
On oxidation with alkaline $KMn{O_4}$ , $'X'$ compound gives ${C_3}{H_6}{O_2}$ and ${C_2}{H_4}{O_2}$ as two carboxylic acids. What would be the IUPAC name of alkyne $'X'$?
A.But-$2$-yne
B.But-$1$-yne
C.Pent-$2$-yne
D.Hex-$1$-yne
Answer
547.5k+ views
Hint:The best way to solve the conversion problems is to follow the reaction step by step. We will focus on the properties of reagent. For example: if the reaction is with an oxidizing agent it will give the oxidized products. The product formed also helps in detecting the reactant.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we will write a reaction in terms of products and reactants. Here $'X'$ on oxidation gives two carboxylic acids as ${C_3}{H_6}{O_2}$ and${C_2}{H_4}{O_2}$.
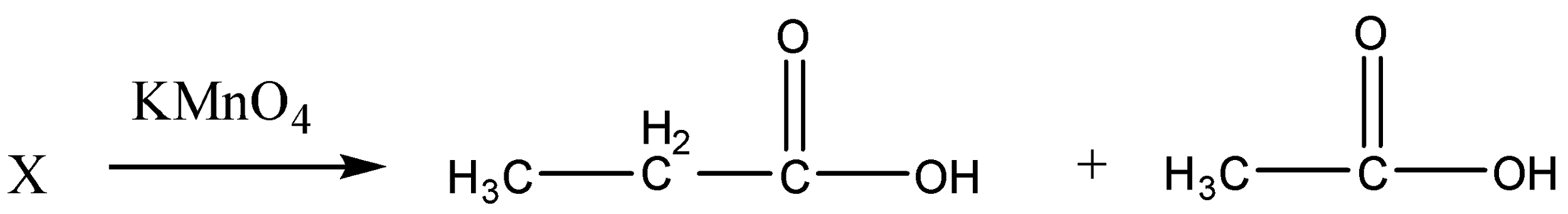
So the reaction given above shows that an alkyne $'X'$ on oxidation gives two carboxylic acids ${C_3}{H_6}{O_2}$ and ${C_2}{H_4}{O_2}$ which is the only possible structure of these given carboxylic acids.
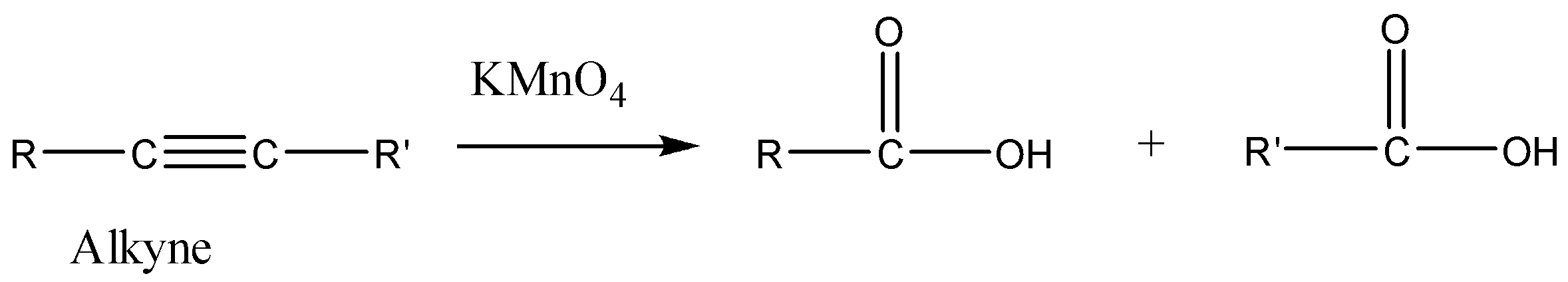
So now we need to find the alkyne $'X'$. We know that oxidation with alkaline $KMn{O_4}$ alkyne gives carboxylic acids. We can understand it with the help of the reaction given below.
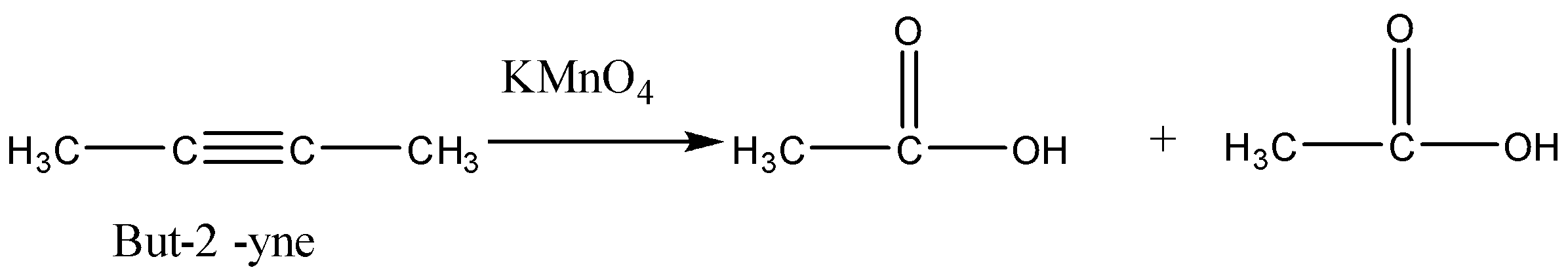
So we will check the options one by one to get the desired product. So consider option (A) But-$2$-yne. This reaction is not giving us the given carboxylic acids.
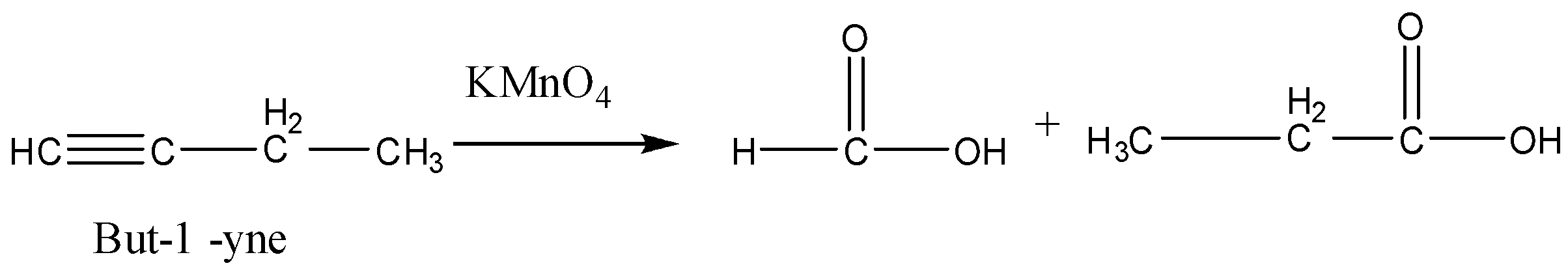
Now we will consider option (B) But-$1$-yne. This alkyne will also not give the required carboxylic acids.
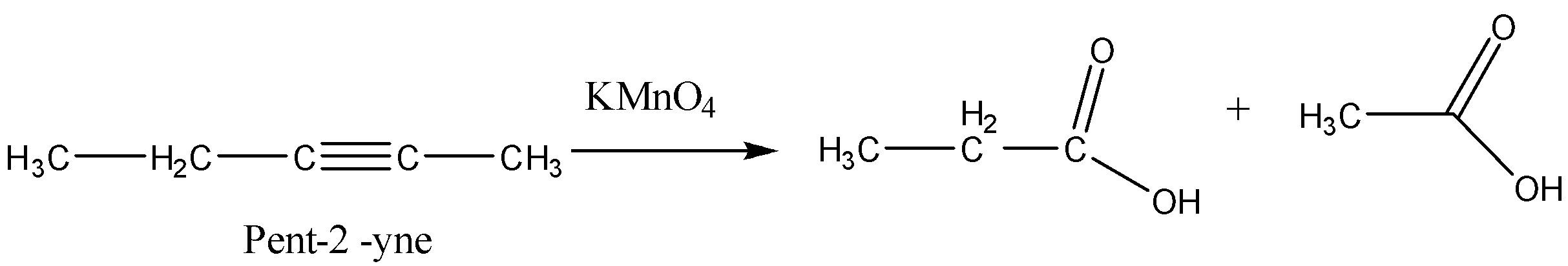
Now we will consider option (C) Pent-$2$-yne. This alkyne will give us the carboxylic acids given in the question.
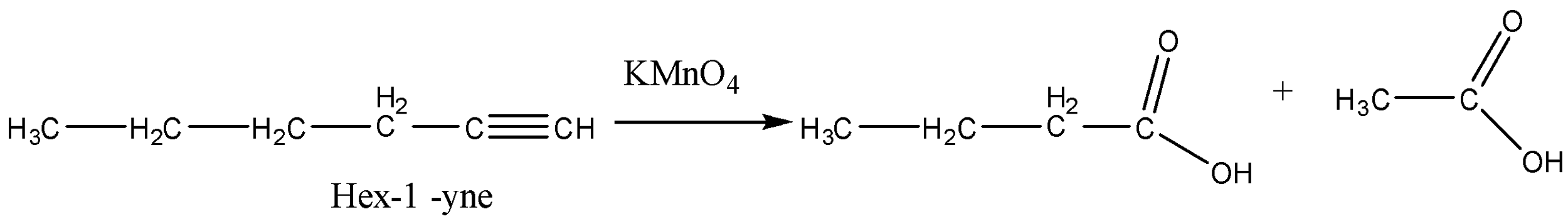
Now the last option (D) Hex-$1$-yne. It will also give different carboxylic acids.
