
Pick out the correct statement with respect to \[{[Mn{(CN)_6}]^{3 - }}\] :
A.It is $ds{p^2}\,hybridised\,$ and square planar.
B.It is $s{p^3}{d^2}\,hybridised\,$ and octahedral
C.It is $s{p^3}{d^2}\,hybridised\,$ and tetrahedral
D.It is ${d^2}s{p^3}\,hybridised\,$ and octahedral
Answer
547.2k+ views
Hint: In these types of questions of having hybridization of complex compounds, we need to state the ground state configuration and then configuration in oxidation state. The type of hybrisation and geometry also depends upon the nature of ligand. Solve taking cyanide as strong ligand which will pair up the electrons.
Complete step-by-step answer:In the above complex as we have manganese connected with cyanide ligand as coordination bond, thus it will make complex where these six cyanide will connect with it. Our first step is to see the oxidation state of manganese and then will consider the d-orbitals.
Oxidation state of manganese will be calculated as, \[{[Mn{(CN)_6}]^{3 - }}\] having $( - 1)$ charge given by each cyanide and hence we get $( + 3)$
$[(x) + 6 \times ( - 1)] = - 3$
$(x) = 6 - 3 = 3$
Now starting consider the complex as having manganese in ground state and then in excited state that is at $( + 3)$
$Mn\,(GS) = \,3{d^5}\,4{s^2}$
$Mn\,( + 3) = \,3{d^4}\,4{s^0}$
Let’s see the orbital diagram where in ground state manganese have two electrons in $4s$ and five electrons in $3d$ but in the excited state when manganese have $( + 3)$ oxidation state the electrons changes to $3{d^4}\,4{s^0}$ . In the presence if a strong ligand the unpaired electrons get paired and we get paired configuration. Here we get the configuration as shown below, now the incoming ligand will have the position in which it donates the lone pair and will have the ${d^2}s{p^3}\,hybridisation$ . The geometry will be as such that manganese will have central position and all the cyanide ligand will have octahedral position.
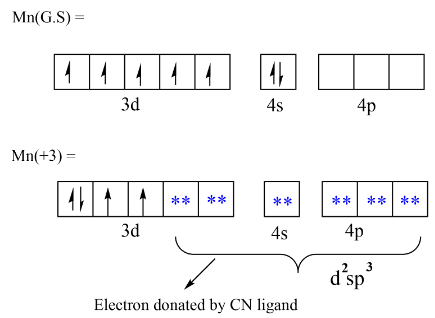
We can also draw the geometry of complex,
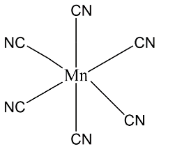
Therefore, the correct answer is option D.
Note:We can also make the complex for a number of transition elements which have partially filled d- orbitals, due to this property they can easily accommodate electrons of ligands in their empty orbitals. A number of properties can be found like magnetic moment, magnetic nature etc. Strong ligands pair up the electrons while weak ligands do not pair up the electrons.
Complete step-by-step answer:In the above complex as we have manganese connected with cyanide ligand as coordination bond, thus it will make complex where these six cyanide will connect with it. Our first step is to see the oxidation state of manganese and then will consider the d-orbitals.
Oxidation state of manganese will be calculated as, \[{[Mn{(CN)_6}]^{3 - }}\] having $( - 1)$ charge given by each cyanide and hence we get $( + 3)$
$[(x) + 6 \times ( - 1)] = - 3$
$(x) = 6 - 3 = 3$
Now starting consider the complex as having manganese in ground state and then in excited state that is at $( + 3)$
$Mn\,(GS) = \,3{d^5}\,4{s^2}$
$Mn\,( + 3) = \,3{d^4}\,4{s^0}$
Let’s see the orbital diagram where in ground state manganese have two electrons in $4s$ and five electrons in $3d$ but in the excited state when manganese have $( + 3)$ oxidation state the electrons changes to $3{d^4}\,4{s^0}$ . In the presence if a strong ligand the unpaired electrons get paired and we get paired configuration. Here we get the configuration as shown below, now the incoming ligand will have the position in which it donates the lone pair and will have the ${d^2}s{p^3}\,hybridisation$ . The geometry will be as such that manganese will have central position and all the cyanide ligand will have octahedral position.

We can also draw the geometry of complex,

Therefore, the correct answer is option D.
Note:We can also make the complex for a number of transition elements which have partially filled d- orbitals, due to this property they can easily accommodate electrons of ligands in their empty orbitals. A number of properties can be found like magnetic moment, magnetic nature etc. Strong ligands pair up the electrons while weak ligands do not pair up the electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




