
Phenol reacts with sodium hydroxide to give sodium phenoxide. The phenoxide ion undergoes electrophilic substitution with carbon dioxide (a weak electrophile) because the phenoxide ion is more reactive than phenol. Salicylic acid is formed as a major product. At a lower temperature, the ortho- isomer is predominant, whereas para- isomer is obtained at higher temperatures. Give the reason behind this:
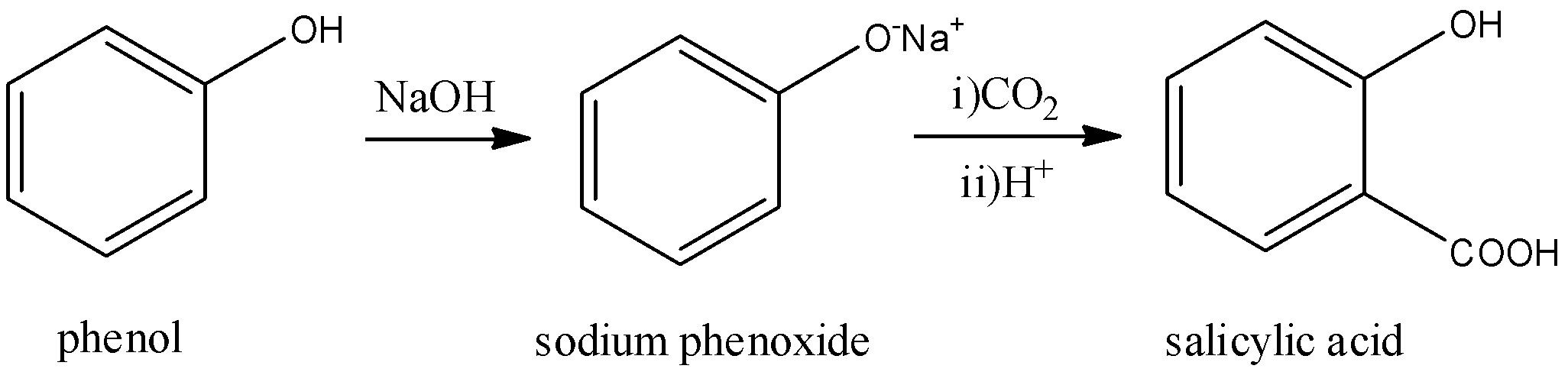

Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: Think about the structures of the ortho- and para-isomers of salicylic acid and the electronegativities of the atoms involved. How will the electronegativity affect the hydrogen bonding in salicylic acid?
Complete step by step answer:
Salicylic acid has many oxygen atoms and all of them will have a partial negative charge due to the difference in electronegativity of oxygen and the surrounding atoms. The most electronegative and easily accessible of all of them is the oxygen atom that shares a double bond with the carbonyl carbon in the acid group. The hydrogen atom present in the hydroxyl group will have a partial positive charge due to the presence of oxygen. The hydrogen bonding will occur between these two atoms.
Now, let us look at the structures of these two isomers and then determine how the hydrogen bonding will occur.

