
How oxygen enters in blood from alveoli of lungs?
A. Pressure of CO2
B. Simple diffusion
C. By Haemoglobin
D. None of the above
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: The air sacs or the alveoli present in the lungs are made up of paper-thin walls to tiny blood vessels called capillaries. Haemoglobin within the red blood cells transports the oxygen throughout the body. The movement of oxygen from the alveoli into the blood is facilitated by the ultra-thin membrane of the alveoli.
Step by step answer: Diffusion is the spontaneous movement of gases without the utilization of any energy or effort by the body. Gas exchange between the air within the alveoli and the pulmonary capillaries occurs by simple diffusion. The oxygen must first dissolve before passing through the respiratory epithelium. Gas moves from a region of high partial pressure to another region of low partial pressure, i.e. it moves along a partial pressure gradient. Further within the alveolar capillaries, the diffusion of gasses occurs: oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the blood & carbon dioxide from the blood into the alveoli. The oxygen is next transported into all parts of the body through the haemoglobin molecules of the RBCs in the blood. The blood brings carbon dioxide to the lungs via pulmonary circulation, i.e. veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues. After the diffusion occurs, the oxygenated blood is brought to the heart and it is transported via systemic circulation.
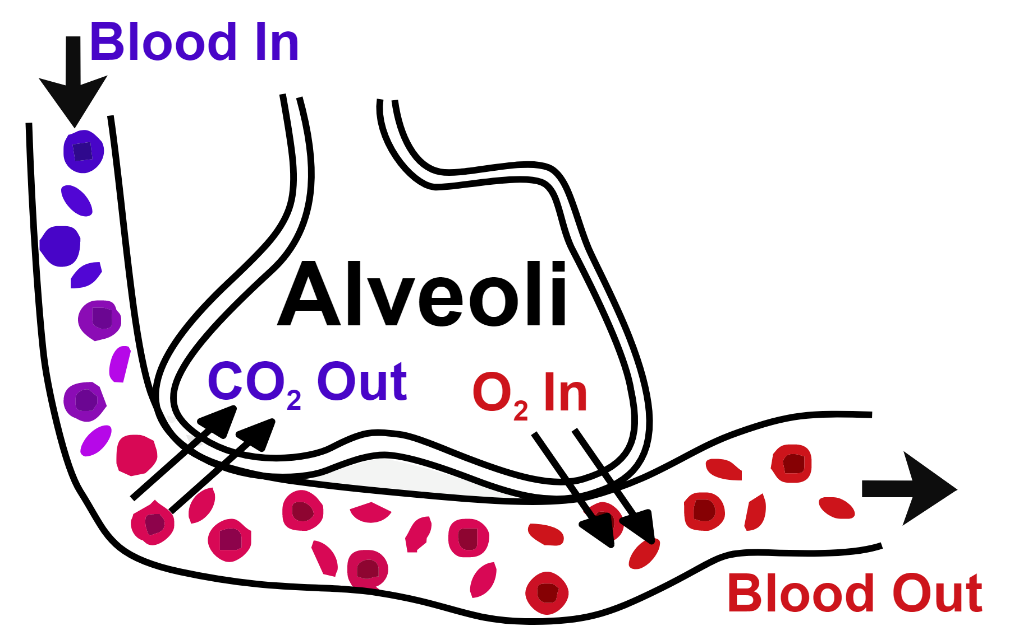
Note: It is important to note that Fick's law gives us an idea of the variety of things that affect the diffusion rate of a gas through a fluid: The partial pressure difference across the diffusion barrier being one of the most important factors. Other factors include the relative molecular mass of the gas.
Step by step answer: Diffusion is the spontaneous movement of gases without the utilization of any energy or effort by the body. Gas exchange between the air within the alveoli and the pulmonary capillaries occurs by simple diffusion. The oxygen must first dissolve before passing through the respiratory epithelium. Gas moves from a region of high partial pressure to another region of low partial pressure, i.e. it moves along a partial pressure gradient. Further within the alveolar capillaries, the diffusion of gasses occurs: oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the blood & carbon dioxide from the blood into the alveoli. The oxygen is next transported into all parts of the body through the haemoglobin molecules of the RBCs in the blood. The blood brings carbon dioxide to the lungs via pulmonary circulation, i.e. veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues. After the diffusion occurs, the oxygenated blood is brought to the heart and it is transported via systemic circulation.

Note: It is important to note that Fick's law gives us an idea of the variety of things that affect the diffusion rate of a gas through a fluid: The partial pressure difference across the diffusion barrier being one of the most important factors. Other factors include the relative molecular mass of the gas.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

Explain the preparation of glucose from the cane s class 11 chemistry CBSE

Father s age is three times the sum of the ages of-class-11-maths-CBSE

The distance of the closest approach of an alphaparticle class 11 physics CBSE

Draw a neat and labelled diagram of a dry cell class 11 chemistry CBSE

1 ton equals to A 100 kg B 1000 kg C 10 kg D 10000 class 11 physics CBSE




