
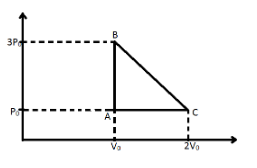
One mole of an ideal monatomic gas is taken along the path ABCA as shown in the PV diagram. The maximum temperature attained by the gas along the path BC is given by:-
A. $\dfrac{{25}}{8}\dfrac{{{P_0}{V_0}}}{R}$
B. $\dfrac{{25}}{4}\dfrac{{{P_0}{V_0}}}{R}$
C. $\dfrac{{25}}{{16}}\dfrac{{{P_0}{V_0}}}{R}$
D. $\dfrac{5}{8}\dfrac{{{P_0}{V_0}}}{R}$

Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: An ideal gas equation is given as $PV = nRT$. We can write the PV equation for the process BC using the equation of straight line $y - {y_1} = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}} \left( {x - {x_1}} \right)$, where $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) and \left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)$ are known points B and C. We can convert this PV equation in terms of temperature T using the ideal gas equation. For maximum temperature $\dfrac{{dT}}{{dV}} = 0$.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that an ideal gas equation is given as $PV = nRT$. Therefore temperature $T = \dfrac{{PV}}{{nR}}$.
Given, number of moles, n$ = 1$.
Temperature of point A$ = \dfrac{{3{P_0}{V_0}}}{R}$
Temperature off point B$ = \dfrac{{{P_0}2{V_0}}}{R}$
Now we write the PV equation for the process BC using the equation of a straight line with two given point.
$
P - 3{P_0} = \dfrac{{{P_0} - 3{P_0}}}{{2{V_0} - {V_0}}}\left( {V - {V_0}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow P - 3{P_0} = \dfrac{{ - 2{P_0}}}{{{V_0}}}\left( {V - {V_0}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow P = \dfrac{{ - 2{P_0}V}}{{{V_0}}} + 5{P_0} \\ $
Multiplying the equation with $V$.
$PV = \dfrac{{ - 2{P_0}{V^2}}}{{{V_0}}} + 5{P_0}V$
Replacing $PV$ with $RT$.
$RT = - \dfrac{{2{P_0}}}{{{V_0}}}{V^2} + 5{P_0}V$
For maximum temperature $\dfrac{{dT}}{{dV}} = 0$.
Therefore we get the maximum temperature t as
$\therefore T =\dfrac{{25}}{8}\dfrac{{{P_0}{V_0}}}{R}$
Note: It is important to know the equation for ideal gas to solve this question ($PV = nRT$). We find the maximum or minimum value of any quantity using differentiation.For the net work involved in a cyclic process is the area enclosed in a P-V diagram, if the cycle goes clockwise, the system does work and if the cycle goes anticlockwise, then work is done on the system.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that an ideal gas equation is given as $PV = nRT$. Therefore temperature $T = \dfrac{{PV}}{{nR}}$.
Given, number of moles, n$ = 1$.
Temperature of point A$ = \dfrac{{3{P_0}{V_0}}}{R}$
Temperature off point B$ = \dfrac{{{P_0}2{V_0}}}{R}$
Now we write the PV equation for the process BC using the equation of a straight line with two given point.
$
P - 3{P_0} = \dfrac{{{P_0} - 3{P_0}}}{{2{V_0} - {V_0}}}\left( {V - {V_0}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow P - 3{P_0} = \dfrac{{ - 2{P_0}}}{{{V_0}}}\left( {V - {V_0}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow P = \dfrac{{ - 2{P_0}V}}{{{V_0}}} + 5{P_0} \\ $
Multiplying the equation with $V$.
$PV = \dfrac{{ - 2{P_0}{V^2}}}{{{V_0}}} + 5{P_0}V$
Replacing $PV$ with $RT$.
$RT = - \dfrac{{2{P_0}}}{{{V_0}}}{V^2} + 5{P_0}V$
For maximum temperature $\dfrac{{dT}}{{dV}} = 0$.
Therefore we get the maximum temperature t as
$\therefore T =\dfrac{{25}}{8}\dfrac{{{P_0}{V_0}}}{R}$
Note: It is important to know the equation for ideal gas to solve this question ($PV = nRT$). We find the maximum or minimum value of any quantity using differentiation.For the net work involved in a cyclic process is the area enclosed in a P-V diagram, if the cycle goes clockwise, the system does work and if the cycle goes anticlockwise, then work is done on the system.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE




