
How can you obtain $ \text{Butan}-\text{2}-\text{one} $ from $ \text{But}-\text{2}-\text{yne} $ ?
Answer
515.1k+ views
Hint :For the given conversion, first convert the alkyne into unsaturated alcohol i.e., unsaturated hydrocarbon consisting of a hydroxyl group and then perform tautomerism to convert it into the required compound containing ketonic group.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
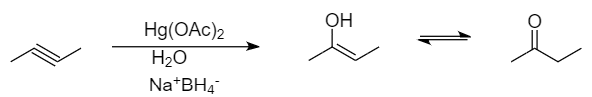
The mechanism for the given conversion is followed by acid catalysed hydration of $ \text{But}-\text{2}-\text{yne} $ .
Conversion takes place as follows:
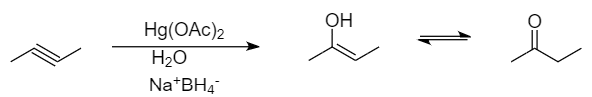
The mechanism followed in the given reaction is known as oxymercuration-demercuration. It is a type of an electrophilic addition reaction in which the unsaturated hydrocarbons are converted into respective alcohols in the presence of mercuric acetate, water or sulphuric acid and sodium tetrahydridoborate.
The major advantage of this reaction is that the product formed follows Markovnikov’s addition rule and the yields of the products are comparatively higher in mild conditions also.
The reaction mechanism is as follows:
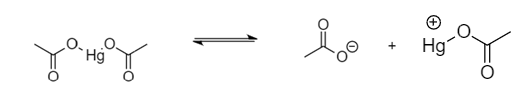
Step-1: Dissociation of mercuric acetate into respective ions:
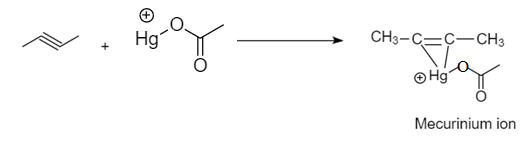
Step-2: Attack of an electrophile on the unsaturated carbon atom to form Mercurinium ion as an intermediate:
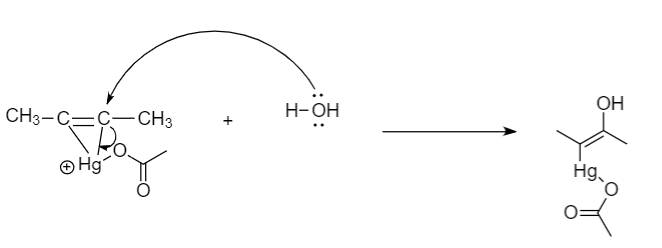
Step-3: Nucleophilic attack of water molecule on carbon atom and opening of ring takes place:
Step-4: Reduction of the compound takes place in the presence of sodium tetrahydridoborate along with the removal of mercury and acetate ion.
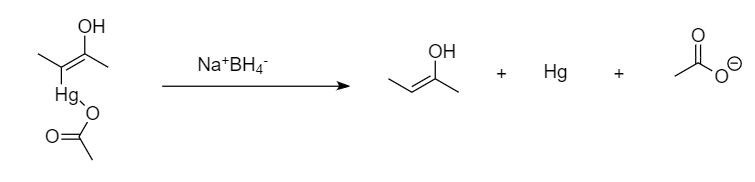
Step-5: Enol structure tautomerize to form keto structure of the compound.
Hence, $ \text{Butan}-\text{2}-\text{one} $ is obtained as the final product.
Note :
Tautomerism: It is a phenomenon in which a single compound has a tendency to exhibit more than one interconvertible structure. The structures differ in terms of the relative position of only one proton.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The mechanism for the given conversion is followed by acid catalysed hydration of $ \text{But}-\text{2}-\text{yne} $ .
Conversion takes place as follows:

The mechanism followed in the given reaction is known as oxymercuration-demercuration. It is a type of an electrophilic addition reaction in which the unsaturated hydrocarbons are converted into respective alcohols in the presence of mercuric acetate, water or sulphuric acid and sodium tetrahydridoborate.
The major advantage of this reaction is that the product formed follows Markovnikov’s addition rule and the yields of the products are comparatively higher in mild conditions also.
The reaction mechanism is as follows:
Step-1: Dissociation of mercuric acetate into respective ions:

Step-2: Attack of an electrophile on the unsaturated carbon atom to form Mercurinium ion as an intermediate:

Step-3: Nucleophilic attack of water molecule on carbon atom and opening of ring takes place:

Step-4: Reduction of the compound takes place in the presence of sodium tetrahydridoborate along with the removal of mercury and acetate ion.

Step-5: Enol structure tautomerize to form keto structure of the compound.

Hence, $ \text{Butan}-\text{2}-\text{one} $ is obtained as the final product.
Note :
Tautomerism: It is a phenomenon in which a single compound has a tendency to exhibit more than one interconvertible structure. The structures differ in terms of the relative position of only one proton.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




