
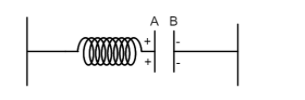
Plate A of a parallel air-filled capacitor is connected to a non-conducting spring having force constant \[k\] and the plate \[B\] Is fixed. If a charge \[ + {\text{ }}q\] is placed on plate \[A\] and charge \[-q\] on the plate \[B\] then find out an extension in the spring in equilibrium. Assume the area of the plate is \['A'\].

Answer
576k+ views
Hint:
-The spring is expanded by the attraction force between the two plates.
-Find the electrostatic force from the stored potential energy of the capacitor.
-The electrostatic force is equal to the attraction force between the two plates. Find the expanded length of the spring using the force constant.
Formula used:
the attraction force $F = - kl$
Where,
\[k\]is the force constant of the spring and $l$ is the expanded length of the spring.
The stored potential energy $U = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{C}$
Where, \[q\] is the charge on the capacitor, and $C$ is the capacitance.
$C = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}{y}$
where,
$A$ is the area of the plate,
${\varepsilon _0}$ is the permittivity in air medium,
$y$ is the distance between two parallel plates.
The electrostatic force of the capacitor $F = \dfrac{{dU}}{{dy}}$
Complete step by step answer:
The spring is attached with a parallel plate capacitor and is expanded to a certain length due to the attraction force of the capacitor.
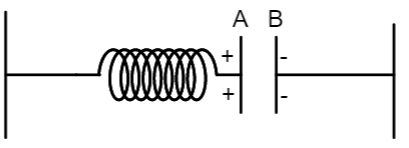
Now, the attraction force $F = - kl...............(1)$
Where,
\[k\]is the force constant of the spring and $l$ is the expanded length of the spring.
Now, if the area of the plates is $A$ and $y$ is the distance between two parallel plates,
The capacitance, $C = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}{y}...............(2)$, ${\varepsilon _0}$ is the permittivity in air medium,
We know, The stored potential energy $U = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{C}.................(3)$
Where, \[q\] is the charge on the capacitor, and $C$ is the capacitance.
From eq. $(2)$ we can write, $U = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}y}}{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}$ [putting the value of $C$]
Since the electrostatic force is conservative, it can be written as the
$F = - \dfrac{{dU}}{{dy}}$
$F = - \dfrac{d}{{dy}}\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}y}}{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow F = - \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}.....................(4)$ [ the negative sign implies the attraction force]
From $(1)$ and $(4)$ we get,
$ - kl = - \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}$
$ \Rightarrow kl = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}$
$ \Rightarrow l = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}Ak}}$
Hence the extension in the spring is, $ \Rightarrow l = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}Ak}}$.
Note:The electrostatic force is taken, $F = - \dfrac{{dU}}{{dy}}$
This defines that the electrostatic force is conservative and is the negative gradient of the potential. The potential is the work done. We know to charge a capacitor the required work is stored as potential energy in the capacitor.
Hence the force is taken as the gradient of the stored potential energy of the capacitor.
-The spring is expanded by the attraction force between the two plates.
-Find the electrostatic force from the stored potential energy of the capacitor.
-The electrostatic force is equal to the attraction force between the two plates. Find the expanded length of the spring using the force constant.
Formula used:
the attraction force $F = - kl$
Where,
\[k\]is the force constant of the spring and $l$ is the expanded length of the spring.
The stored potential energy $U = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{C}$
Where, \[q\] is the charge on the capacitor, and $C$ is the capacitance.
$C = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}{y}$
where,
$A$ is the area of the plate,
${\varepsilon _0}$ is the permittivity in air medium,
$y$ is the distance between two parallel plates.
The electrostatic force of the capacitor $F = \dfrac{{dU}}{{dy}}$
Complete step by step answer:
The spring is attached with a parallel plate capacitor and is expanded to a certain length due to the attraction force of the capacitor.

Now, the attraction force $F = - kl...............(1)$
Where,
\[k\]is the force constant of the spring and $l$ is the expanded length of the spring.
Now, if the area of the plates is $A$ and $y$ is the distance between two parallel plates,
The capacitance, $C = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}{y}...............(2)$, ${\varepsilon _0}$ is the permittivity in air medium,
We know, The stored potential energy $U = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{C}.................(3)$
Where, \[q\] is the charge on the capacitor, and $C$ is the capacitance.
From eq. $(2)$ we can write, $U = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}y}}{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}$ [putting the value of $C$]
Since the electrostatic force is conservative, it can be written as the
$F = - \dfrac{{dU}}{{dy}}$
$F = - \dfrac{d}{{dy}}\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}y}}{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow F = - \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}.....................(4)$ [ the negative sign implies the attraction force]
From $(1)$ and $(4)$ we get,
$ - kl = - \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}$
$ \Rightarrow kl = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}$
$ \Rightarrow l = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}Ak}}$
Hence the extension in the spring is, $ \Rightarrow l = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}Ak}}$.
Note:The electrostatic force is taken, $F = - \dfrac{{dU}}{{dy}}$
This defines that the electrostatic force is conservative and is the negative gradient of the potential. The potential is the work done. We know to charge a capacitor the required work is stored as potential energy in the capacitor.
Hence the force is taken as the gradient of the stored potential energy of the capacitor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




