
One face of a rectangular glass plate of thickness ${{6cm}}$ is silvered; an object is placed at a distance of ${{8cm}}$in front of the un silvered face. Its image is formed \[{{10cm}}\]behind the silvered face. The Refractive index of glass plate is:
(A) $\dfrac{5}{3}$
(B) $\dfrac{4}{3}$
(C) $\dfrac{7}{6}$
(D)$\dfrac{3}{2}$
Answer
549.9k+ views
Hint: In order to approach this Question, One thing you should remember is that a surface is silvered then it acts like a plane mirror. & Distance of objects from the mirror is equal to the distance of the image from the mirror.
Formula Used:$ \to $
${{\mu = }}\dfrac{{{{Real Depth}}}}{{{{Apparent Depth}}}}$
Where ${{\mu }}$ is the refractive index.
Complete Step by step Answer:
Here we have given a rectangular glass plate of thickness${{6cm}}$. An object is used to place at a distance ${{8cm}}$in front of the unsilvered face. And the image is forming ${{10cm}}$behind the silver face.
Now, Let us consider a Rectangular glass of thickness${{6cm}}$.
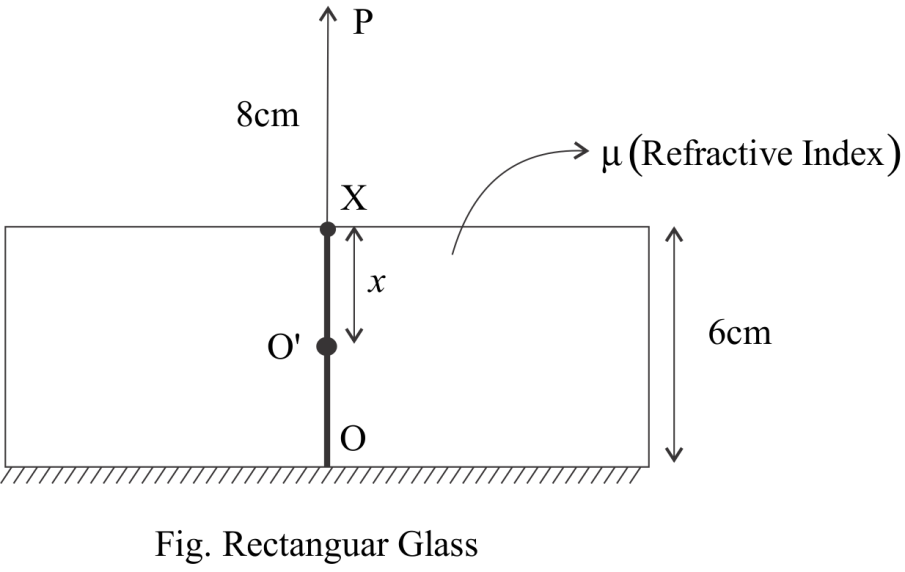
Let point ${{P,}}$ Object is placed at \[{{8cm}}\]from an unsilvered face. Let the refractive index of a glass is ${{\mu }}$.
Now, Because of the Rectangular glass slab the point is shifted upward at ${{o'}}$,(Apparent depth) and Let $x$be the distance from $x$to ${{o'}}$ i. e. $x = o'x$, So $o'o = \left( {6 = x} \right)$
Now we know that
The image formed by a plane mirror is at equal distance from the distance of the object from the mirror. A silvered face will act as a plane mirror and Distance of object from mirror is equal to the distance of image from mirror.
Hence as the point ${{o}}$is shifted to ${{o'}}$because of the refractive index \[{{\mu }}{{.}}\]
So,
Now ,our Object distance will be $8 + x$ and
Distance of image from the ${{o}}$point also get shifted to ${{o'}}$, So image distance will be $10 + \left( {6 - x} \right)$ or $16 - x$.
So, we get $\mu = 8 + x$
$v = 16 - x$
Now, from the property of a plane mirror.
We get
$\mu = v$
$8 + x = 16 - x$
$ \Rightarrow 2x = 8$
$ \Rightarrow x = 4$
So, Actually the Apparent depth is ${{4cm}}$& Real depth is given in question i. e. ${{6cm}}$
Further, we know that
${{Refractive index}}\left( {{\mu }} \right){{ = }}\dfrac{{{{Real depth}}}}{{{{Apparent depth}}}}{{ = }}\dfrac{{{6}}}{{{x}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{\mu }} \right){{ = }}\dfrac{{{6}}}{{{4}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {{(\mu ) = }}\dfrac{{{3}}}{{{2}}}$
$\because {{\mu = }}\dfrac{{{3}}}{{{2}}}$
Hence, the correct option is (D) i. e. ${{\mu = }}\dfrac{{{3}}}{{{2}}}$
Note:
Real Depth is always different from apparent depth. By using formula ${{\mu = }}\dfrac{{{{Real depth}}}}{{{{Apparent depth}}}}$we get the answer. Here, students need to be very careful while doing calculation. Most people get confused and end up writing the wrong formula. This problem is a simple ray optics problem.
Formula Used:$ \to $
${{\mu = }}\dfrac{{{{Real Depth}}}}{{{{Apparent Depth}}}}$
Where ${{\mu }}$ is the refractive index.
Complete Step by step Answer:
Here we have given a rectangular glass plate of thickness${{6cm}}$. An object is used to place at a distance ${{8cm}}$in front of the unsilvered face. And the image is forming ${{10cm}}$behind the silver face.
Now, Let us consider a Rectangular glass of thickness${{6cm}}$.

Let point ${{P,}}$ Object is placed at \[{{8cm}}\]from an unsilvered face. Let the refractive index of a glass is ${{\mu }}$.
Now, Because of the Rectangular glass slab the point is shifted upward at ${{o'}}$,(Apparent depth) and Let $x$be the distance from $x$to ${{o'}}$ i. e. $x = o'x$, So $o'o = \left( {6 = x} \right)$
Now we know that
The image formed by a plane mirror is at equal distance from the distance of the object from the mirror. A silvered face will act as a plane mirror and Distance of object from mirror is equal to the distance of image from mirror.
Hence as the point ${{o}}$is shifted to ${{o'}}$because of the refractive index \[{{\mu }}{{.}}\]
So,
Now ,our Object distance will be $8 + x$ and
Distance of image from the ${{o}}$point also get shifted to ${{o'}}$, So image distance will be $10 + \left( {6 - x} \right)$ or $16 - x$.
So, we get $\mu = 8 + x$
$v = 16 - x$
Now, from the property of a plane mirror.
We get
$\mu = v$
$8 + x = 16 - x$
$ \Rightarrow 2x = 8$
$ \Rightarrow x = 4$
So, Actually the Apparent depth is ${{4cm}}$& Real depth is given in question i. e. ${{6cm}}$
Further, we know that
${{Refractive index}}\left( {{\mu }} \right){{ = }}\dfrac{{{{Real depth}}}}{{{{Apparent depth}}}}{{ = }}\dfrac{{{6}}}{{{x}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{\mu }} \right){{ = }}\dfrac{{{6}}}{{{4}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {{(\mu ) = }}\dfrac{{{3}}}{{{2}}}$
$\because {{\mu = }}\dfrac{{{3}}}{{{2}}}$
Hence, the correct option is (D) i. e. ${{\mu = }}\dfrac{{{3}}}{{{2}}}$
Note:
Real Depth is always different from apparent depth. By using formula ${{\mu = }}\dfrac{{{{Real depth}}}}{{{{Apparent depth}}}}$we get the answer. Here, students need to be very careful while doing calculation. Most people get confused and end up writing the wrong formula. This problem is a simple ray optics problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




