
Phenotypic and genotypic ratio in ${ F }_{ 2 }$ generation in incomplete dominance is
(a)1:2:1 and 1:2:1
(b)9:6 and 1:2:1
(c)9:6 and 3:1
(d)9:3:3:1and 1:2:1:4:1:1:2:1:2:1
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: Incomplete dominance occurs when a dominant allele does not completely mask the effects of the recessive allele, and the resulting phenotype shows a blending of both alleles. One example is shown in the flowers of snapdragon.
Complete answer:
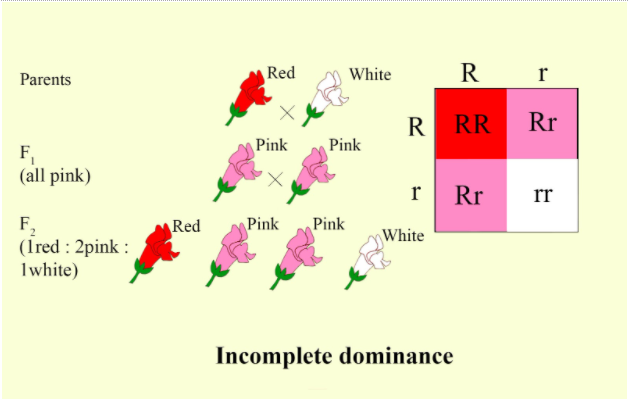
-It is also called semi-dominance or partial dominance.
-The allele for red color is dominant over the allele for white color, but in heterozygous snapdragons, with both alleles, is pink in color.
-In complete dominance, if an individual is heterozygous for a particular gene, the dominant allele will completely mask the recessive allele.
-Flower-like roses, tulips, carnations also show incomplete dominance.
-Incomplete dominance occurs because neither of the two alleles is fully dominant over the other, or because the dominant allele does not fully mask the product of the recessive allele.
-This gives rise to a phenotype that is different from both the dominant and recessive alleles and is a mixture of both.
-The homozygous red flower has two dominant red alleles, represented by RR. The homozygous white flower is represented by rr. Their offspring ($F_1$ generation) are all heterozygous Rr, and they have pink flowers.
-When the $F_1$ generation is cross-pollinated, their offspring ($F_2$ generation) will be RR, Rr, and rr in a 1:2:1 ratio genotypically.
-The RR flowers will have red color, Rr flowers will have a pink color, and rr flowers will have a white color.
So, the correct answer is ‘1:2:1 and 1:2:1’
Note: -Incomplete dominance is different from codominance.
-In codominance, both alleles are expressed at the same time. Example: ‘A’ gene and ‘B’ are expressed together in human blood cells. These both are dominant alleles.
Complete answer:
-It is also called semi-dominance or partial dominance.
-The allele for red color is dominant over the allele for white color, but in heterozygous snapdragons, with both alleles, is pink in color.
-In complete dominance, if an individual is heterozygous for a particular gene, the dominant allele will completely mask the recessive allele.
-Flower-like roses, tulips, carnations also show incomplete dominance.
-Incomplete dominance occurs because neither of the two alleles is fully dominant over the other, or because the dominant allele does not fully mask the product of the recessive allele.
-This gives rise to a phenotype that is different from both the dominant and recessive alleles and is a mixture of both.
-The homozygous red flower has two dominant red alleles, represented by RR. The homozygous white flower is represented by rr. Their offspring ($F_1$ generation) are all heterozygous Rr, and they have pink flowers.
-When the $F_1$ generation is cross-pollinated, their offspring ($F_2$ generation) will be RR, Rr, and rr in a 1:2:1 ratio genotypically.
-The RR flowers will have red color, Rr flowers will have a pink color, and rr flowers will have a white color.
So, the correct answer is ‘1:2:1 and 1:2:1’

Note: -Incomplete dominance is different from codominance.
-In codominance, both alleles are expressed at the same time. Example: ‘A’ gene and ‘B’ are expressed together in human blood cells. These both are dominant alleles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




