
Name the transcriptionally active region of chromatin in the nucleus.
Answer
573k+ views
Hint: Chromatin is found in the nucleus which is made up of DNA and proteins. The loosely packed chromatin is one of the transcriptionally active regions of chromatin.
Complete answer:
Chromatin is a complex of RNA, DNA and protein. The main function is in packaging of long DNA molecules into denser shape, compact which stops the strands from becoming tangled and play a crucial role in strengthening the DNA during cell division. In mitosis and meiosis chromatin is useful in separation of the chromosomes in anaphase, the typical shapes of chromosomes visible during this stage is the result of DNA being looped into a highly condensed system of chromatin. The main protein constituents of chromatin are histones, which is attached to the DNA and acts as an anchors around where components are wound. Chromatin inside a cell may be condensed to varying degrees depending on the cell's stage in the cell cycle. In nucleus chromatin occurs as euchromatin and heterochromatin. Most of the chromatin is in less compressed form called euchromatin where most of the DNA is visible permitting replication and DNA transcription to occur. In transcription the DNA double helix unwinds and opens to allow the genes coding for the protein to be replicated. DNA replication and transcription are essential for the cell in making DNA, proteins and organelles for cell division. Euchromatin is involved in the active transcription of DNA into Mrna. It is more open which allows the recruitment of RNA polymerase complexes and regulatory proteins so transcription is initiated. Euchromatin is in transcriptionally functional cells because it contains DNA, which helps in folding heterochromatin which helps in the transcription by inhibiting the access of RNA polymerase and other regulatory proteins to the DNA.
Heterochromatin has low gene density along with highly compact chromatin structure which do not allow gene transcription to occur.
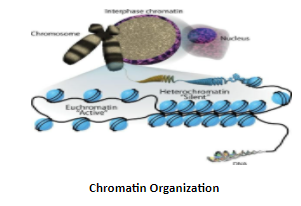
Note: The major protein present in chromatin is histone which is a positively charged protein which is helpful in the packaging of DNA which is a negatively charged molecule in the eukaryotic cell.
Complete answer:
Chromatin is a complex of RNA, DNA and protein. The main function is in packaging of long DNA molecules into denser shape, compact which stops the strands from becoming tangled and play a crucial role in strengthening the DNA during cell division. In mitosis and meiosis chromatin is useful in separation of the chromosomes in anaphase, the typical shapes of chromosomes visible during this stage is the result of DNA being looped into a highly condensed system of chromatin. The main protein constituents of chromatin are histones, which is attached to the DNA and acts as an anchors around where components are wound. Chromatin inside a cell may be condensed to varying degrees depending on the cell's stage in the cell cycle. In nucleus chromatin occurs as euchromatin and heterochromatin. Most of the chromatin is in less compressed form called euchromatin where most of the DNA is visible permitting replication and DNA transcription to occur. In transcription the DNA double helix unwinds and opens to allow the genes coding for the protein to be replicated. DNA replication and transcription are essential for the cell in making DNA, proteins and organelles for cell division. Euchromatin is involved in the active transcription of DNA into Mrna. It is more open which allows the recruitment of RNA polymerase complexes and regulatory proteins so transcription is initiated. Euchromatin is in transcriptionally functional cells because it contains DNA, which helps in folding heterochromatin which helps in the transcription by inhibiting the access of RNA polymerase and other regulatory proteins to the DNA.
Heterochromatin has low gene density along with highly compact chromatin structure which do not allow gene transcription to occur.

Note: The major protein present in chromatin is histone which is a positively charged protein which is helpful in the packaging of DNA which is a negatively charged molecule in the eukaryotic cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




