
What is the output $X$of the following logic gate circuit?
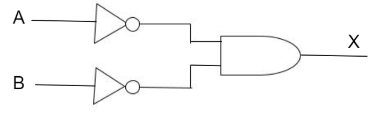
A. $\overline {A \bullet B} $
B. $\overline A \bullet \overline B $
C. $\overline{\overline {A \bullet B}} $
D. $A + B$

Answer
496.8k+ views
Hint:A logic gate is an idealistic model of computing or a practical electronic device that implements a Boolean function, which is a logical operation that creates a single binary output from one or more binary inputs. Depending on the context, the term can refer to either an ideal logic gate with zero rise time and limitless fan-out or a non-perfect physical device.
Complete step by step answer:
Diodes or transistors operate as electronic switches in logic gates, but they can also be built with vacuum tubes, electromagnetic relays (relay logic), fluidic logic, pneumatic logic, optics, molecules, or even mechanical parts. Amplification allows the building of a physical model of all Boolean logic, and thus all of the algorithms and mathematics that can be expressed with Boolean logic, in the same manner that Boolean functions may be built.
Let us know about NOT gate. An inverter, often known as a NOT gate, is a logic gate that provides logical negation in digital logic. It is equivalent to the logical negation operator in mathematical logic. On the right, you can see the truth table.
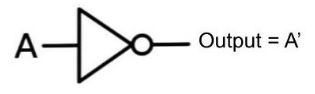
Out of the NOT gate will be $Out = \overline A $
Let us know about AND gate. The AND gate is a fundamental digital logic gate that implements mathematical logic's logical conjunction; it behaves as shown in the truth table above. The AND gate produces a HIGH output only if all of its inputs are HIGH. The output is LOW if none of the AND gate's inputs are HIGH. Any number of inputs can be added to the function.
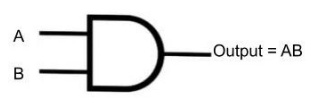
Output of the And gate will be $A \bullet B$
Now let us solve the problem by a logic diagram.
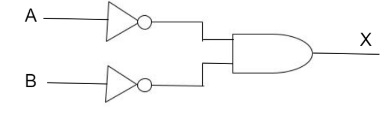
So from the above discussion we can say that :
$X = \overline A \bullet \overline B $
Therefore, option B is correct.
Note:Multiplexers, registers, arithmetic logic units (ALUs), and computer memory are all examples of logic circuits, as are entire microprocessors, which can have over \[100\] million gates. MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) are used to make most gates nowadays.
Complete step by step answer:
Diodes or transistors operate as electronic switches in logic gates, but they can also be built with vacuum tubes, electromagnetic relays (relay logic), fluidic logic, pneumatic logic, optics, molecules, or even mechanical parts. Amplification allows the building of a physical model of all Boolean logic, and thus all of the algorithms and mathematics that can be expressed with Boolean logic, in the same manner that Boolean functions may be built.
Let us know about NOT gate. An inverter, often known as a NOT gate, is a logic gate that provides logical negation in digital logic. It is equivalent to the logical negation operator in mathematical logic. On the right, you can see the truth table.
| Input | Output |
| A | NOT A |
| \[0\] | \[1\] |
| \[1\] | \[0\] |

Out of the NOT gate will be $Out = \overline A $
Let us know about AND gate. The AND gate is a fundamental digital logic gate that implements mathematical logic's logical conjunction; it behaves as shown in the truth table above. The AND gate produces a HIGH output only if all of its inputs are HIGH. The output is LOW if none of the AND gate's inputs are HIGH. Any number of inputs can be added to the function.
| A | B | A AND B |
| \[0\] | \[0\] | \[0\] |
| \[0\] | \[1\] | \[0\] |
| \[1\] | \[0\] | \[0\] |
| \[1\] | \[1\] | \[1\] |

Output of the And gate will be $A \bullet B$
Now let us solve the problem by a logic diagram.

So from the above discussion we can say that :
$X = \overline A \bullet \overline B $
Therefore, option B is correct.
Note:Multiplexers, registers, arithmetic logic units (ALUs), and computer memory are all examples of logic circuits, as are entire microprocessors, which can have over \[100\] million gates. MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) are used to make most gates nowadays.
Recently Updated Pages
Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

The coating formed on the metals such as iron silver class 12 chemistry CBSE

Metals are refined by using different methods Which class 12 chemistry CBSE

What do you understand by denaturation of proteins class 12 chemistry CBSE

Assertion Nitrobenzene is used as a solvent in FriedelCrafts class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE




