
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of a dry cell.
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: The zinc-carbon dry cell consists of a zinc anode and graphite cathode. The electrolyte is in the form of a low moisture paste made up of ammonium chloride and zinc chloride.
Complete Solution :
-First of all let us see what a dry cell is.
- A dry cell is basically a type of an electrochemical cell or a battery which is mostly used for the house equipment and portable electronic devices. The electrolytes present in it are in the form of a paste to form low moisture immobilized electrolytes, which restricts it from flowing and the moisture is low but enough to allow the current to flow. This also makes it easy to transport.
- An example of a dry cell is a Zinc-Carbon cell. It is a type of primary cell and also known as a Leclanche cell. It can produce a maximum of 1.5V of voltage. It consists of a Zinc container which acts as the anode (negative electrode) and a carbon graphite rod which acts as a cathode (positive electrode). The remaining space between both the electrodes is filled with manganese dioxide ($Mn{O_2}$) and a low moisture electrolyte made up of ammonium chloride ($N{H_4}Cl$) and zinc chloride paste ($ZnC{l_2}$).
The overall reaction involved in this cell is given below:
$Zn + 2Mn{O_2} + 2N{H_4}Cl \to M{n_2}{O_3} + Zn{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)_2}C{l_2} + {H_2}O$
The labelled diagram for this dry cell is shown below:
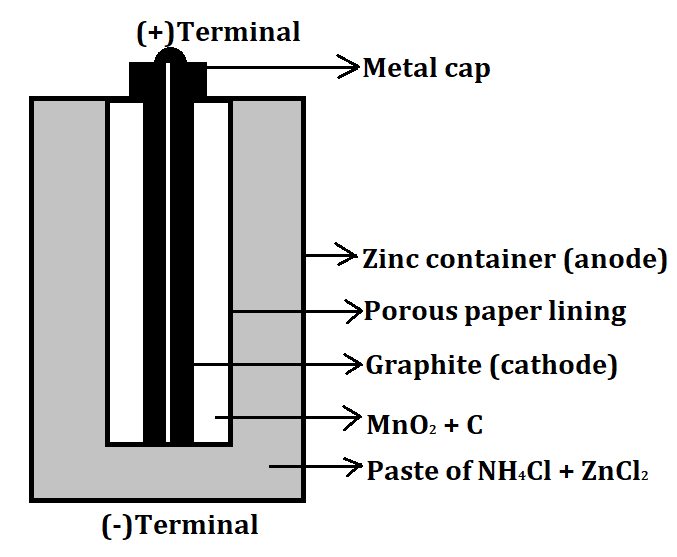
Note: A dry cell is basically of 2 types: primary and secondary. A primary dry cell is the one in which the electrochemical reactions consume all the chemical reagents, thus fail to produce electricity and so are neither reusable nor rechargeable. For example: zinc-carbon cell, lithium cell, mercury cell, silver oxide cell, etc.
- While the secondary dry cell has the ability to regenerate the chemical reactions and hence can be recharged with the help of battery chargers. For example: Nickel metal hydride cell, nickel-cadmium cell, lithium ion cell, etc.
Complete Solution :
-First of all let us see what a dry cell is.
- A dry cell is basically a type of an electrochemical cell or a battery which is mostly used for the house equipment and portable electronic devices. The electrolytes present in it are in the form of a paste to form low moisture immobilized electrolytes, which restricts it from flowing and the moisture is low but enough to allow the current to flow. This also makes it easy to transport.
- An example of a dry cell is a Zinc-Carbon cell. It is a type of primary cell and also known as a Leclanche cell. It can produce a maximum of 1.5V of voltage. It consists of a Zinc container which acts as the anode (negative electrode) and a carbon graphite rod which acts as a cathode (positive electrode). The remaining space between both the electrodes is filled with manganese dioxide ($Mn{O_2}$) and a low moisture electrolyte made up of ammonium chloride ($N{H_4}Cl$) and zinc chloride paste ($ZnC{l_2}$).
The overall reaction involved in this cell is given below:
$Zn + 2Mn{O_2} + 2N{H_4}Cl \to M{n_2}{O_3} + Zn{\left( {N{H_3}} \right)_2}C{l_2} + {H_2}O$
The labelled diagram for this dry cell is shown below:

Note: A dry cell is basically of 2 types: primary and secondary. A primary dry cell is the one in which the electrochemical reactions consume all the chemical reagents, thus fail to produce electricity and so are neither reusable nor rechargeable. For example: zinc-carbon cell, lithium cell, mercury cell, silver oxide cell, etc.
- While the secondary dry cell has the ability to regenerate the chemical reactions and hence can be recharged with the help of battery chargers. For example: Nickel metal hydride cell, nickel-cadmium cell, lithium ion cell, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE




