
Phenol on treatment with $C{O_2}$ in the presence of $NaOH$ followed by acidification produces compound X as the major product. X on treatment with ${(C{H_3}CO)_2}O$ in the presence of a catalytic amount of ${H_2}S{O_4}$ produces.
(A)
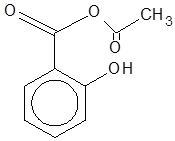
(B)
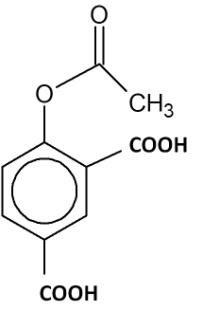
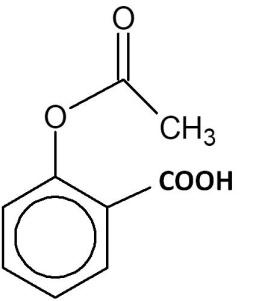
(C)
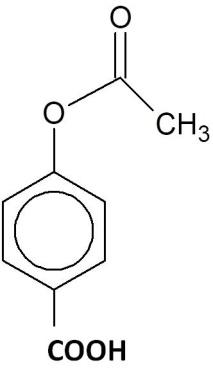
(D)




Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: The reaction of phenols with carbon dioxide in the presence of alkalies is Kolbe–Schmitt reaction. It is a carboxylation reaction of phenols giving sodium phenoxide salts which on acidification give aromatic hydroxyl acids. These acids act as precursors for many industrially important compounds and aspirin is one of them.
Complete step by step answer:
Two different reactions are taking place here Kolbe–Schmitt reaction and esterification reaction (treatment of the product of Kolbe–Schmitt reaction with ${(C{H_3}CO)_2}O$ ester). The two reactions can be written as follows:
$1.$ Kolbe–Schmitt reaction: reaction of phenol with carbon dioxide in the presence of sodium hydroxide, followed by acidification converts phenol to $1 - $ hydroxybenzoic acid (Salicylic acid).
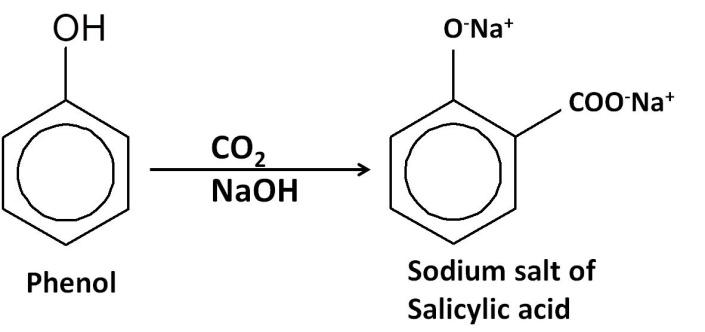
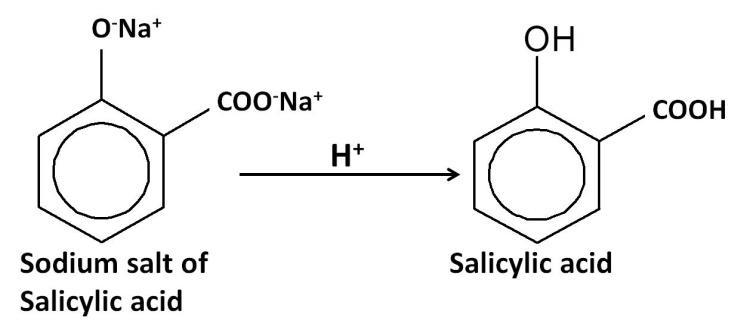
$2.$Esterification reaction: The salicylic acid is then reacted with acetic anhydride (${(C{H_3}CO)_2}O$) to form aspirin.
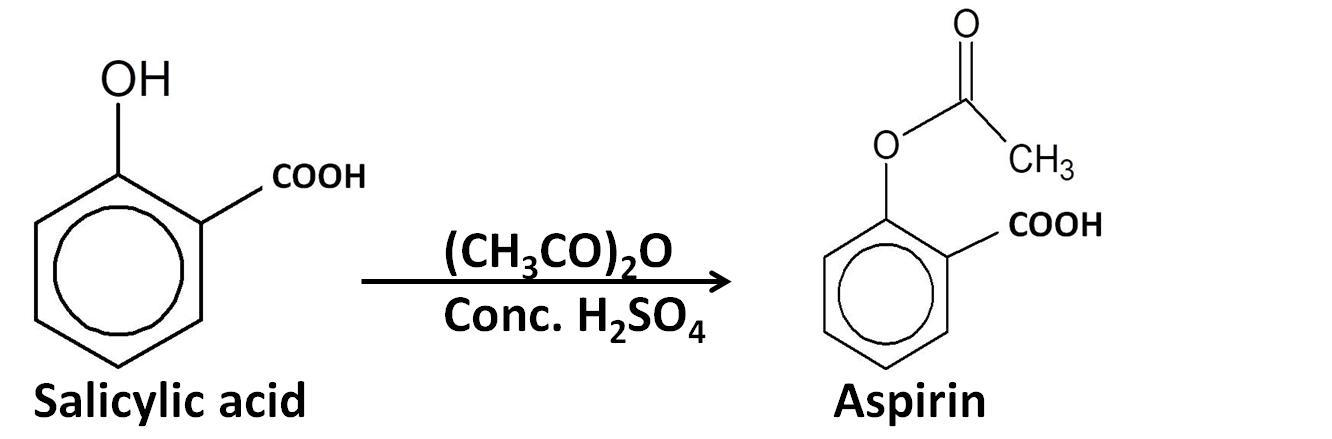
Hence, the correct answer is option ‘C’.
Additional information: Aspirin is an analgesic used to relieve pain during minor aches, cold and sometimes fever also. It is synthesized in industry by esterification of salicylic acid (which acts as precursor) with excess anhydride. The reaction is catalysed by the presence of small amounts of acid and the acetic acid formed as a side product is quenched by using small amounts of water. The Kolbe–Schmitt reaction or Kolbe process is carried out at very high pressure and temperature.
Note:
The reactions should be written and it is always better to remember the common names of some important compounds like salicylic acid, acetic anhydride and aspirin used in this reaction. These common names are generally used for commercially important compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
Two different reactions are taking place here Kolbe–Schmitt reaction and esterification reaction (treatment of the product of Kolbe–Schmitt reaction with ${(C{H_3}CO)_2}O$ ester). The two reactions can be written as follows:
$1.$ Kolbe–Schmitt reaction: reaction of phenol with carbon dioxide in the presence of sodium hydroxide, followed by acidification converts phenol to $1 - $ hydroxybenzoic acid (Salicylic acid).


$2.$Esterification reaction: The salicylic acid is then reacted with acetic anhydride (${(C{H_3}CO)_2}O$) to form aspirin.

Hence, the correct answer is option ‘C’.
Additional information: Aspirin is an analgesic used to relieve pain during minor aches, cold and sometimes fever also. It is synthesized in industry by esterification of salicylic acid (which acts as precursor) with excess anhydride. The reaction is catalysed by the presence of small amounts of acid and the acetic acid formed as a side product is quenched by using small amounts of water. The Kolbe–Schmitt reaction or Kolbe process is carried out at very high pressure and temperature.
Note:
The reactions should be written and it is always better to remember the common names of some important compounds like salicylic acid, acetic anhydride and aspirin used in this reaction. These common names are generally used for commercially important compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




