
What is the nature of image formed by the concave lens?
A) Virtual and inverted
B) Real and erect
C) Virtual and erect
D) Real and inverted
Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: There are two types of lens: Concave and Convex. When an incoming light ray is diverged by the lens, it is called a concave lens and if it is converged to a point, it is called a convex lens. We have to understand this fact before understanding the type of image formation in the concave lens.
Complete answer:
Lens is an optical device that is used to focus or disperse a ray of light through the principles of refraction of light, wherein there is a change in the direction of the light after travelling from one medium to another medium. Lens is usually made of glass or plastic or any other transparent medium.
There are two major types of lens namely, biconcave (or simply concave) lens and biconvex (or simply convex) lens.
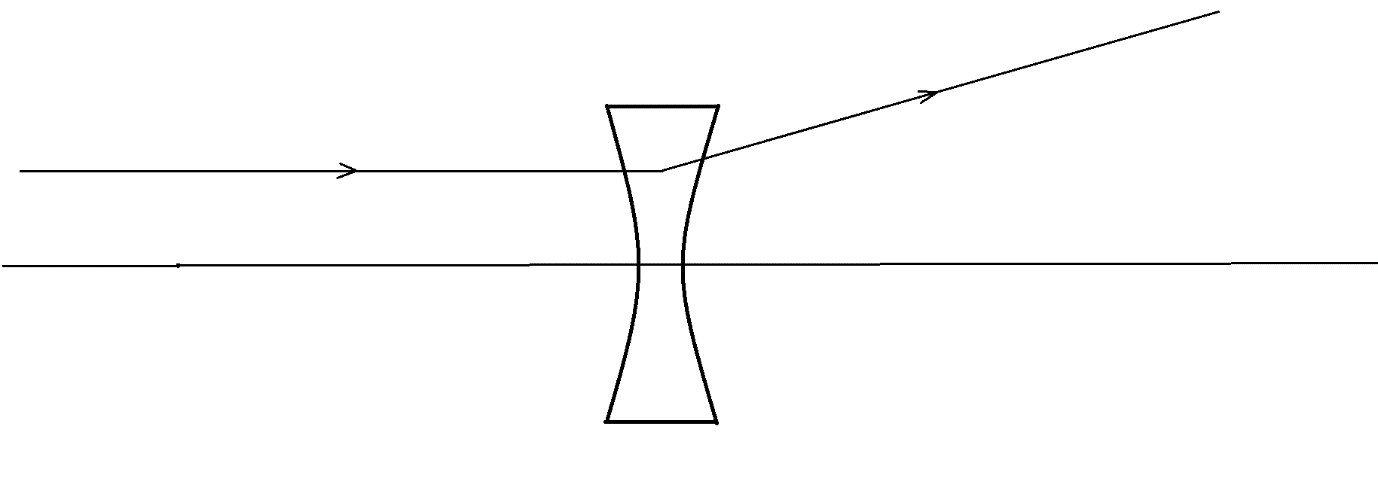
A biconcave lens is the lens that diverges a ray originating from infinity parallel to the principal axis, as shown:
 Consider an object placed at any distance from infinity to the proximity of a concave lens as shown. The image formation by the lens is displayed in the figure below:
Consider an object placed at any distance from infinity to the proximity of a concave lens as shown. The image formation by the lens is displayed in the figure below:
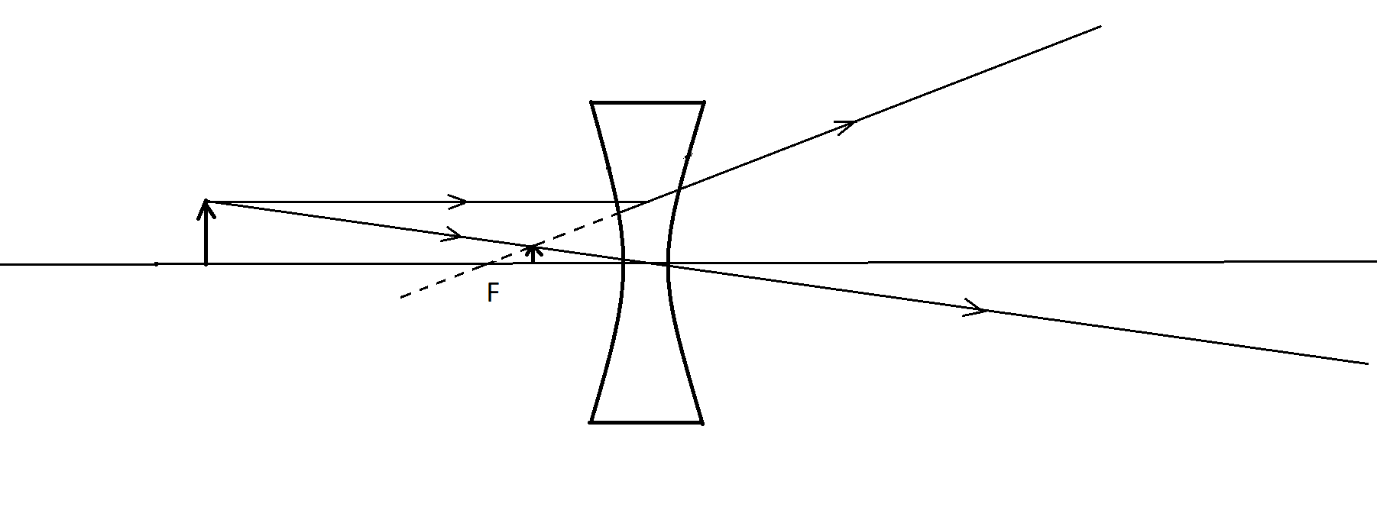
Two rays emerge from the object as shown:
i) The first ray goes undeviated through the centre of the lens
ii) The second ray goes parallel to the principal axis and diverges away. When the diverged ray is reproduced back, it appears to pass through a point known as the principal focus of the lens.
The image is formed as shown, where the two rays meet, between F and the lens.
The image formed is virtual as we see that the light appears to pass through the focus behind the lens. Thus, the image does not exist in reality but the image appears to be formed at the point between focus and the lens.
The image formed is erect as shown in the figure.
Hence, the image formed by a concave lens is always erect and virtual.
Hence, the correct option is Option C.
Note: We can see that the image formed by the concave lens, in addition to virtual and erect, is also highly diminished. This feature of the lens is applicable in terrestrial telescopes to cover a larger region of vision.
Complete answer:
Lens is an optical device that is used to focus or disperse a ray of light through the principles of refraction of light, wherein there is a change in the direction of the light after travelling from one medium to another medium. Lens is usually made of glass or plastic or any other transparent medium.
There are two major types of lens namely, biconcave (or simply concave) lens and biconvex (or simply convex) lens.
A biconcave lens is the lens that diverges a ray originating from infinity parallel to the principal axis, as shown:


Two rays emerge from the object as shown:
i) The first ray goes undeviated through the centre of the lens
ii) The second ray goes parallel to the principal axis and diverges away. When the diverged ray is reproduced back, it appears to pass through a point known as the principal focus of the lens.
The image is formed as shown, where the two rays meet, between F and the lens.
The image formed is virtual as we see that the light appears to pass through the focus behind the lens. Thus, the image does not exist in reality but the image appears to be formed at the point between focus and the lens.
The image formed is erect as shown in the figure.
Hence, the image formed by a concave lens is always erect and virtual.
Hence, the correct option is Option C.
Note: We can see that the image formed by the concave lens, in addition to virtual and erect, is also highly diminished. This feature of the lens is applicable in terrestrial telescopes to cover a larger region of vision.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




