
On which of the following lines lies the point of intersection of the line, \[\dfrac{x-4}{2}=\dfrac{y-5}{2}=\dfrac{z-3}{1}\] and the plane $x+y+z=2$?
A. \[\dfrac{x-2}{2}=\dfrac{y-3}{2}=\dfrac{z+3}{3}\]
B. \[\dfrac{x-4}{1}=\dfrac{y-5}{1}=\dfrac{z-5}{-1}\]
C. \[\dfrac{x-1}{1}=\dfrac{y-3}{2}=\dfrac{z+4}{-5}\]
D. \[\dfrac{x+3}{3}=\dfrac{4-y}{3}=\dfrac{z+1}{-2}\]
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we should know how to rewrite the equation of a line using a parameter when the Cartesian equation of the line is given. The general form of the point lying on the line\[\dfrac{x-{{x}_{1}}}{a}=\dfrac{y-{{y}_{1}}}{b}=\dfrac{z-{{z}_{1}}}{c}\] is given by $\left( {{x}_{1}}+ka,{{y}_{1}}+kb,{{z}_{1}}+kc \right)$ where k is the parameter. Using this statement, we can write the general form of the point of the given line \[\dfrac{x-4}{2}=\dfrac{y-5}{2}=\dfrac{z-3}{1}\]. We know that the point of intersection of the given line and the plane satisfies the equation of the plane. Using this, we can substitute the general point in the plane and get the value of the parameter, and finally, we can get the point.
Complete step-by-step solution
We are given a line \[\dfrac{x-4}{2}=\dfrac{y-5}{2}=\dfrac{z-3}{1}\] and a plane $x+y+z=2$. We are asked to find the point of intersection of the line and the plane.
We know that the general form of the point lying on the line\[\dfrac{x-{{x}_{1}}}{a}=\dfrac{y-{{y}_{1}}}{b}=\dfrac{z-{{z}_{1}}}{c}\] is given by $\left( {{x}_{1}}+ka,{{y}_{1}}+kb,{{z}_{1}}+kc \right)$ where k is the parameter. We get this form by taking \[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{x-{{x}_{1}}}{a}=\dfrac{y-{{y}_{1}}}{b}=\dfrac{z-{{z}_{1}}}{c}=k \\
& x={{x}_{1}}+ka \\
& y={{y}_{1}}+kb \\
& z={{z}_{1}}+kc \\
\end{align}\]
By using this form, we can get the general form of the point on the line \[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{x-4}{2}=\dfrac{y-5}{2}=\dfrac{z-3}{1}=k \\
& x=2k+4 \\
& y=2k+5 \\
& z=k+3 \\
& \left( x,y,z \right)=\left( 2k+4,2k+5,k+3 \right) \\
\end{align}\]
This general form of the point should satisfy the equation of the plane $x+y+z=2$ to be the point of intersection. Substituting the general equation of the point in the plane, we get
$\begin{align}
& 2k+4+2k+5+k+3=2 \\
& \Rightarrow 5k+12=2 \\
& \Rightarrow 5k=-10 \\
& \Rightarrow k=-2 \\
\end{align}$
Using this value of k in the general form, we get
$A=\left( 2\left( -2 \right)+4,2\left( -2 \right)+5,-2+3 \right)=\left( 0,1,1 \right)$
We should verify the options to know the line which passes through the point-A.
Let us consider option-A
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{x-2}{2}=\dfrac{y-3}{2}=\dfrac{z+3}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{0-2}{2}=\dfrac{1-3}{2}=\dfrac{1+3}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow -1=-1=\dfrac{4}{3} \\
\end{align}\]
We can see that A is not satisfying option-A.
Let us consider option-B
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{x-4}{1}=\dfrac{y-5}{1}=\dfrac{z-5}{-1} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{0-4}{1}=\dfrac{1-5}{1}=\dfrac{1-5}{-1} \\
& \Rightarrow -4=-4=4 \\
\end{align}\]
We can see that A is not satisfying option-B.
Let us consider option-C
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{x-1}{1}=\dfrac{y-3}{2}=\dfrac{z+4}{-5} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{0-1}{1}=\dfrac{1-3}{2}=\dfrac{1+4}{-5} \\
& \Rightarrow -1=-1=-1 \\
\end{align}\]
So, the point of intersection A satisfies the line equation given in option-C
$\therefore $ The point of intersection lies on the line \[\dfrac{x-1}{1}=\dfrac{y-3}{2}=\dfrac{z+4}{-5}\]. The answer is option-C.
