
Pigment system connected with oxidation of water
A. Photosystem I
B. Photosystem II
C. Phycobilisome
D. Carotenoids
Answer
567k+ views
Hint: Photosystems have the pigment molecules known as chlorophyll for the light reaction. Carotenoids are the accessory pigments and Phycobilisomes are the antennae of Photosystem II.
Complete answer:
Photosynthesis is a method in which the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP occurs with the help of sunlight called photophosphorylation. It is either cyclic or non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
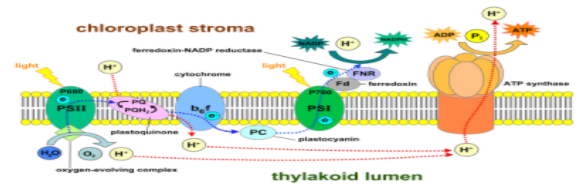
In cyclic phosphorylation: In this process electrons are reduced only the photosystem I is involved. Photosystem I is an integral membrane protein complex which absorbs the solar energy and mediates electron transfer from the cytochrome on the luminal side of the thylakoid membrane and utilizes the light energy to shift them across the membrane to the ferredoxin. P700 is the active reaction centre there. ATP molecules are generated with no NADPH. In this process water is not required and the process is ideal only for bacteria.
Photosystem II: uses water as an electron donor to fill the hole left as the energized electron moves through the row. When the electron is removed from the water molecule the photosystem II separates the oxygen gas. This reaction is the source for all the oxygen we breathe. Electrons pass in the non-cyclic manner. ATP molecules and NADPH are generated. In this process water is required for the photolysis and the process is ideal only for green plants.
Carotenoids: are the pigments which are helpful in photosynthesis in which light energy is transformed to chemical energy. These are of yellow, red and orange colour. These are formed by algae, plants etc.
Phycobilisomes are the antennae of Photosystem II which helps in the light harvesting process. These are composed of chromophore related proteins. These are seen in red algae and blue green algae.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: The naming of the Photosystem I and Photosystem II is based on their discovery and not on any other criteria. In cyclic photophosphorylation of Photosystem I is involved but both are involved in non- cyclic photophosphorylation.
Complete answer:
Photosynthesis is a method in which the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP occurs with the help of sunlight called photophosphorylation. It is either cyclic or non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
In cyclic phosphorylation: In this process electrons are reduced only the photosystem I is involved. Photosystem I is an integral membrane protein complex which absorbs the solar energy and mediates electron transfer from the cytochrome on the luminal side of the thylakoid membrane and utilizes the light energy to shift them across the membrane to the ferredoxin. P700 is the active reaction centre there. ATP molecules are generated with no NADPH. In this process water is not required and the process is ideal only for bacteria.
Photosystem II: uses water as an electron donor to fill the hole left as the energized electron moves through the row. When the electron is removed from the water molecule the photosystem II separates the oxygen gas. This reaction is the source for all the oxygen we breathe. Electrons pass in the non-cyclic manner. ATP molecules and NADPH are generated. In this process water is required for the photolysis and the process is ideal only for green plants.

Carotenoids: are the pigments which are helpful in photosynthesis in which light energy is transformed to chemical energy. These are of yellow, red and orange colour. These are formed by algae, plants etc.
Phycobilisomes are the antennae of Photosystem II which helps in the light harvesting process. These are composed of chromophore related proteins. These are seen in red algae and blue green algae.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: The naming of the Photosystem I and Photosystem II is based on their discovery and not on any other criteria. In cyclic photophosphorylation of Photosystem I is involved but both are involved in non- cyclic photophosphorylation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




