
What is the placenta? Write two functions of the placenta.
Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: The placenta refers to the temporary vascular organ found in mammals that during pregnancy binds the mother and baby in the womb. It helps to exchange gases. It serves as an immunological barrier.
Complete step by step answer:
The placenta is a disc-shaped organ or special tissue that nourishes and protects the fetus through the umbilical cord in the uterus of the pregnant mammal. The placenta that organ of the body that helps in connecting the developing fetus to the uterine wall and functions in enabling nutrient absorption, waste elimination, thermo- regulation, and gas exchange through the mother's blood supply; to combat internal infection, and to develop hormones that facilitate pregnancy.
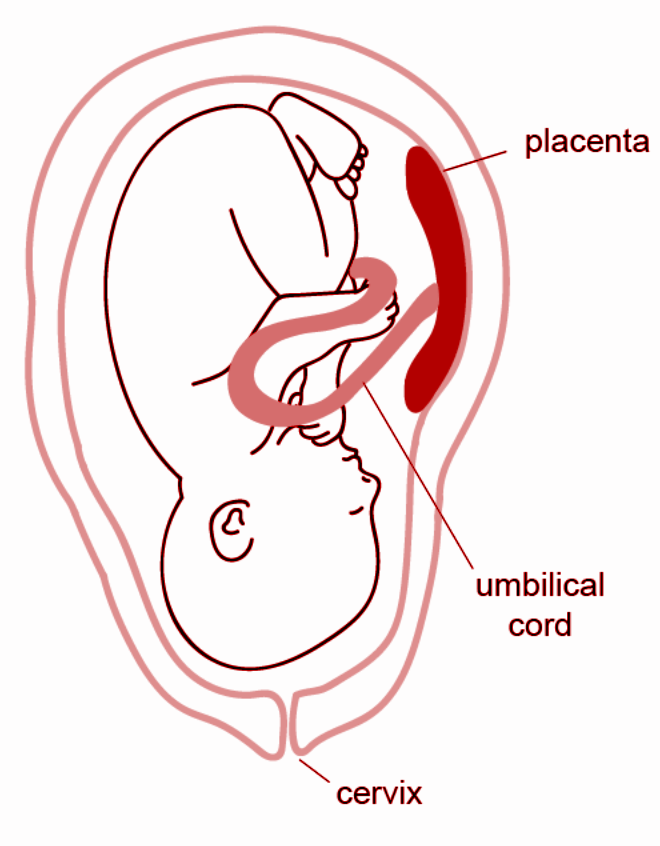
Placenta's Function:
- Provides a large surface area to pass from mother to embryo for glucose and oxygen.
- Removal of waste produced in the growing fetus into the mother's blood.
The placenta attaches to the uterus wall, and the umbilical cord of the baby arises from it. The organ is normally attached to the uterus's top, side, front, or back. The placenta can be attached to the lower region of the uterus in exceptional cases. It's called a low- lying placenta when this occurs.
Note: There are two types of the placenta in mammals, namely the yolk sac placenta and the chorioallantoic placenta. The placenta is disc-shaped and measures a length of up to 22 cm. The placenta is abundant in vessels in the blood, too. As a two-component fetomaternal organ, the placenta works the foetal placenta (Chorion frondosum), which grows from the same blastocyst forming the fetus, and the maternal placenta (Decidua basalis), which grows from the uterine maternal tissue. It metabolizes a variety of substances and is capable of releasing metabolic products into the bloodstream of the mother or fetus. After the fetus is born, the placenta is expelled from the body.
Complete step by step answer:
The placenta is a disc-shaped organ or special tissue that nourishes and protects the fetus through the umbilical cord in the uterus of the pregnant mammal. The placenta that organ of the body that helps in connecting the developing fetus to the uterine wall and functions in enabling nutrient absorption, waste elimination, thermo- regulation, and gas exchange through the mother's blood supply; to combat internal infection, and to develop hormones that facilitate pregnancy.

Placenta's Function:
- Provides a large surface area to pass from mother to embryo for glucose and oxygen.
- Removal of waste produced in the growing fetus into the mother's blood.
The placenta attaches to the uterus wall, and the umbilical cord of the baby arises from it. The organ is normally attached to the uterus's top, side, front, or back. The placenta can be attached to the lower region of the uterus in exceptional cases. It's called a low- lying placenta when this occurs.
Note: There are two types of the placenta in mammals, namely the yolk sac placenta and the chorioallantoic placenta. The placenta is disc-shaped and measures a length of up to 22 cm. The placenta is abundant in vessels in the blood, too. As a two-component fetomaternal organ, the placenta works the foetal placenta (Chorion frondosum), which grows from the same blastocyst forming the fetus, and the maternal placenta (Decidua basalis), which grows from the uterine maternal tissue. It metabolizes a variety of substances and is capable of releasing metabolic products into the bloodstream of the mother or fetus. After the fetus is born, the placenta is expelled from the body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




