
$Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$ is:
(A) Tetrahedral and paramagnetic
(B) Square planar and diamagnetic
(C) Tetrahedral and diamagnetic
(D) Square planar and paramagnetic
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint:The molecular geometry of a compound shows its $3 - D$ arrangement of an atom within a molecule. It depends upon the hybridization, whereas magnetic behavior of an atom can either be paramagnetic or diamagnetic based upon the pairing of electrons in the molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
$Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$ is nickel tetracarbonyl. It is a colourless liquid, high in toxicity.
The atomic number of Nickel ($Ni$) is $28$ and its electronic configuration is $3{d^8}4{s^2}$
In ground state,
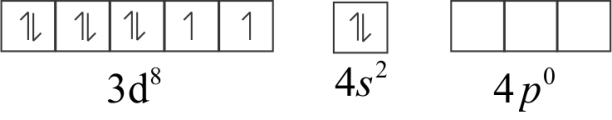
In an excited state, when $CO$ ligand approaches it.

In an excited state, all the ten electrons are shifted into the $3d - $ orbital and get paired up.
The $4s$ and three $4p$ orbitals are empty, so they undergo $s{p^3}$ hybridization. Upon hybridization, the form bonds with $CO$ ligands and give rise to $Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$
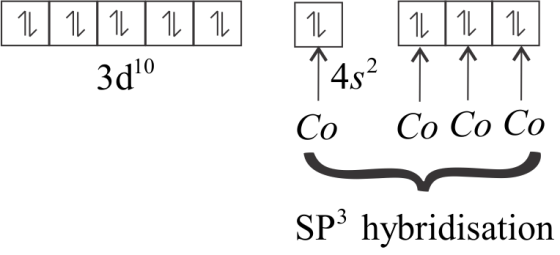
As all the electrons in $Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$ are paired. Thus, the geometry of the molecule depends upon the hybridization. So, the geometry of $Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$ will be tetrahedral due to $s{p^3}$ hybridization.
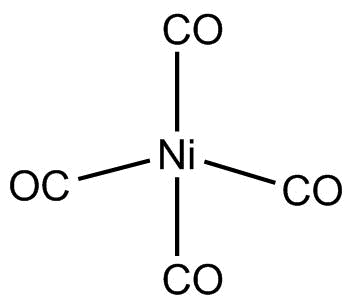
Hence, $Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$ is tetrahedral and diamagnetic in nature.
Hence, the correct option is C, tetrahedral and diamagnetic.
Additional Information:
Ludwig Mond synthesized $Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$ for the first time in $1890$ the performed direct reaction of $CO$ with $Ni$ to obtain $Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$.
Now-a-days it is prepared in laboratories by carbonylation of bis(cyclooctadiene) nickel ($O$).
The vapours of $Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$ are able to auto ignite and decompose in air quickly.
Note:
Oxidation state of nickel in $Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$ can be found mathematically as:
We know the oxidation state of $CO$ is neutral, that is zero.
Let oxidation state of $Ni = x$
Therefore, $x + \left( {4 \times 0} \right) = 0$
$x = 0$
Hence, oxidation state of nickel is zero in $Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$
Complete step by step answer:
$Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$ is nickel tetracarbonyl. It is a colourless liquid, high in toxicity.
The atomic number of Nickel ($Ni$) is $28$ and its electronic configuration is $3{d^8}4{s^2}$
In ground state,
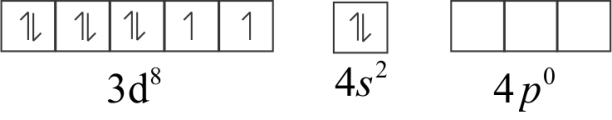
In an excited state, when $CO$ ligand approaches it.

In an excited state, all the ten electrons are shifted into the $3d - $ orbital and get paired up.
The $4s$ and three $4p$ orbitals are empty, so they undergo $s{p^3}$ hybridization. Upon hybridization, the form bonds with $CO$ ligands and give rise to $Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$

As all the electrons in $Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$ are paired. Thus, the geometry of the molecule depends upon the hybridization. So, the geometry of $Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$ will be tetrahedral due to $s{p^3}$ hybridization.

Hence, $Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$ is tetrahedral and diamagnetic in nature.
Hence, the correct option is C, tetrahedral and diamagnetic.
Additional Information:
Ludwig Mond synthesized $Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$ for the first time in $1890$ the performed direct reaction of $CO$ with $Ni$ to obtain $Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$.
Now-a-days it is prepared in laboratories by carbonylation of bis(cyclooctadiene) nickel ($O$).
The vapours of $Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$ are able to auto ignite and decompose in air quickly.
Note:
Oxidation state of nickel in $Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$ can be found mathematically as:
We know the oxidation state of $CO$ is neutral, that is zero.
Let oxidation state of $Ni = x$
Therefore, $x + \left( {4 \times 0} \right) = 0$
$x = 0$
Hence, oxidation state of nickel is zero in $Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




