
Order of stability of carbocation is:
(I)
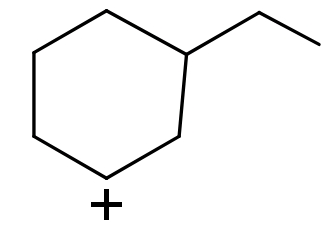
(II)
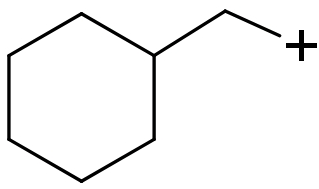
(III)
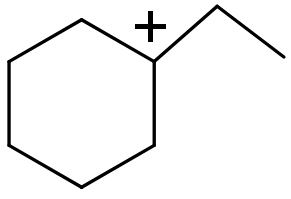
(IV)
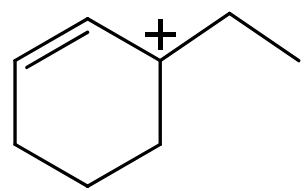
(A) \[\text{I}\,\rangle \,\text{II}\,\rangle \,\text{III}\,\rangle \,\text{IV}\]
(B) \[\text{IV}\,\rangle \,\text{III}\,\rangle \,\text{I}\,\rangle \,\text{II}\]
(C) \[\text{I}\,\rangle \,\text{II}\,\rangle \,\text{III}\,\rangle \,\text{IV}\]
(D) \[\text{IV}\,\rangle \,\text{III}\,\rangle \,\text{II}\,\rangle \,\text{I}\]




Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: Carbocation is a reaction intermediate which is formed due to the heterolytic cleavage of $\text{C-X}$ bond (where $\text{X}$ is more electronegative atom than carbon).
A carbocation is a positively charged and planer in shape ($\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$hybridized carbon atom) with $6e$in the outermost shell.
Electron donating group (which have positive inductive and mesomeric effect) and hyperconjugation stabilize the carbocation, where electron withdrawing group (have negative inductive and mesomeric effect) destabilise the carbocation
A ${{3}^{\circ }}$ carbocation is more stable than${{2}^{\circ }}$carbocation, and a ${{2}^{\circ }}$carbocation molecule is more stable than ${{1}^{\circ }}$ carbocation molecule.
Resonance is the most stabilizing factor for a conjugate cation and anion because the excess charge on carbon atoms in carbocation and Carbanion can be delocalized by resonance.
Complete answer:
Order of stability of carbocation is ${{3}^{\circ }}\rangle {{2}^{\circ }}\rangle {{1}^{\circ }}$
(I) In this compound carbocation is present on a $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$hybridized ${{2}^{\circ }}$carbon atom.
(II) In this compound carbocation is present on a $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ hybridized ${{1}^{\circ }}$ carbon atom. So, this carbocation will be least stable.
(III) In this this compound carbocation is present on a $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ hybridized ${{3}^{\circ }}$ carbon atom.
(IV) In this compound carbocation is present on a $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ hybridized ${{3}^{\circ }}$ carbon atom and this carbocation is also stabilised by the resonance. Hence this carbocation has the highest stability.
Hence the order of stability is \[\text{IV}\,\rangle \,\text{III}\,\rangle \,\text{I}\,\rangle \,\text{II}\]
So, option (B) will be the correct option.
Note:
More the number of carbons attached to the carbon carrying positive charge, more the stability of carbocation because bonding electrons attached to the carbocation helps in alleviating the positive charge by overlapping the unoccupied p-orbital of the carbocation.
A carbocation is a positively charged and planer in shape ($\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$hybridized carbon atom) with $6e$in the outermost shell.
Electron donating group (which have positive inductive and mesomeric effect) and hyperconjugation stabilize the carbocation, where electron withdrawing group (have negative inductive and mesomeric effect) destabilise the carbocation
A ${{3}^{\circ }}$ carbocation is more stable than${{2}^{\circ }}$carbocation, and a ${{2}^{\circ }}$carbocation molecule is more stable than ${{1}^{\circ }}$ carbocation molecule.
Resonance is the most stabilizing factor for a conjugate cation and anion because the excess charge on carbon atoms in carbocation and Carbanion can be delocalized by resonance.
Complete answer:
Order of stability of carbocation is ${{3}^{\circ }}\rangle {{2}^{\circ }}\rangle {{1}^{\circ }}$
(I) In this compound carbocation is present on a $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$hybridized ${{2}^{\circ }}$carbon atom.
(II) In this compound carbocation is present on a $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ hybridized ${{1}^{\circ }}$ carbon atom. So, this carbocation will be least stable.
(III) In this this compound carbocation is present on a $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ hybridized ${{3}^{\circ }}$ carbon atom.
(IV) In this compound carbocation is present on a $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ hybridized ${{3}^{\circ }}$ carbon atom and this carbocation is also stabilised by the resonance. Hence this carbocation has the highest stability.
Hence the order of stability is \[\text{IV}\,\rangle \,\text{III}\,\rangle \,\text{I}\,\rangle \,\text{II}\]
So, option (B) will be the correct option.
Note:
More the number of carbons attached to the carbon carrying positive charge, more the stability of carbocation because bonding electrons attached to the carbocation helps in alleviating the positive charge by overlapping the unoccupied p-orbital of the carbocation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