Now, let us consider all the partial charges and how the hydrogen bonding will occur.
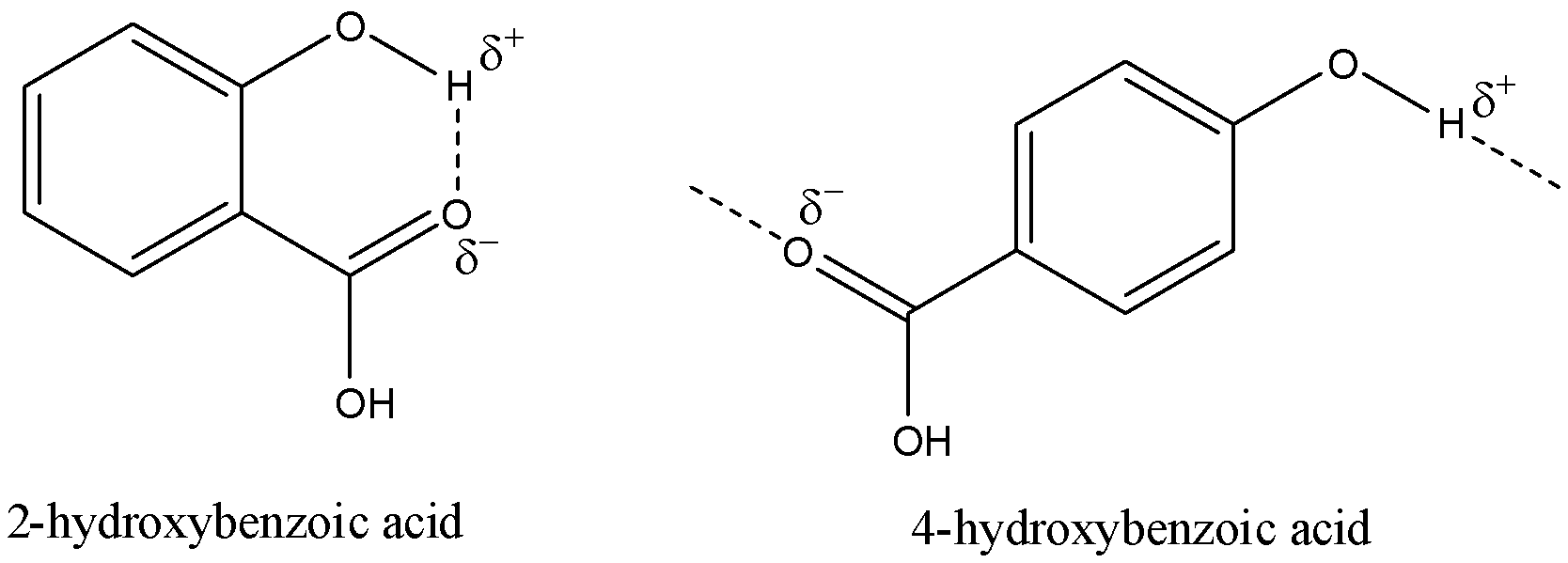
Here, we can see that 2-hydroxybenzoic acid undergoes intra-molecular hydrogen bonding and 4-hydroxybenzoic acid will form hydrogen bonds with sites on other molecules and form intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
The intermolecular hydrogen bonding will increase the boiling point of the para-isomer greatly as compared to the boiling point of 2-hydroxybenzoic acid.
Since, the boiling point 4-hydroxybenzoic acid is higher than that of 2-hydroxybenzoic acid it will require more energy for formation. At higher temperatures, this energy will be provided and the reaction will tend to the formation of the para-isomers. At lower temperatures, the formation of para-isomers will not be favourable and thus the ortho-isomers will be formed.
Note: For the hydrogen bonding in 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, both the hydrogen bonds can be formed with either the same molecule or two different molecules of p-hydroxybenzoic acid. This will not affect the melting point in any way since the number of hydrogen bonds will remain the same. Also note that 4-hydroxybenzoic acid does not have a boiling point since it directly decomposes at higher temperatures.
Complete step by step answer:
Salicylic acid has many oxygen atoms and all of them will have a partial negative charge due to the difference in electronegativity of oxygen and the surrounding atoms. The most electronegative and easily accessible of all of them is the oxygen atom that shares a double bond with the carbonyl carbon in the acid group. The hydrogen atom present in the hydroxyl group will have a partial positive charge due to the presence of oxygen. The hydrogen bonding will occur between these two atoms.
Now, let us look at the structures of these two isomers and then determine how the hydrogen bonding will occur.

Now, let us consider all the partial charges and how the hydrogen bonding will occur.

Here, we can see that 2-hydroxybenzoic acid undergoes intra-molecular hydrogen bonding and 4-hydroxybenzoic acid will form hydrogen bonds with sites on other molecules and form intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
The intermolecular hydrogen bonding will increase the boiling point of the para-isomer greatly as compared to the boiling point of 2-hydroxybenzoic acid.
Since, the boiling point 4-hydroxybenzoic acid is higher than that of 2-hydroxybenzoic acid it will require more energy for formation. At higher temperatures, this energy will be provided and the reaction will tend to the formation of the para-isomers. At lower temperatures, the formation of para-isomers will not be favourable and thus the ortho-isomers will be formed.
Note: For the hydrogen bonding in 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, both the hydrogen bonds can be formed with either the same molecule or two different molecules of p-hydroxybenzoic acid. This will not affect the melting point in any way since the number of hydrogen bonds will remain the same. Also note that 4-hydroxybenzoic acid does not have a boiling point since it directly decomposes at higher temperatures.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




