the positions of the substituents that are attached to both the carbon atoms. Now, the relative orientation of these functional groups should remain constant throughout the projections for the molecule. Let us now discuss the molecule given to us:
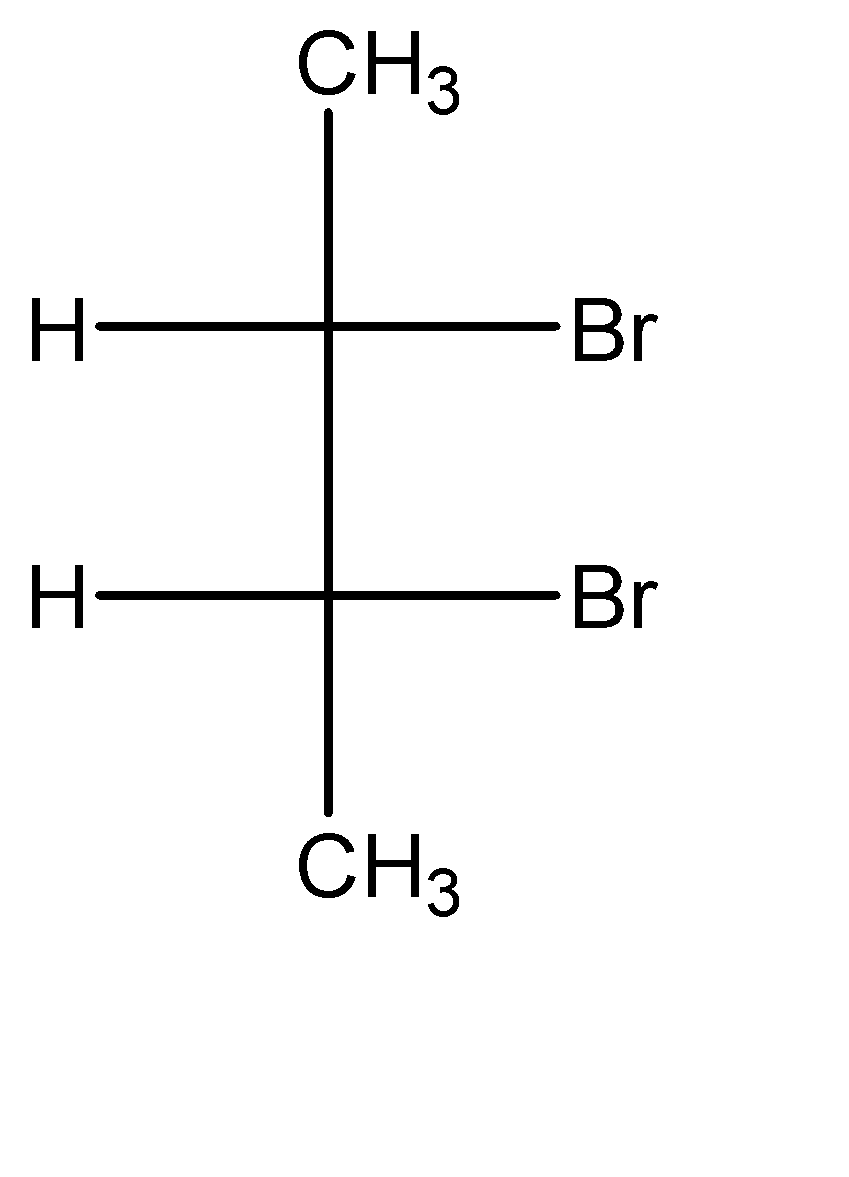
In this molecule, we can observe that for the carbon at position 01, the placement of the hydrogen atom is to the left and the placement of the bromine atom is to the right of the methyl group.
Similarly, for the carbon at position 02, the placement of the hydrogen atom is to the right and the placement of the bromine atom is to the left of the methyl group.
Hence, all the sawhorse projections must have this exact orientation pattern to represent the molecule correctly. We can observe that in option A, the positions of the functional groups on the position 01 carbon atom is reversed. Hence, incorrect sawhorse drawing(s) for the given compound is option A
Hence, Option A is the correct option
Note: Groups connected to both the front and back carbons are drawn using sticks at \[{120^\circ }\] angle. A sawhorse projection is similar to a Newman projection, but it shows the carbon-carbon bond that is hidden in a Newman projection.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
Sawhorse projection can be explained as a form of molecular projection, that helps us in visualizing the positions of the substituent molecules placed along a carbon – carbon bond. To make the sawhorse projection structures of a molecule, we need to first decide the carbon – carbon bond that we are going to use for projection. Then we need to assess the positions of the substituents that are attached to both the carbon atoms. Now, the relative orientation of these functional groups should remain constant throughout the projections for the molecule. Let us now discuss the molecule given to us:

In this molecule, we can observe that for the carbon at position 01, the placement of the hydrogen atom is to the left and the placement of the bromine atom is to the right of the methyl group.
Similarly, for the carbon at position 02, the placement of the hydrogen atom is to the right and the placement of the bromine atom is to the left of the methyl group.
Hence, all the sawhorse projections must have this exact orientation pattern to represent the molecule correctly. We can observe that in option A, the positions of the functional groups on the position 01 carbon atom is reversed. Hence, incorrect sawhorse drawing(s) for the given compound is option A
Hence, Option A is the correct option
Note: Groups connected to both the front and back carbons are drawn using sticks at \[{120^\circ }\] angle. A sawhorse projection is similar to a Newman projection, but it shows the carbon-carbon bond that is hidden in a Newman projection.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




