
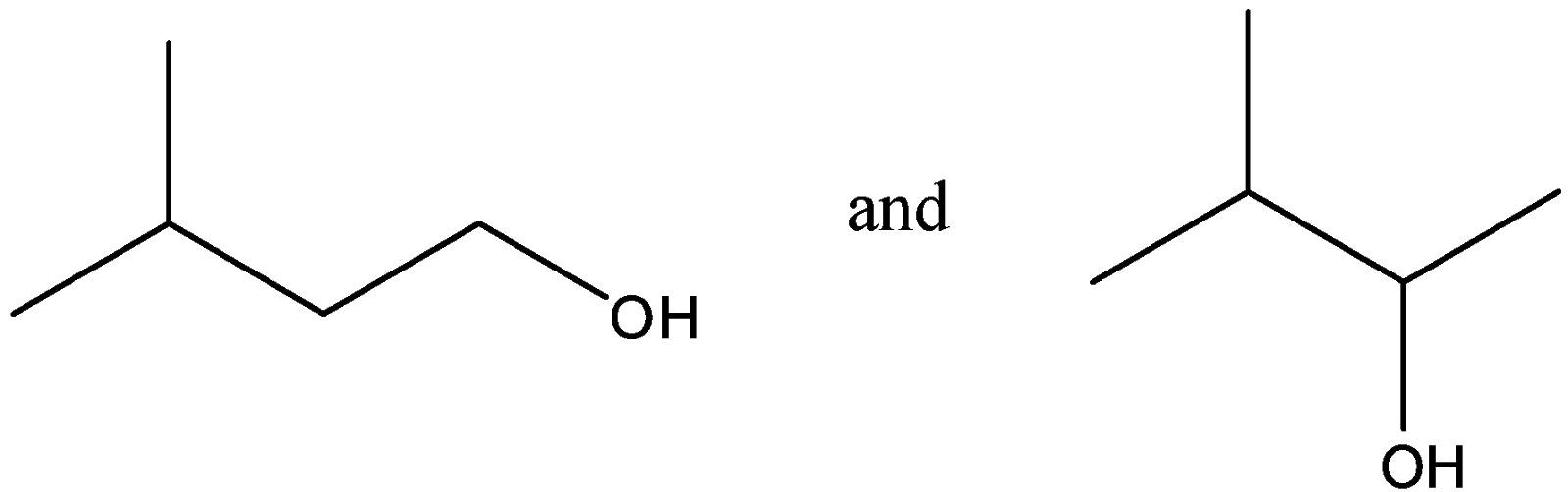
Out of (ref. image), which one is optically active and why?

Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: To check for the optical activity, we need to check for the presence of a chiral centre first. Also we need to check if there is any presence of symmetry if there are more than 1 chiral carbon atom because the presence of symmetry makes the compound inactive.
Complete step by step solution:
-The carbon atom with 4 different groups associated with it is called chiral carbon atom and the compound is optically active, thus rotates plane polarised light in clockwise and anti-clockwise direction.
-When 2 carbon atoms in a compound are chiral, the resulting molecule can either be diastereomer or enantiomer. Enantiomers are the isomers which are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. Diastereomers are the stereoisomers which are not the mirror images of each other.
-Diastereomers have different physical and chemical properties and so can easily be separated.
-Enantiomers have identical physical properties and chemical properties if they react with achiral molecules but different properties if they react with chiral molecules.
-But if we take equimolar concentration of pure dextro (d) and pure leavo (l) form of an optically active compound, then the mixture thus formed is the racemic mixture.
-In the given compounds, we see that there are no 4 different groups associated with any of the carbon atoms in the first figure. So it cannot be a chiral compound and so it is optically inactive.
-In the second figure, we see that there is 1 carbon atom which is chiral as it has four different groups attached to it. As there is only 1 carbon which is chiral, we need not check for meso, diastereomers or enantiomers.
