
How many non-equivalent hydrogens are there in aspirin?
Answer
544.2k+ views
Hint:Equivalent hydrogen are the hydrogen atoms that are completely interchangeable as to their role in a molecule. For instance, consider a methane molecule, it consists of a carbon atom and 4 hydrogen atoms bonded to it. But during the formation of methanol, the 4th hydrogen atom is replaced by an oxygen atom, however the replaced hydrogen is still in the compound but is attached to the oxygen atom instead of the carbon atom.
Formulas used: No formulas will be used in the solution of the given problem.
Complete step-by-step answer:Aspirin as we know is used as a form of medication to reduce pain, fever or inflammation. Aspirin is a medically relevant and important drug for it is given shortly after a heart attack to decrease the chances of death. So, in a way aspirin is a life saver drug.
This life saver drug, aspirin has a complex chemical structure and is given by the IUPAC name acetylsalicylic acid or 2-Acetoxybenzoic acid. One way to identify the equivalent hydrogens of a molecule is to replace the hydrogen atoms with a different group of atoms and see if we get a different compound.
So, the structure of aspirin of 2-Acetoxybenzoic acid or ${C_9}{H_8}{O_4}$ is:
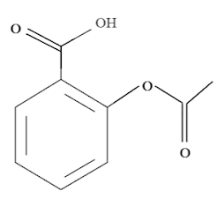
As we can see that the benzene ring usually has 6 hydrogen atoms and thus would be equivalent, but now, with the addition of a oic functional group and an acetyl substituent group, we have the following sets of equivalent hydrogen: $C{H_3},COOH,H - 3,H - 4,H - 5,H - 6$ .
They have 5 sets of different non-equivalent hydrogen which cannot be interchanged for any other functional group.
Note:The equivalence of hydrogen atoms in a compound are related and confirmed by the spectroscopy of these compounds.
Formulas used: No formulas will be used in the solution of the given problem.
Complete step-by-step answer:Aspirin as we know is used as a form of medication to reduce pain, fever or inflammation. Aspirin is a medically relevant and important drug for it is given shortly after a heart attack to decrease the chances of death. So, in a way aspirin is a life saver drug.
This life saver drug, aspirin has a complex chemical structure and is given by the IUPAC name acetylsalicylic acid or 2-Acetoxybenzoic acid. One way to identify the equivalent hydrogens of a molecule is to replace the hydrogen atoms with a different group of atoms and see if we get a different compound.
So, the structure of aspirin of 2-Acetoxybenzoic acid or ${C_9}{H_8}{O_4}$ is:

As we can see that the benzene ring usually has 6 hydrogen atoms and thus would be equivalent, but now, with the addition of a oic functional group and an acetyl substituent group, we have the following sets of equivalent hydrogen: $C{H_3},COOH,H - 3,H - 4,H - 5,H - 6$ .
They have 5 sets of different non-equivalent hydrogen which cannot be interchanged for any other functional group.
Note:The equivalence of hydrogen atoms in a compound are related and confirmed by the spectroscopy of these compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




