
Name the spherical mirror which converges the beam of light incident on it. Justify your answer by drawing a ray diagram.
Answer
510.9k+ views
Hint:A mirror is a flat surface that reflects light in a regular pattern. The reflection of light creates a clear image of an item put in front of a mirror. A mirror is a reflecting surface that is flat and well-polished. A mirror creates an image when it reflects light.
Light may be reflected and reconvened to create pictures in physics mirrors. Concave and convex mirrors are two different types of mirrors with differing features. The actual image and the virtual image are two sorts of images created by mirrors.
Complete step-by-step solution:
When a hollow spherical is divided into pieces and the exterior surface of each cut portion is painted, it forms a mirror, with the inner surface reflecting the light. A concave mirror is the name for this sort of mirror. When light strikes and reflects back from the concave mirror reflecting surface, it converges at a point. As a result, it's also called a converging mirror.
An enlarged and simulated picture is generated when the concave mirror is put extremely close to the item.
When the distance between the item and the mirror is increased, however, the size of the image decreases and a true picture is generated.
The concave mirror may produce a little or big picture, which can be real or virtual.
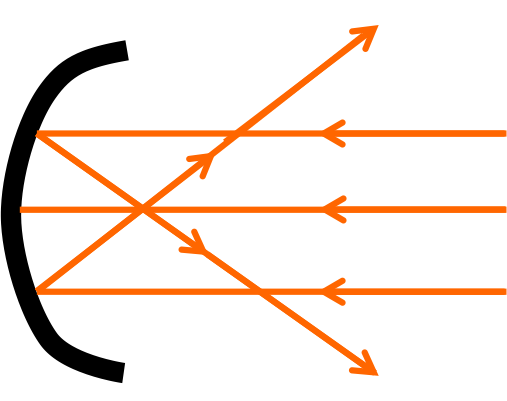
After reflection, parallel rays emanating from the object converge at the primary focus, F, of a concave mirror. As a result, the picture will develop at F when the item is at infinity.
Image properties include: Real and inverted, point sized, highly decreased.
Note:Because they tend to gather light that falls on them, directing parallel incoming rays toward a focus, these mirrors are referred to as "converging mirrors." Because the normal to the mirror surface varies at different points on the mirror, light is reflected at varying angles at different points.
Light may be reflected and reconvened to create pictures in physics mirrors. Concave and convex mirrors are two different types of mirrors with differing features. The actual image and the virtual image are two sorts of images created by mirrors.
Complete step-by-step solution:
When a hollow spherical is divided into pieces and the exterior surface of each cut portion is painted, it forms a mirror, with the inner surface reflecting the light. A concave mirror is the name for this sort of mirror. When light strikes and reflects back from the concave mirror reflecting surface, it converges at a point. As a result, it's also called a converging mirror.
An enlarged and simulated picture is generated when the concave mirror is put extremely close to the item.
When the distance between the item and the mirror is increased, however, the size of the image decreases and a true picture is generated.
The concave mirror may produce a little or big picture, which can be real or virtual.

After reflection, parallel rays emanating from the object converge at the primary focus, F, of a concave mirror. As a result, the picture will develop at F when the item is at infinity.
Image properties include: Real and inverted, point sized, highly decreased.
Note:Because they tend to gather light that falls on them, directing parallel incoming rays toward a focus, these mirrors are referred to as "converging mirrors." Because the normal to the mirror surface varies at different points on the mirror, light is reflected at varying angles at different points.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