The carbon atom which is chiral has 4 different groups of –OH, -H, methyl and the bulky group attached to the rest of the carbon atom. It can be shown as
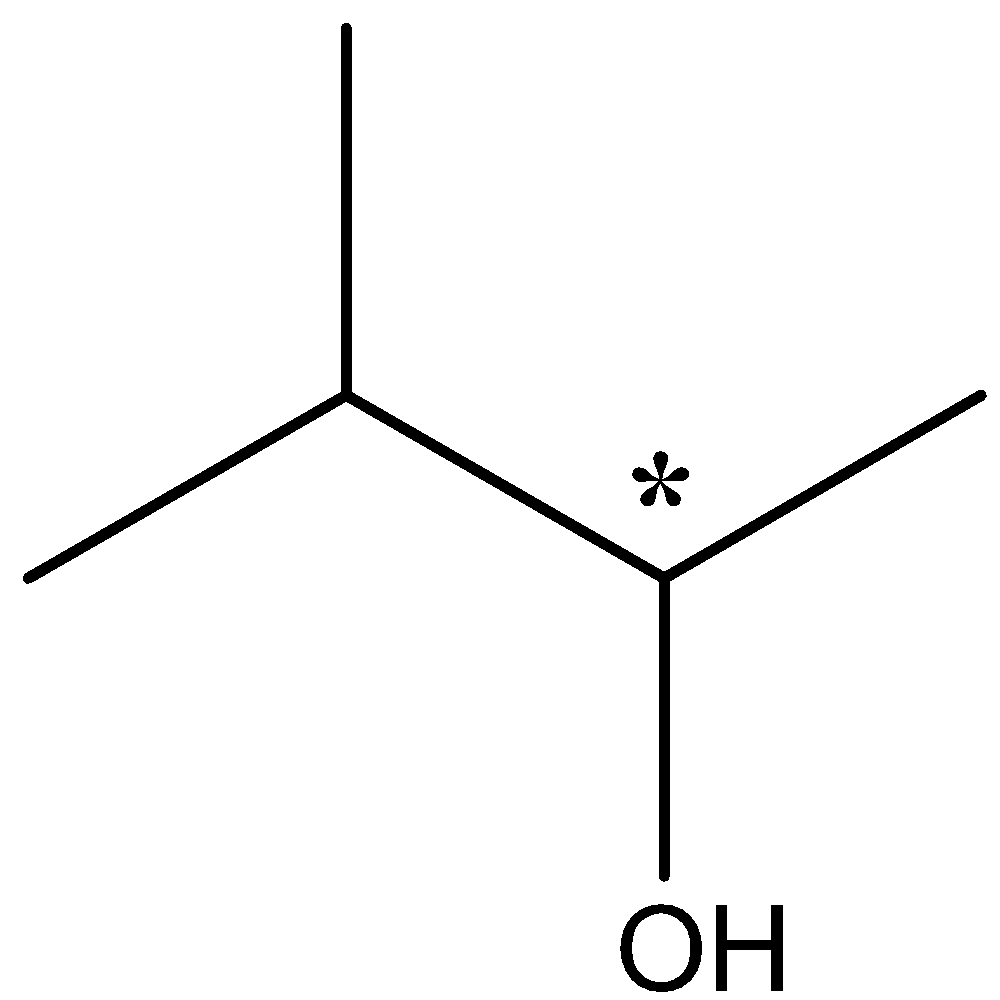
So the second compound is optically active due to presence of a chiral carbon atom which is called chiral centre.
Note: The racemic mixtures have chiral atoms but they are not optically active due to the cancellation of the opposite effects. It is called external compensation. The meso compounds also have chiral centres but they are also inactive due to the presence of symmetry. So not all chiral carbon compounds are optically active.
Complete step by step solution:
-The carbon atom with 4 different groups associated with it is called chiral carbon atom and the compound is optically active, thus rotates plane polarised light in clockwise and anti-clockwise direction.
-When 2 carbon atoms in a compound are chiral, the resulting molecule can either be diastereomer or enantiomer. Enantiomers are the isomers which are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. Diastereomers are the stereoisomers which are not the mirror images of each other.
-Diastereomers have different physical and chemical properties and so can easily be separated.
-Enantiomers have identical physical properties and chemical properties if they react with achiral molecules but different properties if they react with chiral molecules.
-But if we take equimolar concentration of pure dextro (d) and pure leavo (l) form of an optically active compound, then the mixture thus formed is the racemic mixture.
-In the given compounds, we see that there are no 4 different groups associated with any of the carbon atoms in the first figure. So it cannot be a chiral compound and so it is optically inactive.
-In the second figure, we see that there is 1 carbon atom which is chiral as it has four different groups attached to it. As there is only 1 carbon which is chiral, we need not check for meso, diastereomers or enantiomers.
The carbon atom which is chiral has 4 different groups of –OH, -H, methyl and the bulky group attached to the rest of the carbon atom. It can be shown as

So the second compound is optically active due to presence of a chiral carbon atom which is called chiral centre.
Note: The racemic mixtures have chiral atoms but they are not optically active due to the cancellation of the opposite effects. It is called external compensation. The meso compounds also have chiral centres but they are also inactive due to the presence of symmetry. So not all chiral carbon compounds are optically active.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




