
On oxidation with a mild oxidizing agent like \[B{r_2}/{H_2}O\], the glucose is oxidized to?
A. saccharic acid
B. glucaric acid
C. gluconic acid
D. valeric acid
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: The product obtained by the oxidation of monosaccharides is used as the tool for the determination of the structure of the sugar sometimes. Several reagents are employed for this purpose.
Complete step by step answer:
-Glucose is a monosaccharide and is the simplest sugar molecule. It is one of the primary sources of energy required by our body. The molecular formula of glucose is \[{C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}\] . It belongs to the carbohydrate family of organic compounds. Glucose is obtained from the variety of food products we intake daily.
-The oxidation of sugar is a very important reaction to determine the structure of carbohydrates in consideration. Several reagents are used for the oxidation reactions of which some are mild and some are strong.
-\[B{r_2}\] in presence of water is a mild oxidizing agent and nitric acid mediated oxidation is a strong reducing agent. On oxidation with a mild oxidizing agent like \[B{r_2}/{H_2}O\] , the glucose molecule is oxidized to a carboxylic acid containing a six carbon chain. The product of the reaction gives the confirmation of the presence of the aldehyde group in the starting material.
-The reaction is shown as:
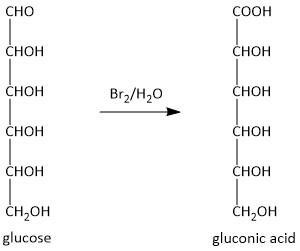
Hence glucose is oxidized to gluconic acid, i.e. option C is the correct answer. The formation of gluconic acid indicated that the glucose is an aldose and not a ketose.
Saccharic acid and glucaric acid are the same compounds. They are \[1,6\]-dicarboxylic acids and obtain the oxidation of glucose with nitric acid.
Valeric acid is pentanoic acid which cannot be obtained from oxidation with mild oxidizing agents like \[B{r_2}/{H_2}O\] as it has one carbon atom less than the glucose molecule.
Note:
Aldehydes also referred to as aldoses are oxidized to mono carboxylic acids in the presence of \[B{r_2}\] in \[{H_2}O\]. The reaction differentiates aldoses from ketoses. A solution of \[B{r_2}\] with brown color changes on reaction with aldoses, but will undergo no change with ketoses.
Complete step by step answer:
-Glucose is a monosaccharide and is the simplest sugar molecule. It is one of the primary sources of energy required by our body. The molecular formula of glucose is \[{C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}\] . It belongs to the carbohydrate family of organic compounds. Glucose is obtained from the variety of food products we intake daily.
-The oxidation of sugar is a very important reaction to determine the structure of carbohydrates in consideration. Several reagents are used for the oxidation reactions of which some are mild and some are strong.
-\[B{r_2}\] in presence of water is a mild oxidizing agent and nitric acid mediated oxidation is a strong reducing agent. On oxidation with a mild oxidizing agent like \[B{r_2}/{H_2}O\] , the glucose molecule is oxidized to a carboxylic acid containing a six carbon chain. The product of the reaction gives the confirmation of the presence of the aldehyde group in the starting material.
-The reaction is shown as:

Hence glucose is oxidized to gluconic acid, i.e. option C is the correct answer. The formation of gluconic acid indicated that the glucose is an aldose and not a ketose.
Saccharic acid and glucaric acid are the same compounds. They are \[1,6\]-dicarboxylic acids and obtain the oxidation of glucose with nitric acid.
Valeric acid is pentanoic acid which cannot be obtained from oxidation with mild oxidizing agents like \[B{r_2}/{H_2}O\] as it has one carbon atom less than the glucose molecule.
Note:
Aldehydes also referred to as aldoses are oxidized to mono carboxylic acids in the presence of \[B{r_2}\] in \[{H_2}O\]. The reaction differentiates aldoses from ketoses. A solution of \[B{r_2}\] with brown color changes on reaction with aldoses, but will undergo no change with ketoses.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