So from the above reactions, we can conclude that $'X'$ is Pent-$2$-yne.
Therefore, option (C) is correct.
Note:
Alkaline $KMn{O_4}$ is a powerful oxidizing agent. The oxidation state of $Mn$ is $ + 7$. It is the highest oxidation state of manganese.
Terminal alkyne is the alkyne in which the carbon-carbon triple bond is at last.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we will write a reaction in terms of products and reactants. Here $'X'$ on oxidation gives two carboxylic acids as ${C_3}{H_6}{O_2}$ and${C_2}{H_4}{O_2}$.

So the reaction given above shows that an alkyne $'X'$ on oxidation gives two carboxylic acids ${C_3}{H_6}{O_2}$ and ${C_2}{H_4}{O_2}$ which is the only possible structure of these given carboxylic acids.
So now we need to find the alkyne $'X'$. We know that oxidation with alkaline $KMn{O_4}$ alkyne gives carboxylic acids. We can understand it with the help of the reaction given below.

So we will check the options one by one to get the desired product. So consider option (A) But-$2$-yne. This reaction is not giving us the given carboxylic acids.

Now we will consider option (B) But-$1$-yne. This alkyne will also not give the required carboxylic acids.

Now we will consider option (C) Pent-$2$-yne. This alkyne will give us the carboxylic acids given in the question.

Now the last option (D) Hex-$1$-yne. It will also give different carboxylic acids.

So from the above reactions, we can conclude that $'X'$ is Pent-$2$-yne.
Therefore, option (C) is correct.
Note:
Alkaline $KMn{O_4}$ is a powerful oxidizing agent. The oxidation state of $Mn$ is $ + 7$. It is the highest oxidation state of manganese.
Terminal alkyne is the alkyne in which the carbon-carbon triple bond is at last.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