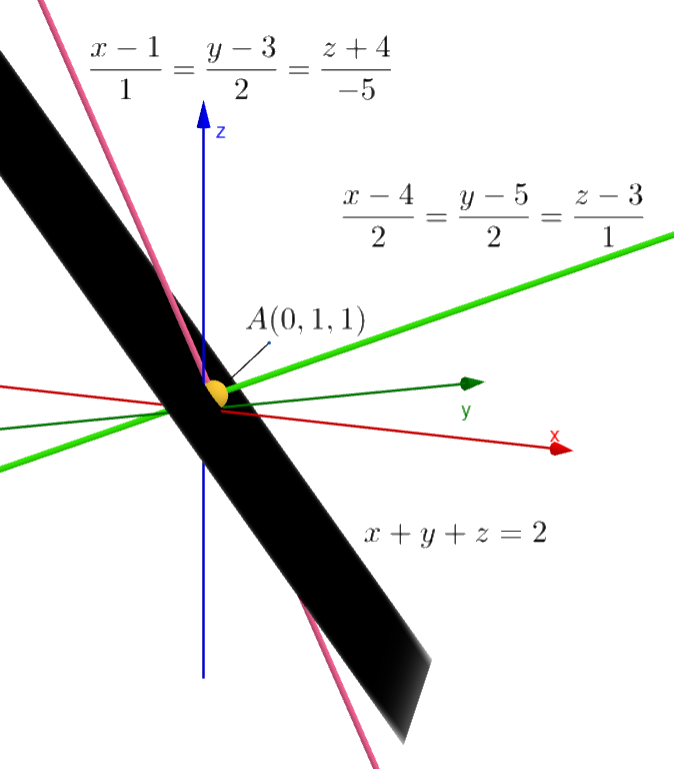
Note: We can see the diagram which shows the above scenario. The green line is the given line\[\dfrac{x-4}{2}=\dfrac{y-5}{2}=\dfrac{z-3}{1}\] and the pink line is the line that we got as the answer\[\dfrac{x-1}{1}=\dfrac{y-3}{2}=\dfrac{z+4}{-5}\]. The black color plane is the plane that was given in the question$x+y+z=2$. Some students try to check whether the point of intersection of the given line and the line in the options satisfy the plane or not. We will get the answer in this way also but we should do more process. So, we should minimize the process that we do by substituting rather than increasing it.
Complete step-by-step solution
We are given a line \[\dfrac{x-4}{2}=\dfrac{y-5}{2}=\dfrac{z-3}{1}\] and a plane $x+y+z=2$. We are asked to find the point of intersection of the line and the plane.
We know that the general form of the point lying on the line\[\dfrac{x-{{x}_{1}}}{a}=\dfrac{y-{{y}_{1}}}{b}=\dfrac{z-{{z}_{1}}}{c}\] is given by $\left( {{x}_{1}}+ka,{{y}_{1}}+kb,{{z}_{1}}+kc \right)$ where k is the parameter. We get this form by taking \[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{x-{{x}_{1}}}{a}=\dfrac{y-{{y}_{1}}}{b}=\dfrac{z-{{z}_{1}}}{c}=k \\
& x={{x}_{1}}+ka \\
& y={{y}_{1}}+kb \\
& z={{z}_{1}}+kc \\
\end{align}\]
By using this form, we can get the general form of the point on the line \[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{x-4}{2}=\dfrac{y-5}{2}=\dfrac{z-3}{1}=k \\
& x=2k+4 \\
& y=2k+5 \\
& z=k+3 \\
& \left( x,y,z \right)=\left( 2k+4,2k+5,k+3 \right) \\
\end{align}\]
This general form of the point should satisfy the equation of the plane $x+y+z=2$ to be the point of intersection. Substituting the general equation of the point in the plane, we get
$\begin{align}
& 2k+4+2k+5+k+3=2 \\
& \Rightarrow 5k+12=2 \\
& \Rightarrow 5k=-10 \\
& \Rightarrow k=-2 \\
\end{align}$
Using this value of k in the general form, we get
$A=\left( 2\left( -2 \right)+4,2\left( -2 \right)+5,-2+3 \right)=\left( 0,1,1 \right)$
We should verify the options to know the line which passes through the point-A.
Let us consider option-A
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{x-2}{2}=\dfrac{y-3}{2}=\dfrac{z+3}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{0-2}{2}=\dfrac{1-3}{2}=\dfrac{1+3}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow -1=-1=\dfrac{4}{3} \\
\end{align}\]
We can see that A is not satisfying option-A.
Let us consider option-B
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{x-4}{1}=\dfrac{y-5}{1}=\dfrac{z-5}{-1} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{0-4}{1}=\dfrac{1-5}{1}=\dfrac{1-5}{-1} \\
& \Rightarrow -4=-4=4 \\
\end{align}\]
We can see that A is not satisfying option-B.
Let us consider option-C
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{x-1}{1}=\dfrac{y-3}{2}=\dfrac{z+4}{-5} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{0-1}{1}=\dfrac{1-3}{2}=\dfrac{1+4}{-5} \\
& \Rightarrow -1=-1=-1 \\
\end{align}\]
So, the point of intersection A satisfies the line equation given in option-C
$\therefore $ The point of intersection lies on the line \[\dfrac{x-1}{1}=\dfrac{y-3}{2}=\dfrac{z+4}{-5}\]. The answer is option-C.
Note: We can see the diagram which shows the above scenario. The green line is the given line\[\dfrac{x-4}{2}=\dfrac{y-5}{2}=\dfrac{z-3}{1}\] and the pink line is the line that we got as the answer\[\dfrac{x-1}{1}=\dfrac{y-3}{2}=\dfrac{z+4}{-5}\]. The black color plane is the plane that was given in the question$x+y+z=2$. Some students try to check whether the point of intersection of the given line and the line in the options satisfy the plane or not. We will get the answer in this way also but we should do more process. So, we should minimize the process that we do by substituting rather than increasing it.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




