
Phenols are more acidic than alcohols. Explain why?
Answer
519.7k+ views
Hint: Try to recall that acidity of any compound is generally directly proportional to its tendency to release ${{H}^{+}}$ ion and stable the conjugate base, stronger is the acid. Now, by using this you can easily answer the given question.
Complete step by step answer:
- We know that comparison of acidic nature is simply attributed to relative stability of conjugate base formed by abstraction of ${{H}^{+}}$from acid.
- Alcohols: Alcohols after removal of ${{H}^{+}}$ forms alkoxide ion which is the conjugate base of alcohol. The negative charge present on oxygen atoms in alkoxide ion increases due to the $+I$ inductive effect of the alkyl group attached to it and this destabilizes the conjugate base and makes alcohol less acidic.
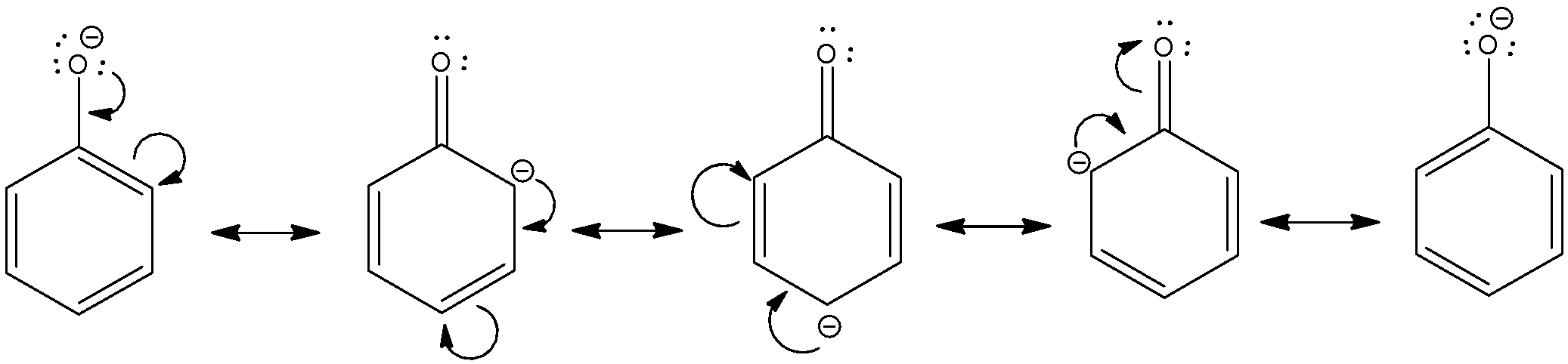
- In case of phenols, phenols lose ${{H}^{+}}$ to form phenoxide ions in which negative charge on the oxygen atom is delocalised around the ring through resonance. In this way, negative charge on oxygen is delocalized on to the ortho and para carbon atoms and phenoxide ion becomes a stable resonating structure. This stabilizes the phenoxide ion and makes phenol more acidic than alcohols.
Note: Note that phenol is more acidic than water whereas water is more acidic than alcohols. Nowadays, phenol is manufactured by Dow’s process (from chlorobenzene by cumene process). Also, you should remember that the liquid solution of phenol containing about 5% water is known as carbolic acid. Phenol turns pink on exposure to air and light.
Complete step by step answer:
- We know that comparison of acidic nature is simply attributed to relative stability of conjugate base formed by abstraction of ${{H}^{+}}$from acid.
- Alcohols: Alcohols after removal of ${{H}^{+}}$ forms alkoxide ion which is the conjugate base of alcohol. The negative charge present on oxygen atoms in alkoxide ion increases due to the $+I$ inductive effect of the alkyl group attached to it and this destabilizes the conjugate base and makes alcohol less acidic.
- In case of phenols, phenols lose ${{H}^{+}}$ to form phenoxide ions in which negative charge on the oxygen atom is delocalised around the ring through resonance. In this way, negative charge on oxygen is delocalized on to the ortho and para carbon atoms and phenoxide ion becomes a stable resonating structure. This stabilizes the phenoxide ion and makes phenol more acidic than alcohols.

Note: Note that phenol is more acidic than water whereas water is more acidic than alcohols. Nowadays, phenol is manufactured by Dow’s process (from chlorobenzene by cumene process). Also, you should remember that the liquid solution of phenol containing about 5% water is known as carbolic acid. Phenol turns pink on exposure to air and light.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




