
What is the origin of replication? State its function.
Answer
507.6k+ views
Hint: The genetic material is passed on to the next generation by duplication of DNA by semiconservative replication prior to cell division. This ensures that the daughter cells receive a full complement of chromosomes. Origin of replication is also known as Ori.
Complete answer:
Genetic engineering is a branch of biology that deals with altering the chemistry of genetic material of DNA and RNA to be introduced up into host organisms. It thus changes up the phenotype of the organism of the host. Genetic engineering includes creation of recombinant DNA, use of gene cloning and gene transfer, overcome this limitation and allow us to isolate and introduce only one set of desirable genes without introducing undesirable genes into the target organism.
Most likely, the DNA pieces would not be able to multiply itself in the progeny cells of the organism. But when it gets integrated into the genome of the recipient, it may multiply and be inherited along the host DNA. This is because the alien piece of the DNA has become part of the chromosome which has the ability to replicate. In a chromosome there is a specific DNA sequence called the "origin of replication"which is mainly responsible for the initiating replication.
Therefore, for the multiplication of an alien piece of DNA in an organism it needs to be a part of a chromosome which has a specific sequence which is called "origin of replication". Thus, an alien DNA is linked with the origin of replication, so that this alien piece of DNA can replicate and multiply itself in the host organisms. This can be called cloning or making multiple identical copies of any template DNA.
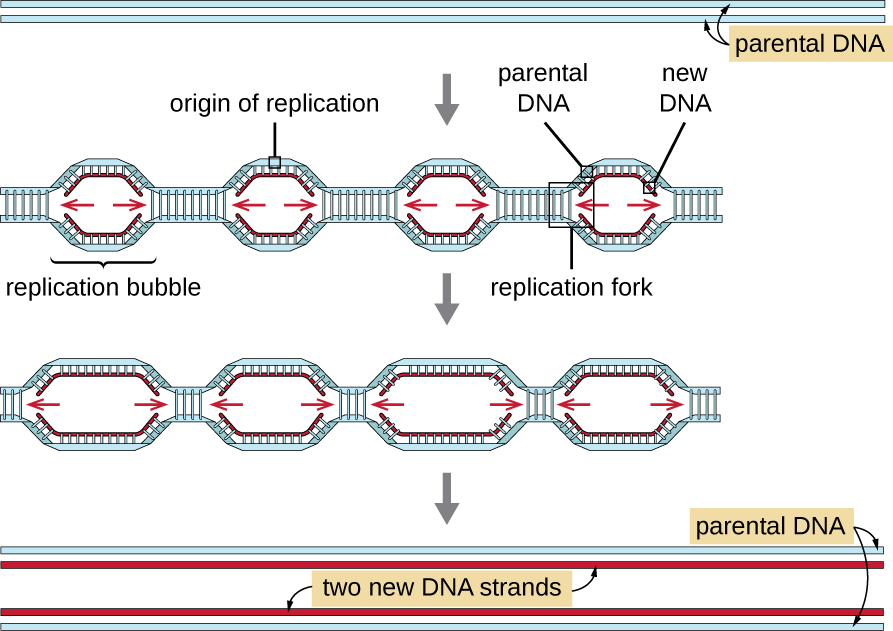
FUNCTION- Ori is mainly the place where the DNA replication begins, enabling a plasmid to reproduce so as to survive within the cells.
Note: Gregor Mendel worked on the inheritance of traits in pea plants suggesting that specific "factors'' are responsible for transferring organismal traits between generations. It was the start of the discovery whereas the isolation of DNA polymerases, the enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of new DNA strands was done by Kornberg and his colleagues from the bacteria E.coli.
Complete answer:
Genetic engineering is a branch of biology that deals with altering the chemistry of genetic material of DNA and RNA to be introduced up into host organisms. It thus changes up the phenotype of the organism of the host. Genetic engineering includes creation of recombinant DNA, use of gene cloning and gene transfer, overcome this limitation and allow us to isolate and introduce only one set of desirable genes without introducing undesirable genes into the target organism.
Most likely, the DNA pieces would not be able to multiply itself in the progeny cells of the organism. But when it gets integrated into the genome of the recipient, it may multiply and be inherited along the host DNA. This is because the alien piece of the DNA has become part of the chromosome which has the ability to replicate. In a chromosome there is a specific DNA sequence called the "origin of replication"which is mainly responsible for the initiating replication.
Therefore, for the multiplication of an alien piece of DNA in an organism it needs to be a part of a chromosome which has a specific sequence which is called "origin of replication". Thus, an alien DNA is linked with the origin of replication, so that this alien piece of DNA can replicate and multiply itself in the host organisms. This can be called cloning or making multiple identical copies of any template DNA.

FUNCTION- Ori is mainly the place where the DNA replication begins, enabling a plasmid to reproduce so as to survive within the cells.
Note: Gregor Mendel worked on the inheritance of traits in pea plants suggesting that specific "factors'' are responsible for transferring organismal traits between generations. It was the start of the discovery whereas the isolation of DNA polymerases, the enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of new DNA strands was done by Kornberg and his colleagues from the bacteria E.coli.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




