
$\text{Ph-C}\equiv \text{C-C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{ }\xrightarrow[{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}]{HgS{{O}_{4}}}\text{ A }$ A is,
(A)
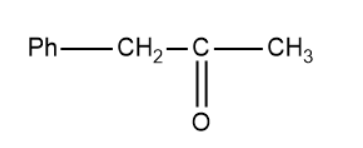
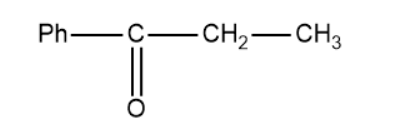
(B)
(C)
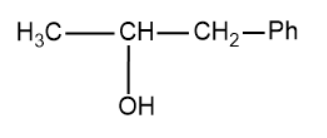
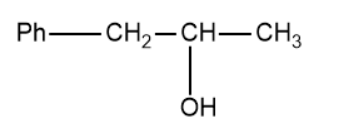
(D)




Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint:. The above reagents are the characteristic reagents for the Kucherov reaction. Understand the reaction mechanism for Kucherov reaction. Now based on the mechanism, perform the chemical reaction on the reactant given in the question and determine the final answer.
Complete step by step answer:
It is observed that alkynes have a low rate of electrophilic addition when compared to alkenes. This is the reason why we use a metal catalyst to increase the rate of reaction. In this case we will be using $\text{HgS}{{\text{O}}_{4}}$.
By experimental analysis we have come to know that alkynes do not undergo the classic carbocation formation mechanism. Instead the non-classical carbocation formation takes place with the help of metal cations.
The Kucherov reaction is used to convert alkyne into a carbonyl compound. The hydrogen ions are supplied by the dilute sulphuric acid. On the other hand, mercuric sulphate facilitates the formation of carbocation.
In the following question instead of following the complete mechanism, we will devise a short method to solve these types of questions quickly.
In this method, we replace the triple bond between the two carbon atoms with a carbonyl group. It is important to know that the carbocation is formed in accordance to the Saytzeff's rule and subsequently the carbonyl compound.
Based on this the products of the above reaction becomes,
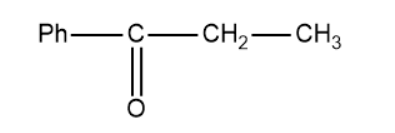
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: It is important to know that in the Kucherov reaction, the sulphuric acid used is dilute. This is because the role of sulphuric acid is a protonating agent. Concentrated sulphuric acid will behave as a dehydrating agent which is not favorable for the reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
It is observed that alkynes have a low rate of electrophilic addition when compared to alkenes. This is the reason why we use a metal catalyst to increase the rate of reaction. In this case we will be using $\text{HgS}{{\text{O}}_{4}}$.
By experimental analysis we have come to know that alkynes do not undergo the classic carbocation formation mechanism. Instead the non-classical carbocation formation takes place with the help of metal cations.
The Kucherov reaction is used to convert alkyne into a carbonyl compound. The hydrogen ions are supplied by the dilute sulphuric acid. On the other hand, mercuric sulphate facilitates the formation of carbocation.
In the following question instead of following the complete mechanism, we will devise a short method to solve these types of questions quickly.
In this method, we replace the triple bond between the two carbon atoms with a carbonyl group. It is important to know that the carbocation is formed in accordance to the Saytzeff's rule and subsequently the carbonyl compound.
Based on this the products of the above reaction becomes,

So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: It is important to know that in the Kucherov reaction, the sulphuric acid used is dilute. This is because the role of sulphuric acid is a protonating agent. Concentrated sulphuric acid will behave as a dehydrating agent which is not favorable for the reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




