
What is the number of depletion layers in a transistor?
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: In order to answer this question, we will discuss what we mean by transistors. We will also study the construction of transistors in order to find out the total number of depletion layers in a single transistor. We will also be using semiconductor theory to reach our answer.
Complete step by step solution:
First of all, what are transistors?
A transistor is a semiconductor component that can conduct as well as insulate. A transistor serves as both a switch and an amplifier. It converts audio waves into electronic waves and controls current flow with a resistor. These components have a long life span, are compact, can operate on lower voltage materials for added protection, and do not require filament current. Germanium was used to build the first transistor. A transistor performs the same purpose as a vacuum tube triode, but instead of excited electrodes in a vacuum chamber, it uses semiconductor junctions.
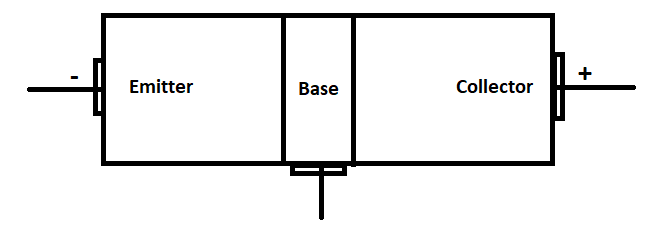
As we can see, a transistor is a key component of today's electronic devices and is used in all modern electronic systems. A transistor is a three-terminal device. Base, emitter, and collector are the three components. The transistor is triggered by the base terminal, the emitter terminals are the negative lead, and the collector terminal is the positive lead. A transistor's basic concept is that it helps you to regulate the current flow through one channel by adjusting the intensity of a much smaller current flowing through another channel.
The base functions as a gate controller for a larger electrical supply. The emitter is the outlet of a larger electrical supply, which is the collector. Sending varying amounts of current from the base will control the current flowing through the gate from the collector. In this way, a very small amount of current, such as that used in amplifiers, can be used to power a huge amount of current.
Transistors are of two types depending on the way of their construction:
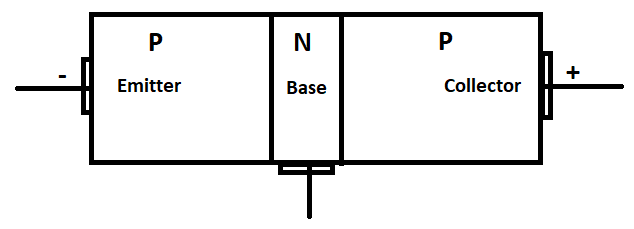
1) PNP transistor
An n-type semiconductor layer is sandwiched between two p-type semiconductor layers in this type of transistor. The following picture depicts the basic block diagram of a PNP transistor.
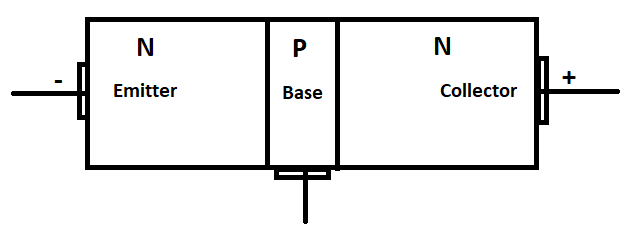
2) NPN transistor
As the name implies, a p-type semiconductor layer is sandwiched between two n-type semiconductor layers in this type of transistor. Look for the simple block diagram in the picture below.
We now know that a transistor is a three-layer semiconductor system in which one type of semiconductor (P-type or N-type) is sandwiched between two types of semiconductor that are identical. The method of sandwiching is known as transistor fabrication. Therefore, according to the theory of semiconducting diodes, if two semiconductors are placed side by side, then a depletion region or a junction is formed between them. Similarly, in a transistor there are three semiconductors and therefore, two junctions or depletion regions are formed in between them. The two junctions formed are:
i) Base-Emitter Junction
ii) Collector-Base Junction
Note:
It is important to note here that in order to understand the above answer, you need to have a certain basic knowledge about semiconductor devices such as diodes and how they work. For a transistor to work appropriately, the emitter-base junction is connected in a forward bias connection whereas the collector-base junction is connected in a reverse bias connection.
Complete step by step solution:
First of all, what are transistors?
A transistor is a semiconductor component that can conduct as well as insulate. A transistor serves as both a switch and an amplifier. It converts audio waves into electronic waves and controls current flow with a resistor. These components have a long life span, are compact, can operate on lower voltage materials for added protection, and do not require filament current. Germanium was used to build the first transistor. A transistor performs the same purpose as a vacuum tube triode, but instead of excited electrodes in a vacuum chamber, it uses semiconductor junctions.

As we can see, a transistor is a key component of today's electronic devices and is used in all modern electronic systems. A transistor is a three-terminal device. Base, emitter, and collector are the three components. The transistor is triggered by the base terminal, the emitter terminals are the negative lead, and the collector terminal is the positive lead. A transistor's basic concept is that it helps you to regulate the current flow through one channel by adjusting the intensity of a much smaller current flowing through another channel.
The base functions as a gate controller for a larger electrical supply. The emitter is the outlet of a larger electrical supply, which is the collector. Sending varying amounts of current from the base will control the current flowing through the gate from the collector. In this way, a very small amount of current, such as that used in amplifiers, can be used to power a huge amount of current.
Transistors are of two types depending on the way of their construction:
1) PNP transistor
An n-type semiconductor layer is sandwiched between two p-type semiconductor layers in this type of transistor. The following picture depicts the basic block diagram of a PNP transistor.

2) NPN transistor
As the name implies, a p-type semiconductor layer is sandwiched between two n-type semiconductor layers in this type of transistor. Look for the simple block diagram in the picture below.

We now know that a transistor is a three-layer semiconductor system in which one type of semiconductor (P-type or N-type) is sandwiched between two types of semiconductor that are identical. The method of sandwiching is known as transistor fabrication. Therefore, according to the theory of semiconducting diodes, if two semiconductors are placed side by side, then a depletion region or a junction is formed between them. Similarly, in a transistor there are three semiconductors and therefore, two junctions or depletion regions are formed in between them. The two junctions formed are:
i) Base-Emitter Junction
ii) Collector-Base Junction
Note:
It is important to note here that in order to understand the above answer, you need to have a certain basic knowledge about semiconductor devices such as diodes and how they work. For a transistor to work appropriately, the emitter-base junction is connected in a forward bias connection whereas the collector-base junction is connected in a reverse bias connection.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




