
Okazaki fragments are:
A) The DNA fragments produced due to radiation
B) The RNA primers required for initiation of DNA synthesis
C) Short DNA fragments on the lagging strand
D) Short fragments on the leading strand
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: The fragments are sequences that are found on the strand of DNA that undergoes replication in a discontinuous manner and requires a slight delay in undergoing the replication process.
Complete Answer:
Okazaki fragments are discontinuous short sequences of DNA nucleotides and are formed during the DNA replication process to synthesize the lagging strand of DNA. After being discontinuously synthesized, these fragments are joined together by enzyme DNA ligase. The size of the Okazaki fragments ranges from 150-200bp in eukaryotes.
During the process of DNA replication, the enzyme DNA helicase unwinds the complementary strands of DNA and a replication fork is formed. The enzymes DNA polymerase and DNA primase are then involved in the creation of new complementary strands. Out of the two strands, the one strand replicates in a continuous manner and is called as the leading strand while the other strand replicates with periodic breaks and is known as lagging strand. Due to the periodic breaks, small complementary fragments of the DNA are synthesized and these are the Okazaki fragments. The enzyme DNA ligase then joins these fragments together and a new complementary strand is formed. Okazaki fragments have been shown in the diagram below -
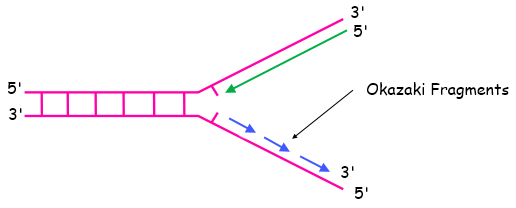
So, the correct answer is, ‘Short DNA fragments on the lagging strands’.
Note: The DNA replication process between prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms differed by the presence of different DNA polymerase enzymes involved between them. Also, Okazaki fragments are small in eukaryotes whereas they are larger in prokaryotic organisms.
Complete Answer:
Okazaki fragments are discontinuous short sequences of DNA nucleotides and are formed during the DNA replication process to synthesize the lagging strand of DNA. After being discontinuously synthesized, these fragments are joined together by enzyme DNA ligase. The size of the Okazaki fragments ranges from 150-200bp in eukaryotes.
During the process of DNA replication, the enzyme DNA helicase unwinds the complementary strands of DNA and a replication fork is formed. The enzymes DNA polymerase and DNA primase are then involved in the creation of new complementary strands. Out of the two strands, the one strand replicates in a continuous manner and is called as the leading strand while the other strand replicates with periodic breaks and is known as lagging strand. Due to the periodic breaks, small complementary fragments of the DNA are synthesized and these are the Okazaki fragments. The enzyme DNA ligase then joins these fragments together and a new complementary strand is formed. Okazaki fragments have been shown in the diagram below -

So, the correct answer is, ‘Short DNA fragments on the lagging strands’.
Note: The DNA replication process between prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms differed by the presence of different DNA polymerase enzymes involved between them. Also, Okazaki fragments are small in eukaryotes whereas they are larger in prokaryotic organisms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




